Madina Hasan
The 2015 Sheffield System for Transcription of Multi-Genre Broadcast Media
Dec 21, 2015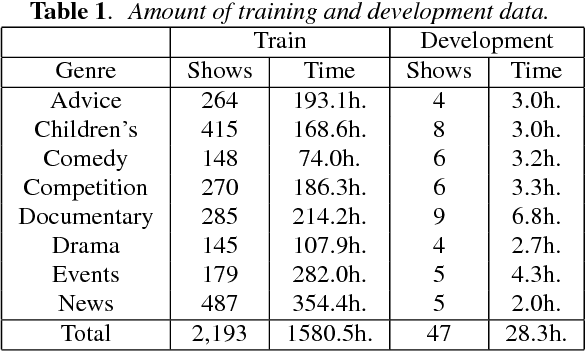
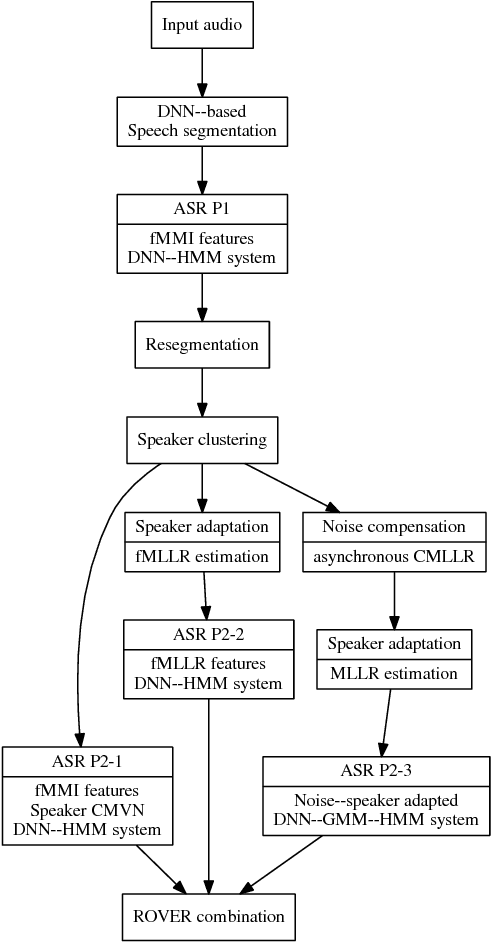
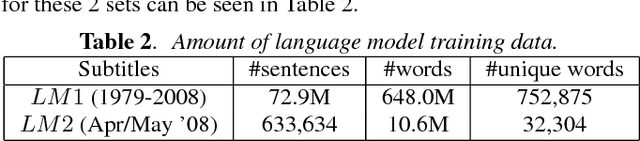
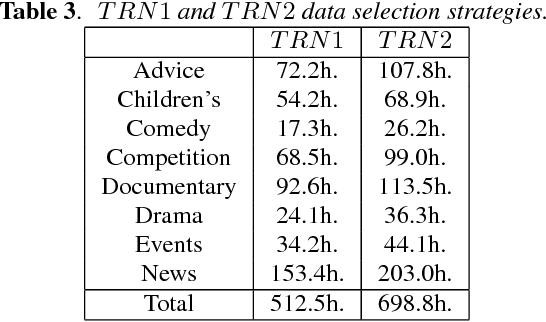
Abstract:We describe the University of Sheffield system for participation in the 2015 Multi-Genre Broadcast (MGB) challenge task of transcribing multi-genre broadcast shows. Transcription was one of four tasks proposed in the MGB challenge, with the aim of advancing the state of the art of automatic speech recognition, speaker diarisation and automatic alignment of subtitles for broadcast media. Four topics are investigated in this work: Data selection techniques for training with unreliable data, automatic speech segmentation of broadcast media shows, acoustic modelling and adaptation in highly variable environments, and language modelling of multi-genre shows. The final system operates in multiple passes, using an initial unadapted decoding stage to refine segmentation, followed by three adapted passes: a hybrid DNN pass with input features normalised by speaker-based cepstral normalisation, another hybrid stage with input features normalised by speaker feature-MLLR transformations, and finally a bottleneck-based tandem stage with noise and speaker factorisation. The combination of these three system outputs provides a final error rate of 27.5% on the official development set, consisting of 47 multi-genre shows.
The USFD Spoken Language Translation System for IWSLT 2014
Sep 13, 2015



Abstract:The University of Sheffield (USFD) participated in the International Workshop for Spoken Language Translation (IWSLT) in 2014. In this paper, we will introduce the USFD SLT system for IWSLT. Automatic speech recognition (ASR) is achieved by two multi-pass deep neural network systems with adaptation and rescoring techniques. Machine translation (MT) is achieved by a phrase-based system. The USFD primary system incorporates state-of-the-art ASR and MT techniques and gives a BLEU score of 23.45 and 14.75 on the English-to-French and English-to-German speech-to-text translation task with the IWSLT 2014 data. The USFD contrastive systems explore the integration of ASR and MT by using a quality estimation system to rescore the ASR outputs, optimising towards better translation. This gives a further 0.54 and 0.26 BLEU improvement respectively on the IWSLT 2012 and 2014 evaluation data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge