Rosanna Milner
A Browser-based Open Source Assistant for Multimodal Content Verification
Mar 03, 2026Abstract:Disinformation and false content produced by generative AI pose a significant challenge for journalists and fact-checkers who must rapidly verify digital media information. While there is an abundance of NLP models for detecting credibility signals such as persuasion techniques, subjectivity, or machine-generated text, such methods often remain inaccessible to non-expert users and are not integrated into their daily workflows as a unified framework. This paper demonstrates the VERIFICATION ASSISTANT, a browser-based tool designed to bridge this gap. The VERIFICATION ASSISTANT, a core component of the widely adopted VERIFICATION PLUGIN (140,000+ users), allows users to submit URLs or media files to a unified interface. It automatically extracts content and routes it to a suite of backend NLP classifiers, delivering actionable credibility signals, estimating AI-generated content, and providing other verification guidance in a clear, easy-to-digest format. This paper showcases the tool architecture, its integration of multiple NLP services, and its real-world application to detecting disinformation.
Empirical Interpretation of the Relationship Between Speech Acoustic Context and Emotion Recognition
Jun 30, 2023



Abstract:Speech emotion recognition (SER) is vital for obtaining emotional intelligence and understanding the contextual meaning of speech. Variations of consonant-vowel (CV) phonemic boundaries can enrich acoustic context with linguistic cues, which impacts SER. In practice, speech emotions are treated as single labels over an acoustic segment for a given time duration. However, phone boundaries within speech are not discrete events, therefore the perceived emotion state should also be distributed over potentially continuous time-windows. This research explores the implication of acoustic context and phone boundaries on local markers for SER using an attention-based approach. The benefits of using a distributed approach to speech emotion understanding are supported by the results of cross-corpora analysis experiments. Experiments where phones and words are mapped to the attention vectors along with the fundamental frequency to observe the overlapping distributions and thereby the relationship between acoustic context and emotion. This work aims to bridge psycholinguistic theory research with computational modelling for SER.
A cross-corpus study on speech emotion recognition
Jul 05, 2022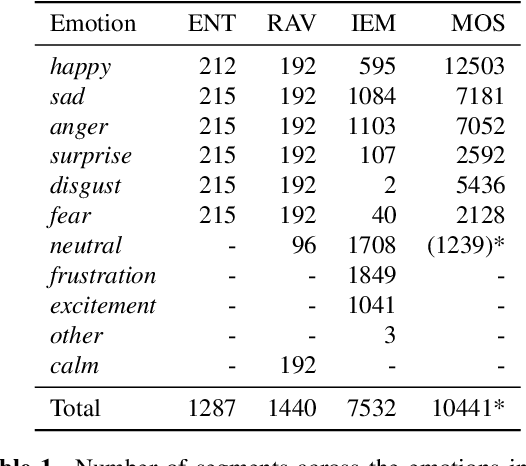
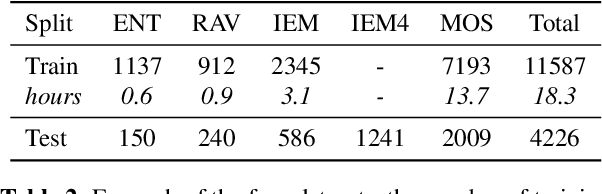
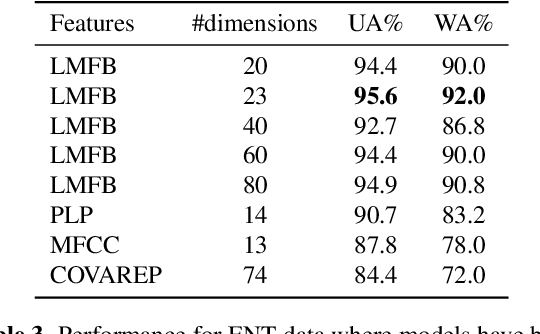
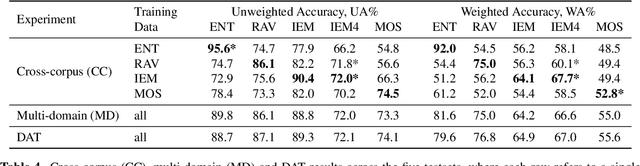
Abstract:For speech emotion datasets, it has been difficult to acquire large quantities of reliable data and acted emotions may be over the top compared to less expressive emotions displayed in everyday life. Lately, larger datasets with natural emotions have been created. Instead of ignoring smaller, acted datasets, this study investigates whether information learnt from acted emotions is useful for detecting natural emotions. Cross-corpus research has mostly considered cross-lingual and even cross-age datasets, and difficulties arise from different methods of annotating emotions causing a drop in performance. To be consistent, four adult English datasets covering acted, elicited and natural emotions are considered. A state-of-the-art model is proposed to accurately investigate the degradation of performance. The system involves a bi-directional LSTM with an attention mechanism to classify emotions across datasets. Experiments study the effects of training models in a cross-corpus and multi-domain fashion and results show the transfer of information is not successful. Out-of-domain models, followed by adapting to the missing dataset, and domain adversarial training (DAT) are shown to be more suitable to generalising to emotions across datasets. This shows positive information transfer from acted datasets to those with more natural emotions and the benefits from training on different corpora.
* ASRU 2019
The 2015 Sheffield System for Transcription of Multi-Genre Broadcast Media
Dec 21, 2015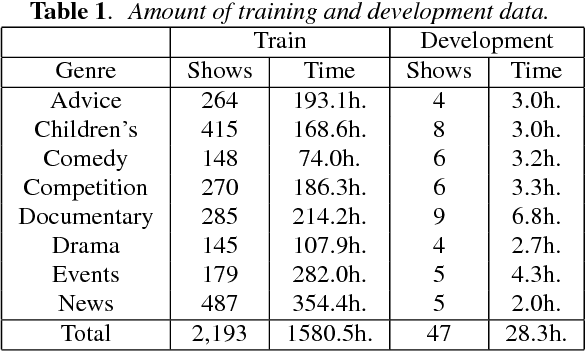
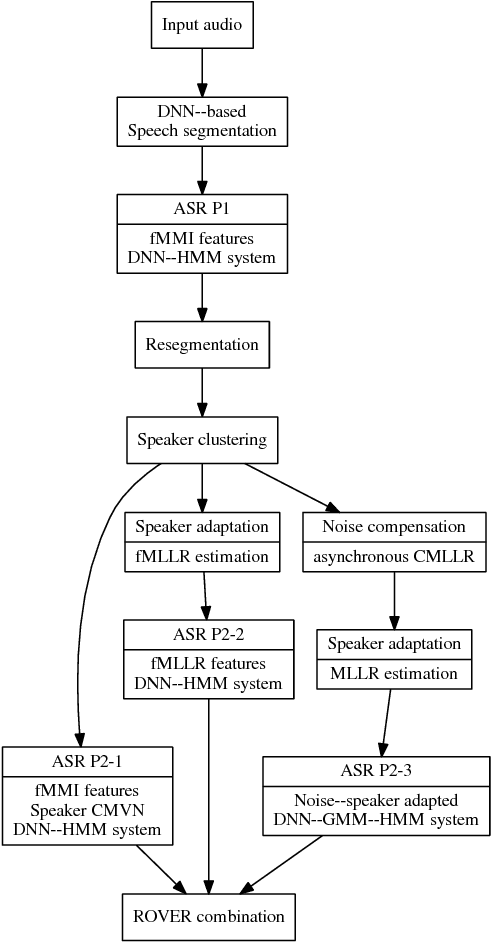
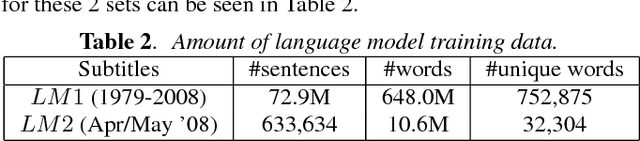
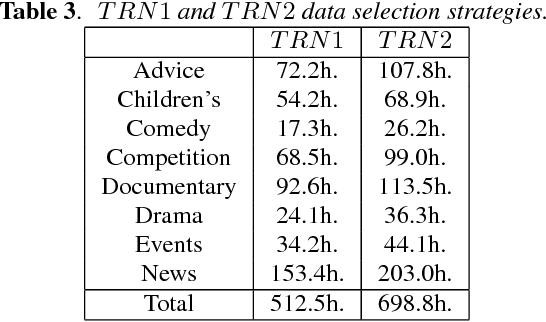
Abstract:We describe the University of Sheffield system for participation in the 2015 Multi-Genre Broadcast (MGB) challenge task of transcribing multi-genre broadcast shows. Transcription was one of four tasks proposed in the MGB challenge, with the aim of advancing the state of the art of automatic speech recognition, speaker diarisation and automatic alignment of subtitles for broadcast media. Four topics are investigated in this work: Data selection techniques for training with unreliable data, automatic speech segmentation of broadcast media shows, acoustic modelling and adaptation in highly variable environments, and language modelling of multi-genre shows. The final system operates in multiple passes, using an initial unadapted decoding stage to refine segmentation, followed by three adapted passes: a hybrid DNN pass with input features normalised by speaker-based cepstral normalisation, another hybrid stage with input features normalised by speaker feature-MLLR transformations, and finally a bottleneck-based tandem stage with noise and speaker factorisation. The combination of these three system outputs provides a final error rate of 27.5% on the official development set, consisting of 47 multi-genre shows.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge