Marco Comuzzi
Measuring the Stability of Process Outcome Predictions in Online Settings
Oct 13, 2023Abstract:Predictive Process Monitoring aims to forecast the future progress of process instances using historical event data. As predictive process monitoring is increasingly applied in online settings to enable timely interventions, evaluating the performance of the underlying models becomes crucial for ensuring their consistency and reliability over time. This is especially important in high risk business scenarios where incorrect predictions may have severe consequences. However, predictive models are currently usually evaluated using a single, aggregated value or a time-series visualization, which makes it challenging to assess their performance and, specifically, their stability over time. This paper proposes an evaluation framework for assessing the stability of models for online predictive process monitoring. The framework introduces four performance meta-measures: the frequency of significant performance drops, the magnitude of such drops, the recovery rate, and the volatility of performance. To validate this framework, we applied it to two artificial and two real-world event logs. The results demonstrate that these meta-measures facilitate the comparison and selection of predictive models for different risk-taking scenarios. Such insights are of particular value to enhance decision-making in dynamic business environments.
Analyzing Process-Aware Information System Updates Using Digital Twins of Organizations
Mar 24, 2022



Abstract:Digital transformation often entails small-scale changes to information systems supporting the execution of business processes. These changes may increase the operational frictions in process execution, which decreases the process performance. The contributions in the literature providing support to the tracking and impact analysis of small-scale changes are limited in scope and functionality. In this paper, we use the recently developed Digital Twins of Organizations (DTOs) to assess the impact of (process-aware) information systems updates. More in detail, we model the updates using the configuration of DTOs and quantitatively assess different types of impacts of information system updates (structural, operational, and performance-related). We implemented a prototype of the proposed approach. Moreover, we discuss a case study involving a standard ERP procure-to-pay business process.
Explainable Predictive Process Monitoring: A User Evaluation
Feb 15, 2022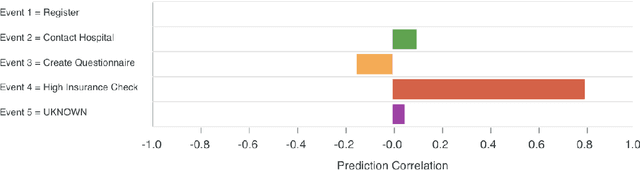
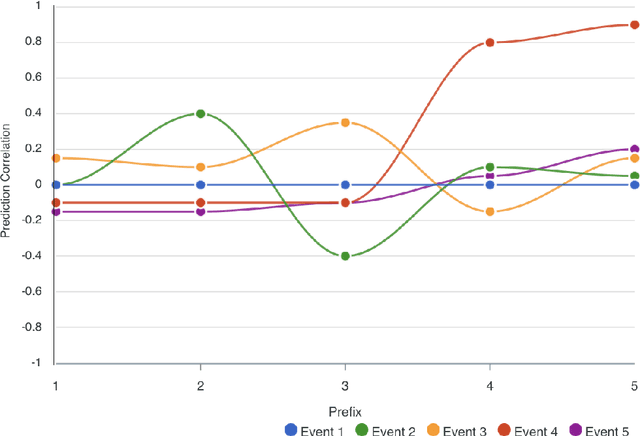
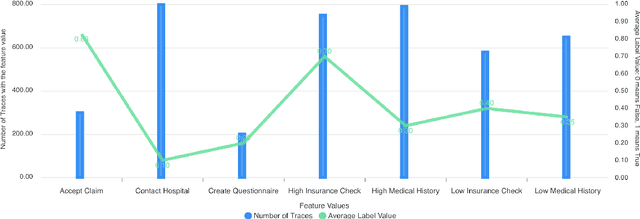
Abstract:Explainability is motivated by the lack of transparency of black-box Machine Learning approaches, which do not foster trust and acceptance of Machine Learning algorithms. This also happens in the Predictive Process Monitoring field, where predictions, obtained by applying Machine Learning techniques, need to be explained to users, so as to gain their trust and acceptance. In this work, we carry on a user evaluation on explanation approaches for Predictive Process Monitoring aiming at investigating whether and how the explanations provided (i) are understandable; (ii) are useful in decision making tasks;(iii) can be further improved for process analysts, with different Machine Learning expertise levels. The results of the user evaluation show that, although explanation plots are overall understandable and useful for decision making tasks for Business Process Management users -- with and without experience in Machine Learning -- differences exist in the comprehension and usage of different plots, as well as in the way users with different Machine Learning expertise understand and use them.
Online anomaly detection using statistical leverage for streaming business process events
Mar 01, 2021



Abstract:While several techniques for detecting trace-level anomalies in event logs in offline settings have appeared recently in the literature, such techniques are currently lacking for online settings. Event log anomaly detection in online settings can be crucial for discovering anomalies in process execution as soon as they occur and, consequently, allowing to promptly take early corrective actions. This paper describes a novel approach to event log anomaly detection on event streams that uses statistical leverage. Leverage has been used extensively in statistics to develop measures to identify outliers and it has been adapted in this paper to the specific scenario of event stream data. The proposed approach has been evaluated on both artificial and real event streams.
An empirical investigation of different classifiers, encoding and ensemble schemes for next event prediction using business process event logs
Aug 24, 2020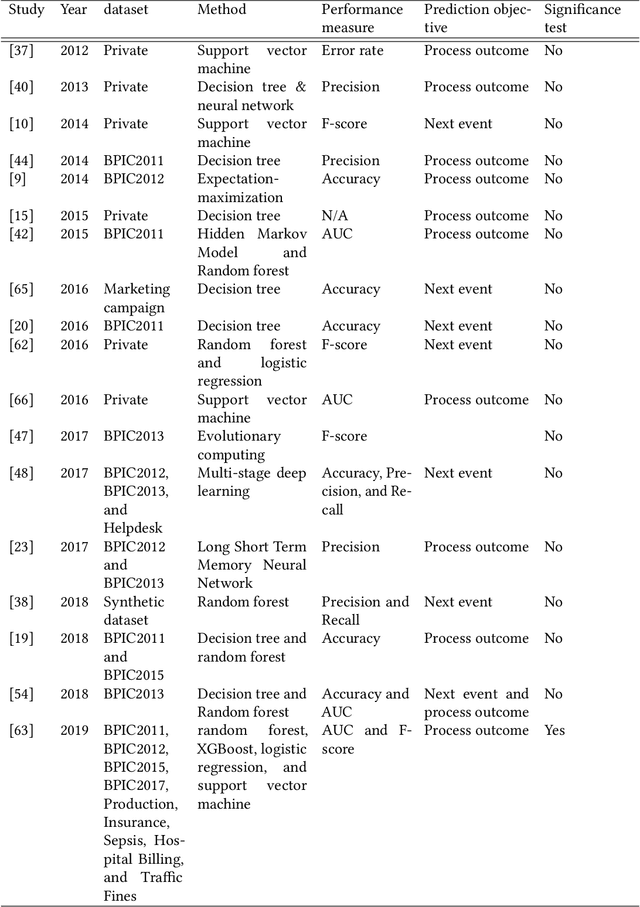
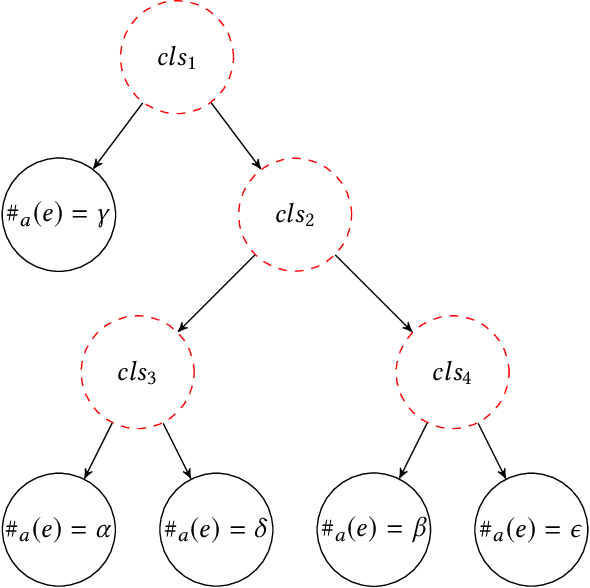
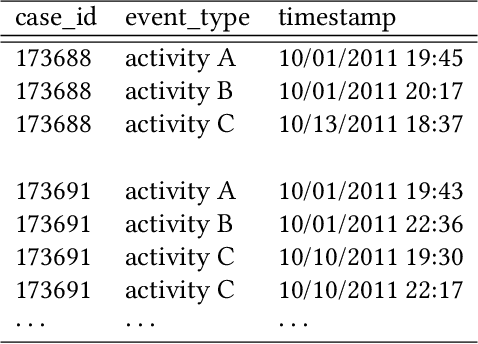
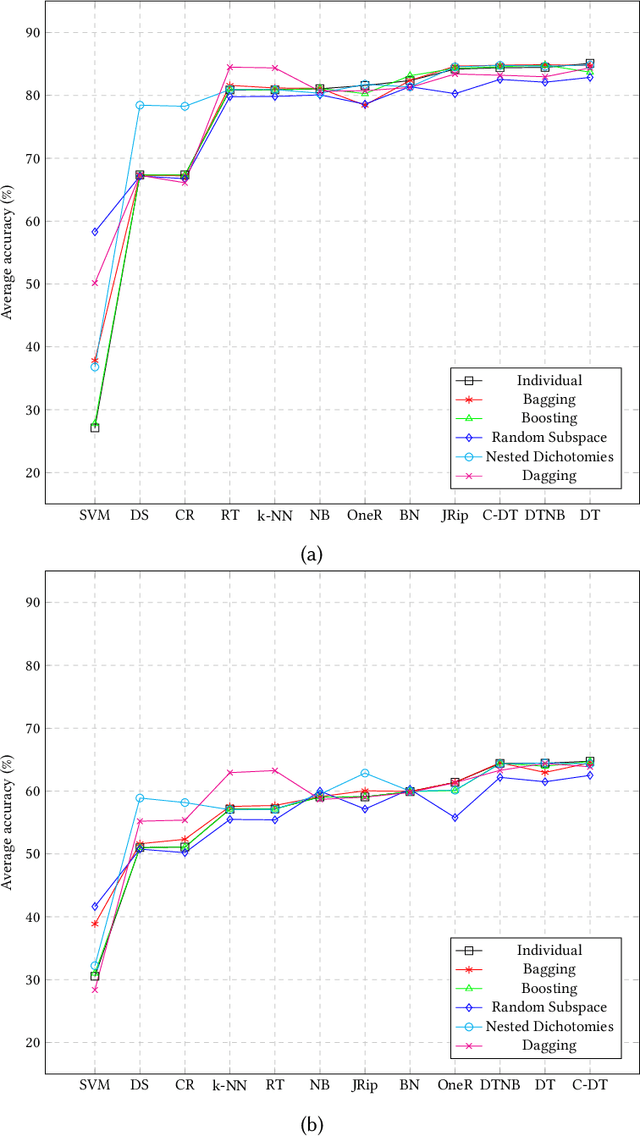
Abstract:There is a growing need for empirical benchmarks that support researchers and practitioners in selecting the best machine learning technique for given prediction tasks. In this paper, we consider the next event prediction task in business process predictive monitoring and we extend our previously published benchmark by studying the impact on the performance of different encoding windows and of using ensemble schemes. The choice of whether to use ensembles and which scheme to use often depends on the type of data and classification task. While there is a general understanding that ensembles perform well in predictive monitoring of business processes, next event prediction is a task for which no other benchmarks involving ensembles are available. The proposed benchmark helps researchers to select a high performing individual classifier or ensemble scheme given the variability at the case level of the event log under consideration. Experimental results show that choosing an optimal number of events for feature encoding is challenging, resulting in the need to consider each event log individually when selecting an optimal value. Ensemble schemes improve the performance of low performing classifiers in this task, such as SVM, whereas high performing classifiers, such as tree-based classifiers, are not better off when ensemble schemes are considered.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge