Mannes Poel
Trajectory Generation, Control, and Safety with Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
Jun 27, 2023Abstract:We present a framework for safety-critical optimal control of physical systems based on denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs). The technology of control barrier functions (CBFs), encoding desired safety constraints, is used in combination with DDPMs to plan actions by iteratively denoising trajectories through a CBF-based guided sampling procedure. At the same time, the generated trajectories are also guided to maximize a future cumulative reward representing a specific task to be optimally executed. The proposed scheme can be seen as an offline and model-based reinforcement learning algorithm resembling in its functionalities a model-predictive control optimization scheme with receding horizon in which the selected actions lead to optimal and safe trajectories.
Unsupervised Representation Learning in Deep Reinforcement Learning: A Review
Aug 27, 2022Abstract:This review addresses the problem of learning abstract representations of the measurement data in the context of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). While the data are often ambiguous, high-dimensional, and complex to interpret, many dynamical systems can be effectively described by a low-dimensional set of state variables. Discovering these state variables from the data is a crucial aspect for improving the data efficiency, robustness and generalization of DRL methods, tackling the curse of dimensionality, and bringing interpretability and insights into black-box DRL. This review provides a comprehensive and complete overview of unsupervised representation learning in DRL by describing the main Deep Learning tools used for learning representations of the world, providing a systematic view of the method and principles, summarizing applications, benchmarks and evaluation strategies, and discussing open challenges and future directions.
Towards Autonomous Pipeline Inspection with Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning
Jul 08, 2021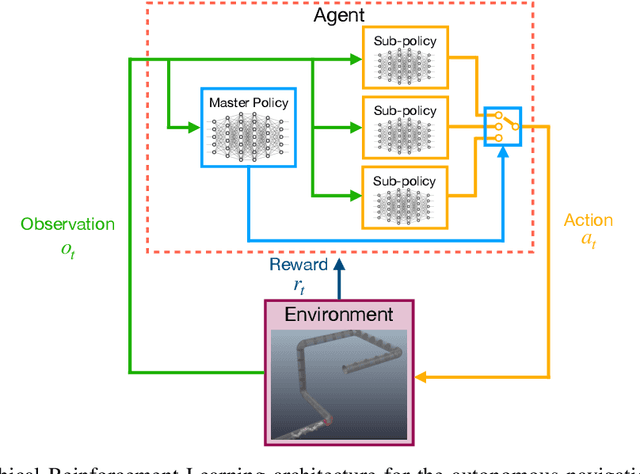
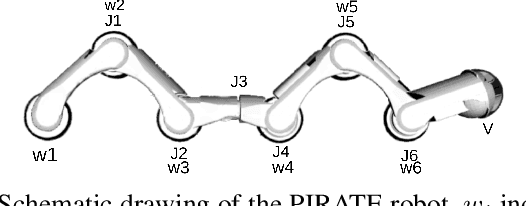

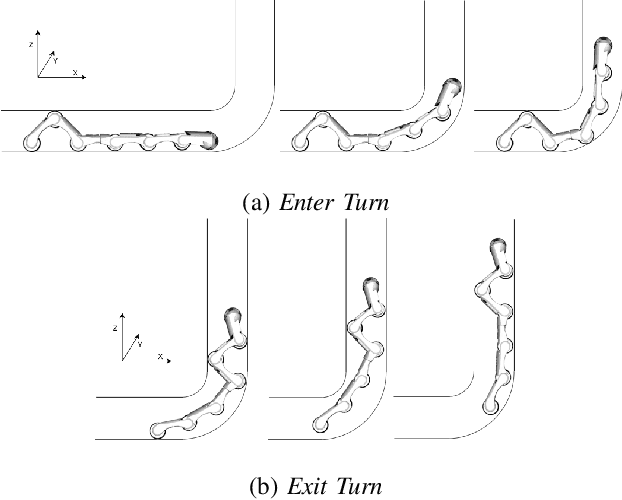
Abstract:Inspection and maintenance are two crucial aspects of industrial pipeline plants. While robotics has made tremendous progress in the mechanic design of in-pipe inspection robots, the autonomous control of such robots is still a big open challenge due to the high number of actuators and the complex manoeuvres required. To address this problem, we investigate the usage of Deep Reinforcement Learning for achieving autonomous navigation of in-pipe robots in pipeline networks with complex topologies. Moreover, we introduce a hierarchical policy decomposition based on Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning to learn robust high-level navigation skills. We show that the hierarchical structure introduced in the policy is fundamental for solving the navigation task through pipes and necessary for achieving navigation performances superior to human-level control.
Low-Dimensional State and Action Representation Learning with MDP Homomorphism Metrics
Jul 04, 2021
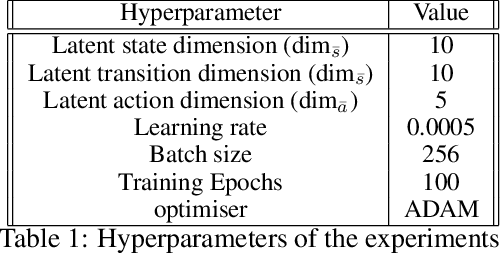
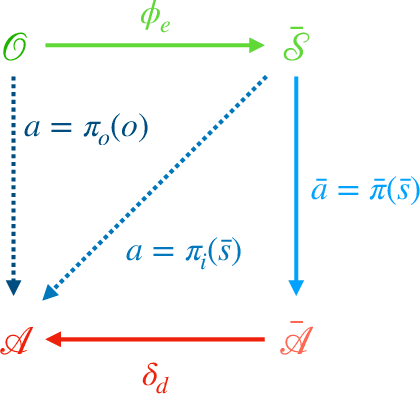

Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning has shown its ability in solving complicated problems directly from high-dimensional observations. However, in end-to-end settings, Reinforcement Learning algorithms are not sample-efficient and requires long training times and quantities of data. In this work, we proposed a framework for sample-efficient Reinforcement Learning that take advantage of state and action representations to transform a high-dimensional problem into a low-dimensional one. Moreover, we seek to find the optimal policy mapping latent states to latent actions. Because now the policy is learned on abstract representations, we enforce, using auxiliary loss functions, the lifting of such policy to the original problem domain. Results show that the novel framework can efficiently learn low-dimensional and interpretable state and action representations and the optimal latent policy.
Low Dimensional State Representation Learning with Robotics Priors in Continuous Action Spaces
Jul 04, 2021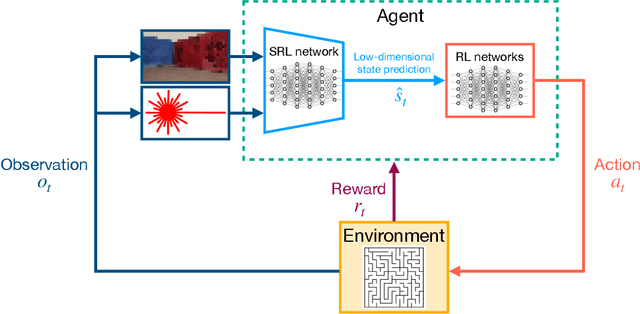
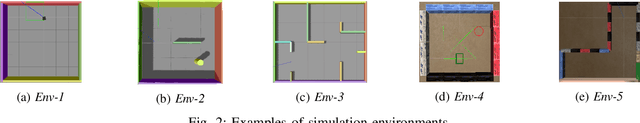
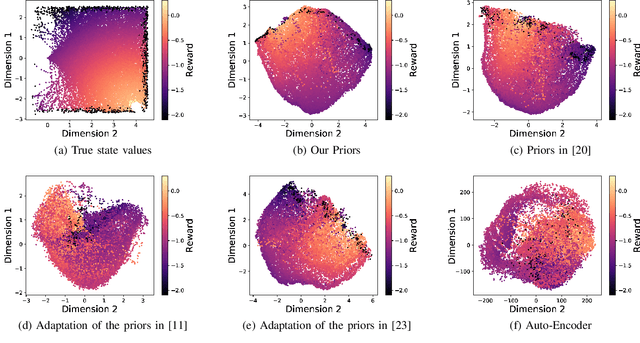
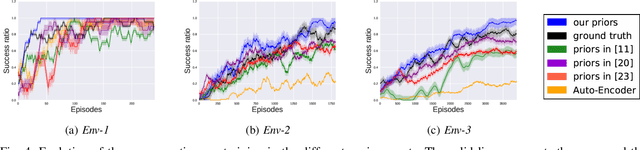
Abstract:Autonomous robots require high degrees of cognitive and motoric intelligence to come into our everyday life. In non-structured environments and in the presence of uncertainties, such degrees of intelligence are not easy to obtain. Reinforcement learning algorithms have proven to be capable of solving complicated robotics tasks in an end-to-end fashion without any need for hand-crafted features or policies. Especially in the context of robotics, in which the cost of real-world data is usually extremely high, reinforcement learning solutions achieving high sample efficiency are needed. In this paper, we propose a framework combining the learning of a low-dimensional state representation, from high-dimensional observations coming from the robot's raw sensory readings, with the learning of the optimal policy, given the learned state representation. We evaluate our framework in the context of mobile robot navigation in the case of continuous state and action spaces. Moreover, we study the problem of transferring what learned in the simulated virtual environment to the real robot without further retraining using real-world data in the presence of visual and depth distractors, such as lighting changes and moving obstacles.
Low Dimensional State Representation Learning with Reward-shaped Priors
Jul 29, 2020



Abstract:Reinforcement Learning has been able to solve many complicated robotics tasks without any need for feature engineering in an end-to-end fashion. However, learning the optimal policy directly from the sensory inputs, i.e the observations, often requires processing and storage of a huge amount of data. In the context of robotics, the cost of data from real robotics hardware is usually very high, thus solutions that achieve high sample-efficiency are needed. We propose a method that aims at learning a mapping from the observations into a lower-dimensional state space. This mapping is learned with unsupervised learning using loss functions shaped to incorporate prior knowledge of the environment and the task. Using the samples from the state space, the optimal policy is quickly and efficiently learned. We test the method on several mobile robot navigation tasks in a simulation environment and also on a real robot.
On Reward Shaping for Mobile Robot Navigation: A Reinforcement Learning and SLAM Based Approach
Feb 10, 2020



Abstract:We present a map-less path planning algorithm based on Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) for mobile robots navigating in unknown environment that only relies on 40-dimensional raw laser data and odometry information. The planner is trained using a reward function shaped based on the online knowledge of the map of the training environment, obtained using grid-based Rao-Blackwellized particle filter, in an attempt to enhance the obstacle awareness of the agent. The agent is trained in a complex simulated environment and evaluated in two unseen ones. We show that the policy trained using the introduced reward function not only outperforms standard reward functions in terms of convergence speed, by a reduction of 36.9\% of the iteration steps, and reduction of the collision samples, but it also drastically improves the behaviour of the agent in unseen environments, respectively by 23\% in a simpler workspace and by 45\% in a more clustered one. Furthermore, the policy trained in the simulation environment can be directly and successfully transferred to the real robot. A video of our experiments can be found at: https://youtu.be/UEV7W6e6ZqI
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge