Martin Gjoreski
Federated Concept-Based Models: Interpretable models with distributed supervision
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Concept-based models (CMs) enhance interpretability in deep learning by grounding predictions in human-understandable concepts. However, concept annotations are expensive to obtain and rarely available at scale within a single data source. Federated learning (FL) could alleviate this limitation by enabling cross-institutional training that leverages concept annotations distributed across multiple data owners. Yet, FL lacks interpretable modeling paradigms. Integrating CMs with FL is non-trivial: CMs assume a fixed concept space and a predefined model architecture, whereas real-world FL is heterogeneous and non-stationary, with institutions joining over time and bringing new supervision. In this work, we propose Federated Concept-based Models (F-CMs), a new methodology for deploying CMs in evolving FL settings. F-CMs aggregate concept-level information across institutions and efficiently adapt the model architecture in response to changes in the available concept supervision, while preserving institutional privacy. Empirically, F-CMs preserve the accuracy and intervention effectiveness of training settings with full concept supervision, while outperforming non-adaptive federated baselines. Notably, F-CMs enable interpretable inference on concepts not available to a given institution, a key novelty with respect to existing approaches.
A Survey on Federated Learning in Human Sensing
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:Human Sensing, a field that leverages technology to monitor human activities, psycho-physiological states, and interactions with the environment, enhances our understanding of human behavior and drives the development of advanced services that improve overall quality of life. However, its reliance on detailed and often privacy-sensitive data as the basis for its machine learning (ML) models raises significant legal and ethical concerns. The recently proposed ML approach of Federated Learning (FL) promises to alleviate many of these concerns, as it is able to create accurate ML models without sending raw user data to a central server. While FL has demonstrated its usefulness across a variety of areas, such as text prediction and cyber security, its benefits in Human Sensing are under-explored, given the particular challenges in this domain. This survey conducts a comprehensive analysis of the current state-of-the-art studies on FL in Human Sensing, and proposes a taxonomy and an eight-dimensional assessment for FL approaches. Through the eight-dimensional assessment, we then evaluate whether the surveyed studies consider a specific FL-in-Human-Sensing challenge or not. Finally, based on the overall analysis, we discuss open challenges and highlight five research aspects related to FL in Human Sensing that require urgent research attention. Our work provides a comprehensive corpus of FL studies and aims to assist FL practitioners in developing and evaluating solutions that effectively address the real-world complexities of Human Sensing.
Evaluating Explanations Through LLMs: Beyond Traditional User Studies
Oct 23, 2024



Abstract:As AI becomes fundamental in sectors like healthcare, explainable AI (XAI) tools are essential for trust and transparency. However, traditional user studies used to evaluate these tools are often costly, time consuming, and difficult to scale. In this paper, we explore the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) to replicate human participants to help streamline XAI evaluation. We reproduce a user study comparing counterfactual and causal explanations, replicating human participants with seven LLMs under various settings. Our results show that (i) LLMs can replicate most conclusions from the original study, (ii) different LLMs yield varying levels of alignment in the results, and (iii) experimental factors such as LLM memory and output variability affect alignment with human responses. These initial findings suggest that LLMs could provide a scalable and cost-effective way to simplify qualitative XAI evaluation.
Causal Concept Embedding Models: Beyond Causal Opacity in Deep Learning
May 28, 2024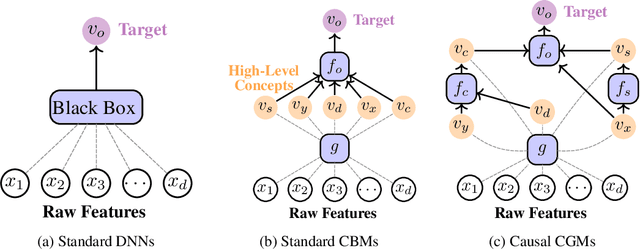
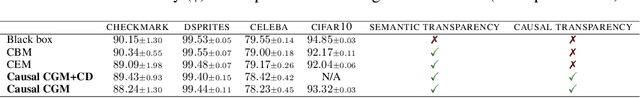
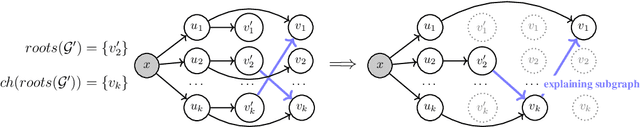

Abstract:Causal opacity denotes the difficulty in understanding the "hidden" causal structure underlying a deep neural network's (DNN) reasoning. This leads to the inability to rely on and verify state-of-the-art DNN-based systems especially in high-stakes scenarios. For this reason, causal opacity represents a key open challenge at the intersection of deep learning, interpretability, and causality. This work addresses this gap by introducing Causal Concept Embedding Models (Causal CEMs), a class of interpretable models whose decision-making process is causally transparent by design. The results of our experiments show that Causal CEMs can: (i) match the generalization performance of causally-opaque models, (ii) support the analysis of interventional and counterfactual scenarios, thereby improving the model's causal interpretability and supporting the effective verification of its reliability and fairness, and (iii) enable human-in-the-loop corrections to mispredicted intermediate reasoning steps, boosting not just downstream accuracy after corrections but also accuracy of the explanation provided for a specific instance.
AnyCBMs: How to Turn Any Black Box into a Concept Bottleneck Model
May 26, 2024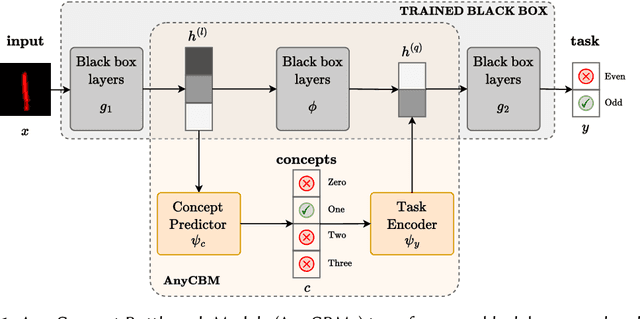
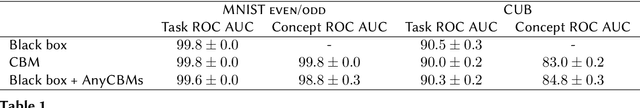
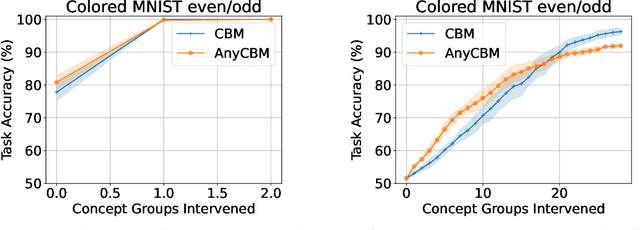
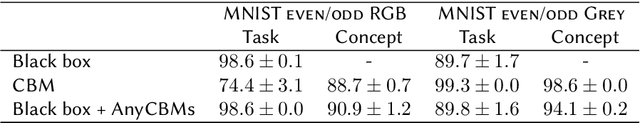
Abstract:Interpretable deep learning aims at developing neural architectures whose decision-making processes could be understood by their users. Among these techniqes, Concept Bottleneck Models enhance the interpretability of neural networks by integrating a layer of human-understandable concepts. These models, however, necessitate training a new model from the beginning, consuming significant resources and failing to utilize already trained large models. To address this issue, we introduce "AnyCBM", a method that transforms any existing trained model into a Concept Bottleneck Model with minimal impact on computational resources. We provide both theoretical and experimental insights showing the effectiveness of AnyCBMs in terms of classification performances and effectivenss of concept-based interventions on downstream tasks.
Federated Behavioural Planes: Explaining the Evolution of Client Behaviour in Federated Learning
May 24, 2024Abstract:Federated Learning (FL), a privacy-aware approach in distributed deep learning environments, enables many clients to collaboratively train a model without sharing sensitive data, thereby reducing privacy risks. However, enabling human trust and control over FL systems requires understanding the evolving behaviour of clients, whether beneficial or detrimental for the training, which still represents a key challenge in the current literature. To address this challenge, we introduce Federated Behavioural Planes (FBPs), a novel method to analyse, visualise, and explain the dynamics of FL systems, showing how clients behave under two different lenses: predictive performance (error behavioural space) and decision-making processes (counterfactual behavioural space). Our experiments demonstrate that FBPs provide informative trajectories describing the evolving states of clients and their contributions to the global model, thereby enabling the identification of clusters of clients with similar behaviours. Leveraging the patterns identified by FBPs, we propose a robust aggregation technique named Federated Behavioural Shields to detect malicious or noisy client models, thereby enhancing security and surpassing the efficacy of existing state-of-the-art FL defense mechanisms.
Differential Privacy for Anomaly Detection: Analyzing the Trade-off Between Privacy and Explainability
Apr 09, 2024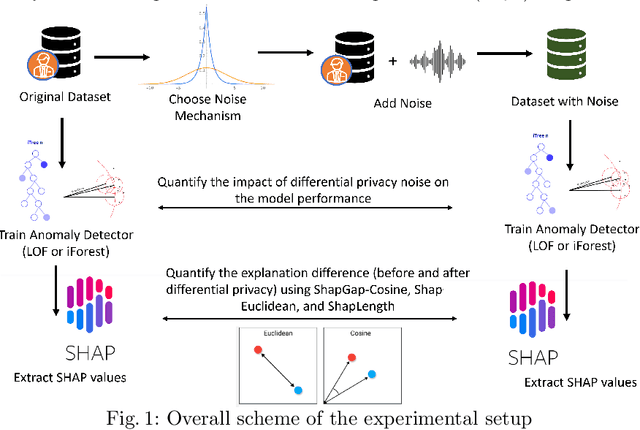
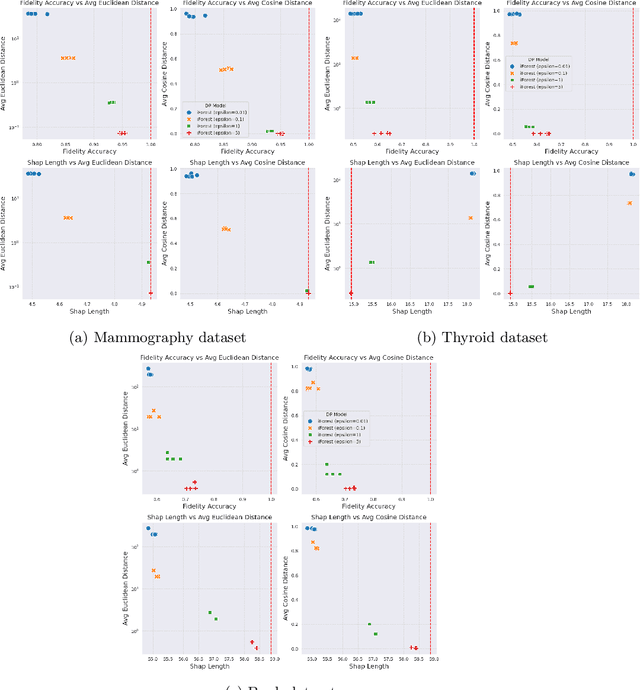
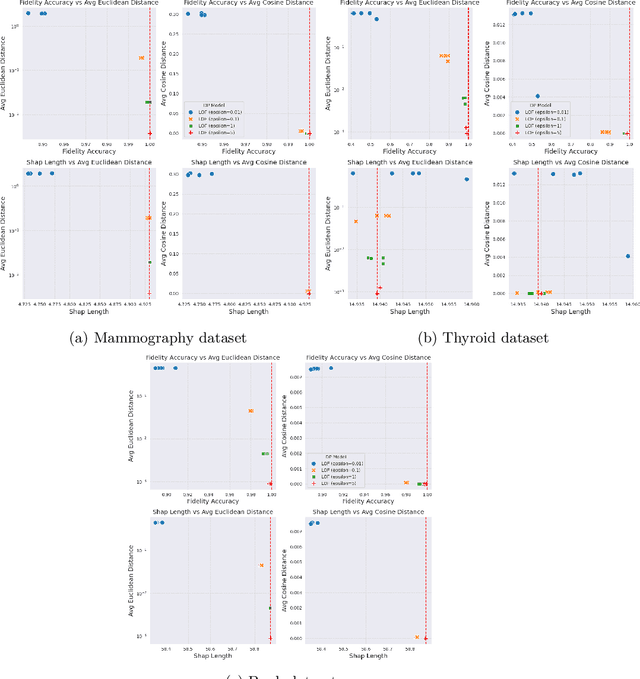
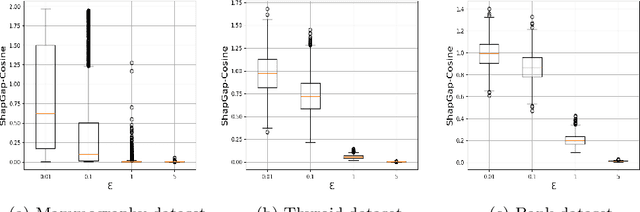
Abstract:Anomaly detection (AD), also referred to as outlier detection, is a statistical process aimed at identifying observations within a dataset that significantly deviate from the expected pattern of the majority of the data. Such a process finds wide application in various fields, such as finance and healthcare. While the primary objective of AD is to yield high detection accuracy, the requirements of explainability and privacy are also paramount. The first ensures the transparency of the AD process, while the second guarantees that no sensitive information is leaked to untrusted parties. In this work, we exploit the trade-off of applying Explainable AI (XAI) through SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) and differential privacy (DP). We perform AD with different models and on various datasets, and we thoroughly evaluate the cost of privacy in terms of decreased accuracy and explainability. Our results show that the enforcement of privacy through DP has a significant impact on detection accuracy and explainability, which depends on both the dataset and the considered AD model. We further show that the visual interpretation of explanations is also influenced by the choice of the AD algorithm.
Climbing the Ladder of Interpretability with Counterfactual Concept Bottleneck Models
Feb 02, 2024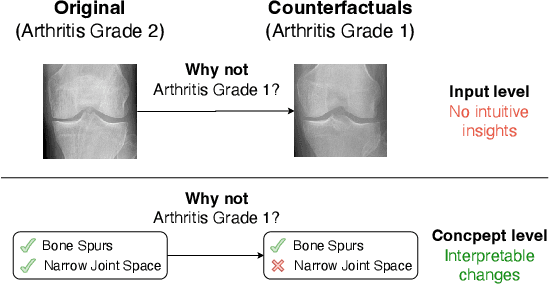
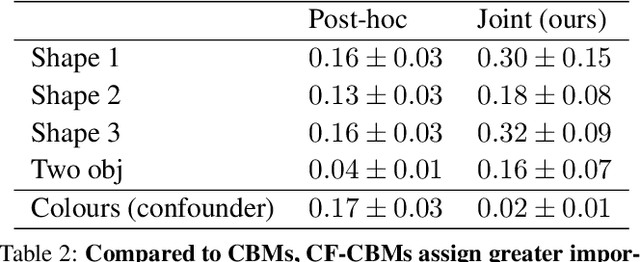
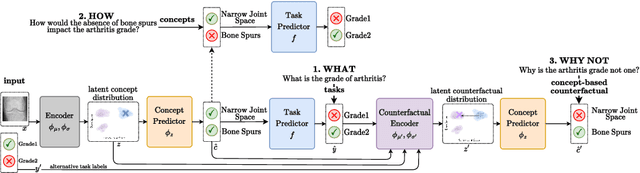
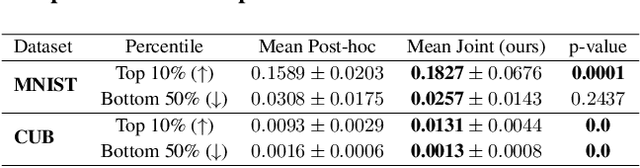
Abstract:Current deep learning models are not designed to simultaneously address three fundamental questions: predict class labels to solve a given classification task (the "What?"), explain task predictions (the "Why?"), and imagine alternative scenarios that could result in different predictions (the "What if?"). The inability to answer these questions represents a crucial gap in deploying reliable AI agents, calibrating human trust, and deepening human-machine interaction. To bridge this gap, we introduce CounterFactual Concept Bottleneck Models (CF-CBMs), a class of models designed to efficiently address the above queries all at once without the need to run post-hoc searches. Our results show that CF-CBMs produce: accurate predictions (the "What?"), simple explanations for task predictions (the "Why?"), and interpretable counterfactuals (the "What if?"). CF-CBMs can also sample or estimate the most probable counterfactual to: (i) explain the effect of concept interventions on tasks, (ii) show users how to get a desired class label, and (iii) propose concept interventions via "task-driven" interventions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge