Mahesh Reddy
Scale-Invariant Monocular Depth Estimation via SSI Depth
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Existing methods for scale-invariant monocular depth estimation (SI MDE) often struggle due to the complexity of the task, and limited and non-diverse datasets, hindering generalizability in real-world scenarios. This is while shift-and-scale-invariant (SSI) depth estimation, simplifying the task and enabling training with abundant stereo datasets achieves high performance. We present a novel approach that leverages SSI inputs to enhance SI depth estimation, streamlining the network's role and facilitating in-the-wild generalization for SI depth estimation while only using a synthetic dataset for training. Emphasizing the generation of high-resolution details, we introduce a novel sparse ordinal loss that substantially improves detail generation in SSI MDE, addressing critical limitations in existing approaches. Through in-the-wild qualitative examples and zero-shot evaluation we substantiate the practical utility of our approach in computational photography applications, showcasing its ability to generate highly detailed SI depth maps and achieve generalization in diverse scenarios.
EdgeRelight360: Text-Conditioned 360-Degree HDR Image Generation for Real-Time On-Device Video Portrait Relighting
Apr 15, 2024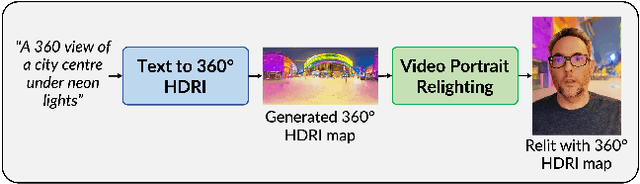
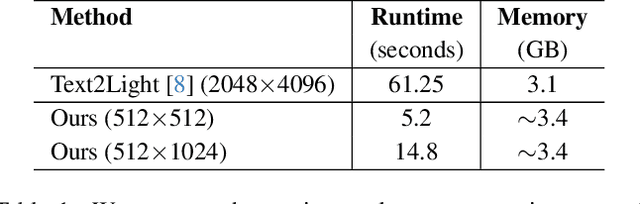
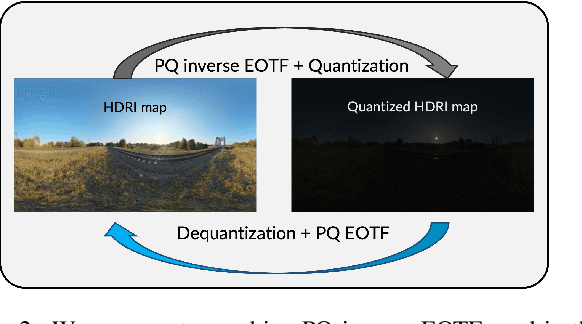
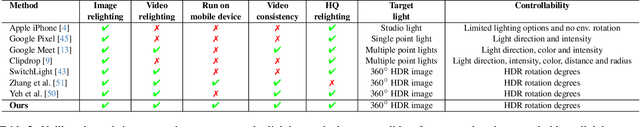
Abstract:In this paper, we present EdgeRelight360, an approach for real-time video portrait relighting on mobile devices, utilizing text-conditioned generation of 360-degree high dynamic range image (HDRI) maps. Our method proposes a diffusion-based text-to-360-degree image generation in the HDR domain, taking advantage of the HDR10 standard. This technique facilitates the generation of high-quality, realistic lighting conditions from textual descriptions, offering flexibility and control in portrait video relighting task. Unlike the previous relighting frameworks, our proposed system performs video relighting directly on-device, enabling real-time inference with real 360-degree HDRI maps. This on-device processing ensures both privacy and guarantees low runtime, providing an immediate response to changes in lighting conditions or user inputs. Our approach paves the way for new possibilities in real-time video applications, including video conferencing, gaming, and augmented reality, by allowing dynamic, text-based control of lighting conditions.
HexaGen3D: StableDiffusion is just one step away from Fast and Diverse Text-to-3D Generation
Jan 15, 2024Abstract:Despite the latest remarkable advances in generative modeling, efficient generation of high-quality 3D assets from textual prompts remains a difficult task. A key challenge lies in data scarcity: the most extensive 3D datasets encompass merely millions of assets, while their 2D counterparts contain billions of text-image pairs. To address this, we propose a novel approach which harnesses the power of large, pretrained 2D diffusion models. More specifically, our approach, HexaGen3D, fine-tunes a pretrained text-to-image model to jointly predict 6 orthographic projections and the corresponding latent triplane. We then decode these latents to generate a textured mesh. HexaGen3D does not require per-sample optimization, and can infer high-quality and diverse objects from textual prompts in 7 seconds, offering significantly better quality-to-latency trade-offs when comparing to existing approaches. Furthermore, HexaGen3D demonstrates strong generalization to new objects or compositions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge