Fatima Ezzeddine
Explanations Leak: Membership Inference with Differential Privacy and Active Learning Defense
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Counterfactual explanations (CFs) are increasingly integrated into Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) systems to improve transparency; however, ML models deployed via APIs are already vulnerable to privacy attacks such as membership inference and model extraction, and the impact of explanations on this threat landscape remains insufficiently understood. In this work, we focus on the problem of how CFs expand the attack surface of MLaaS by strengthening membership inference attacks (MIAs), and on the need to design defense mechanisms that mitigate this emerging risk without undermining utility and explainability. First, we systematically analyze how exposing CFs through query-based APIs enables more effective shadow-based MIAs. Second, we propose a defense framework that integrates Differential Privacy (DP) with Active Learning (AL) to jointly reduce memorization and limit effective training data exposure. Finally, we conduct an extensive empirical evaluation to characterize the three-way trade-off between privacy leakage, predictive performance, and explanation quality. Our findings highlight the need to carefully balance transparency, utility, and privacy in the responsible deployment of explainable MLaaS systems.
Fair Recourse for All: Ensuring Individual and Group Fairness in Counterfactual Explanations
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) is becoming increasingly essential for enhancing the transparency of machine learning (ML) models. Among the various XAI techniques, counterfactual explanations (CFs) hold a pivotal role due to their ability to illustrate how changes in input features can alter an ML model's decision, thereby offering actionable recourse to users. Ensuring that individuals with comparable attributes and those belonging to different protected groups (e.g., demographic) receive similar and actionable recourse options is essential for trustworthy and fair decision-making. In this work, we address this challenge directly by focusing on the generation of fair CFs. Specifically, we start by defining and formulating fairness at: 1) individual fairness, ensuring that similar individuals receive similar CFs, 2) group fairness, ensuring equitable CFs across different protected groups and 3) hybrid fairness, which accounts for both individual and broader group-level fairness. We formulate the problem as an optimization task and propose a novel model-agnostic, reinforcement learning based approach to generate CFs that satisfy fairness constraints at both the individual and group levels, two objectives that are usually treated as orthogonal. As fairness metrics, we extend existing metrics commonly used for auditing ML models, such as equal choice of recourse and equal effectiveness across individuals and groups. We evaluate our approach on three benchmark datasets, showing that it effectively ensures individual and group fairness while preserving the quality of the generated CFs in terms of proximity and plausibility, and quantify the cost of fairness in the different levels separately. Our work opens a broader discussion on hybrid fairness and its role and implications for XAI and beyond CFs.
On the interplay of Explainability, Privacy and Predictive Performance with Explanation-assisted Model Extraction
May 13, 2025Abstract:Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) has gained important attraction as a means for deploying powerful predictive models, offering ease of use that enables organizations to leverage advanced analytics without substantial investments in specialized infrastructure or expertise. However, MLaaS platforms must be safeguarded against security and privacy attacks, such as model extraction (MEA) attacks. The increasing integration of explainable AI (XAI) within MLaaS has introduced an additional privacy challenge, as attackers can exploit model explanations particularly counterfactual explanations (CFs) to facilitate MEA. In this paper, we investigate the trade offs among model performance, privacy, and explainability when employing Differential Privacy (DP), a promising technique for mitigating CF facilitated MEA. We evaluate two distinct DP strategies: implemented during the classification model training and at the explainer during CF generation.
Privacy Implications of Explainable AI in Data-Driven Systems
Jun 22, 2024Abstract:Machine learning (ML) models, demonstrably powerful, suffer from a lack of interpretability. The absence of transparency, often referred to as the black box nature of ML models, undermines trust and urges the need for efforts to enhance their explainability. Explainable AI (XAI) techniques address this challenge by providing frameworks and methods to explain the internal decision-making processes of these complex models. Techniques like Counterfactual Explanations (CF) and Feature Importance play a crucial role in achieving this goal. Furthermore, high-quality and diverse data remains the foundational element for robust and trustworthy ML applications. In many applications, the data used to train ML and XAI explainers contain sensitive information. In this context, numerous privacy-preserving techniques can be employed to safeguard sensitive information in the data, such as differential privacy. Subsequently, a conflict between XAI and privacy solutions emerges due to their opposing goals. Since XAI techniques provide reasoning for the model behavior, they reveal information relative to ML models, such as their decision boundaries, the values of features, or the gradients of deep learning models when explanations are exposed to a third entity. Attackers can initiate privacy breaching attacks using these explanations, to perform model extraction, inference, and membership attacks. This dilemma underscores the challenge of finding the right equilibrium between understanding ML decision-making and safeguarding privacy.
Differential Privacy for Anomaly Detection: Analyzing the Trade-off Between Privacy and Explainability
Apr 09, 2024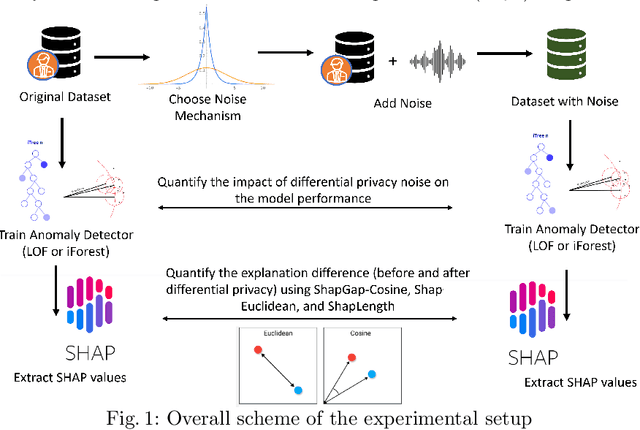
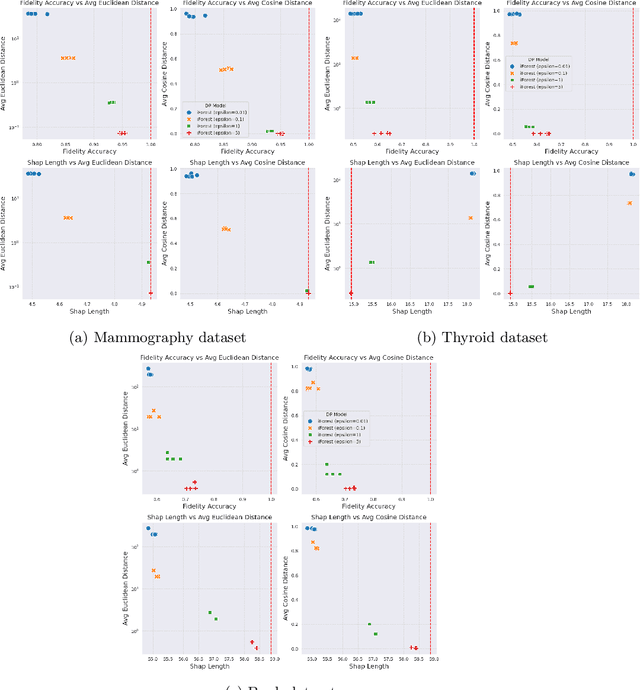
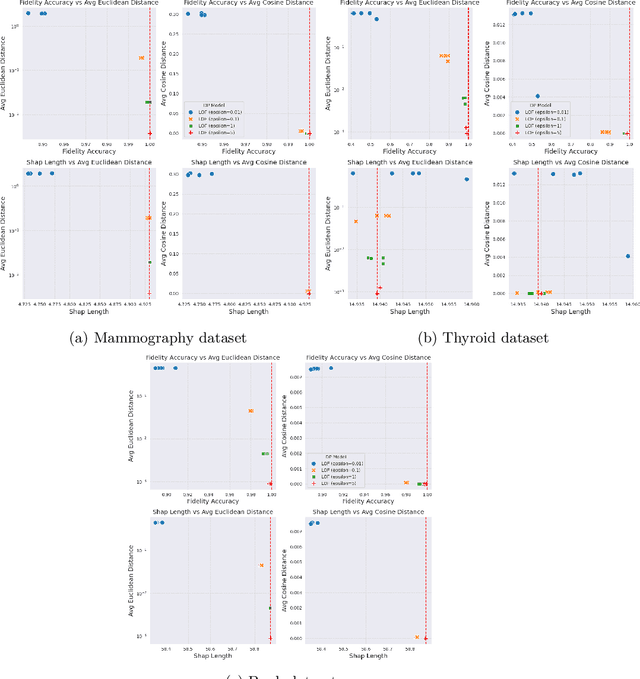
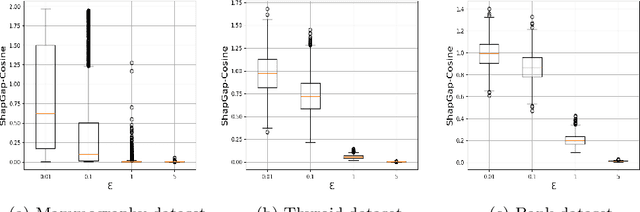
Abstract:Anomaly detection (AD), also referred to as outlier detection, is a statistical process aimed at identifying observations within a dataset that significantly deviate from the expected pattern of the majority of the data. Such a process finds wide application in various fields, such as finance and healthcare. While the primary objective of AD is to yield high detection accuracy, the requirements of explainability and privacy are also paramount. The first ensures the transparency of the AD process, while the second guarantees that no sensitive information is leaked to untrusted parties. In this work, we exploit the trade-off of applying Explainable AI (XAI) through SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) and differential privacy (DP). We perform AD with different models and on various datasets, and we thoroughly evaluate the cost of privacy in terms of decreased accuracy and explainability. Our results show that the enforcement of privacy through DP has a significant impact on detection accuracy and explainability, which depends on both the dataset and the considered AD model. We further show that the visual interpretation of explanations is also influenced by the choice of the AD algorithm.
Knowledge Distillation-Based Model Extraction Attack using Private Counterfactual Explanations
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:In recent years, there has been a notable increase in the deployment of machine learning (ML) models as services (MLaaS) across diverse production software applications. In parallel, explainable AI (XAI) continues to evolve, addressing the necessity for transparency and trustworthiness in ML models. XAI techniques aim to enhance the transparency of ML models by providing insights, in terms of the model's explanations, into their decision-making process. Simultaneously, some MLaaS platforms now offer explanations alongside the ML prediction outputs. This setup has elevated concerns regarding vulnerabilities in MLaaS, particularly in relation to privacy leakage attacks such as model extraction attacks (MEA). This is due to the fact that explanations can unveil insights about the inner workings of the model which could be exploited by malicious users. In this work, we focus on investigating how model explanations, particularly Generative adversarial networks (GANs)-based counterfactual explanations (CFs), can be exploited for performing MEA within the MLaaS platform. We also delve into assessing the effectiveness of incorporating differential privacy (DP) as a mitigation strategy. To this end, we first propose a novel MEA methodology based on Knowledge Distillation (KD) to enhance the efficiency of extracting a substitute model of a target model exploiting CFs. Then, we advise an approach for training CF generators incorporating DP to generate private CFs. We conduct thorough experimental evaluations on real-world datasets and demonstrate that our proposed KD-based MEA can yield a high-fidelity substitute model with reduced queries with respect to baseline approaches. Furthermore, our findings reveal that the inclusion of a privacy layer impacts the performance of the explainer, the quality of CFs, and results in a reduction in the MEA performance.
How "troll" are you? Measuring and detecting troll behavior in online social networks
Oct 17, 2022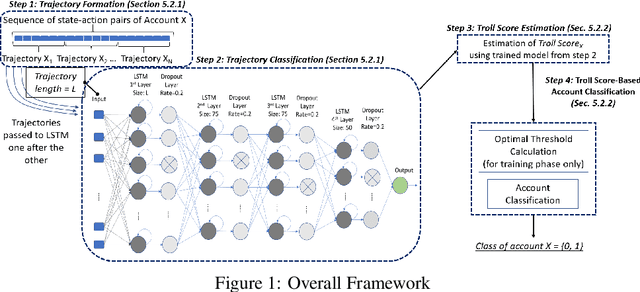
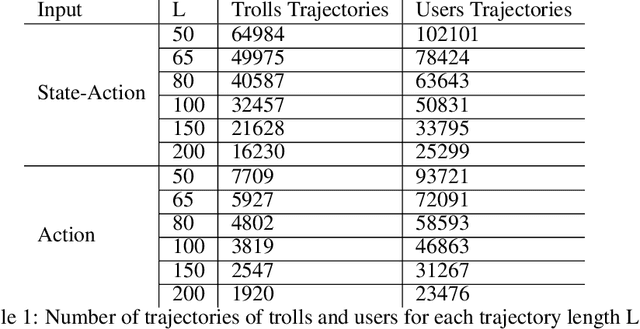
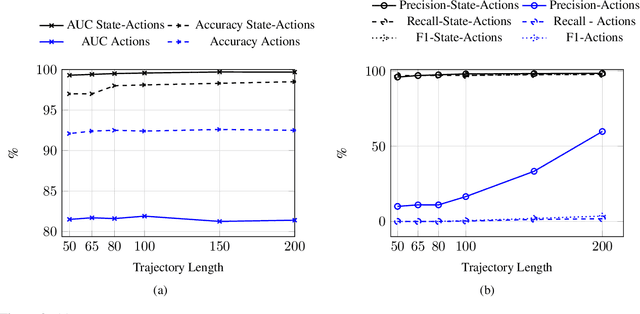

Abstract:The detection of state-sponsored trolls acting in misinformation operations is an unsolved and critical challenge for the research community, with repercussions that go beyond the online realm. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for the detection of troll accounts, which consists of two steps. The first step aims at classifying trajectories of accounts' online activities as belonging to either a troll account or to an organic user account. In the second step, we exploit the classified trajectories to compute a metric, namely "troll score", which allows us to quantify the extent to which an account behaves like a troll. Experimental results show that our approach identifies accounts' trajectories with an AUC close to 99% and, accordingly, classify trolls and organic users with an AUC of 97%. Finally, we evaluate whether the proposed solution can be generalized to different contexts (e.g., discussions about Covid-19) and generic misbehaving users, showing promising results that will be further expanded in our future endeavors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge