M Usman Maqbool Bhutta
Smart-Inspect: Micro Scale Localization and Classification of Smartphone Glass Defects for Industrial Automation
Oct 02, 2020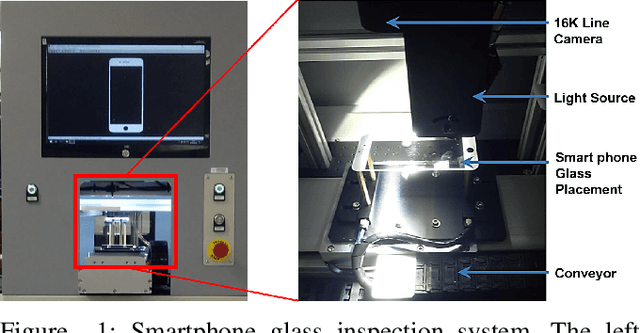
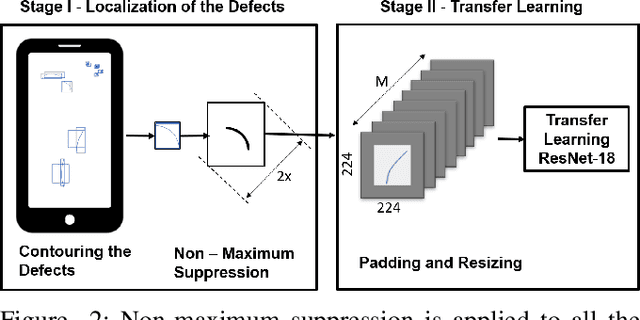
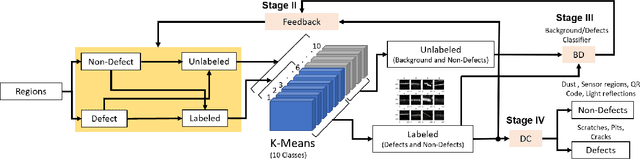

Abstract:The presence of any type of defect on the glass screen of smart devices has a great impact on their quality. We present a robust semi-supervised learning framework for intelligent micro-scaled localization and classification of defects on a 16K pixel image of smartphone glass. Our model features the efficient recognition and labeling of three types of defects: scratches, light leakage due to cracks, and pits. Our method also differentiates between the defects and light reflections due to dust particles and sensor regions, which are classified as non-defect areas. We use a partially labeled dataset to achieve high robustness and excellent classification of defect and non-defect areas as compared to principal components analysis (PCA), multi-resolution and information-fusion-based algorithms. In addition, we incorporated two classifiers at different stages of our inspection framework for labeling and refining the unlabeled defects. We successfully enhanced the inspection depth-limit up to 5 microns. The experimental results show that our method outperforms manual inspection in testing the quality of glass screen samples by identifying defects on samples that have been marked as good by human inspection.
Loop-box: Multi-Agent Direct SLAM Triggered by Single Loop Closure for Large-Scale Mapping
Sep 29, 2020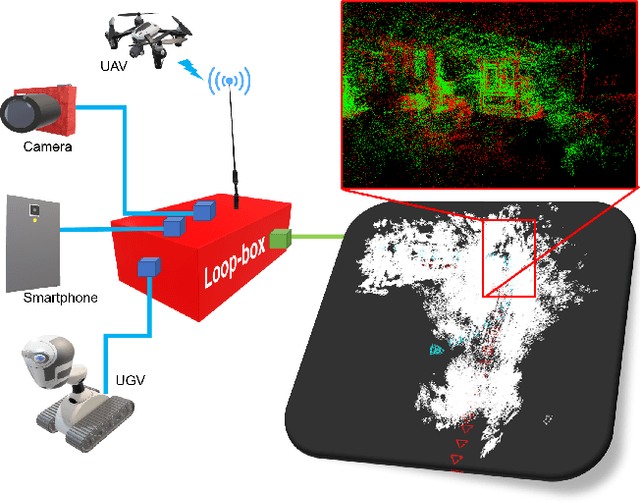
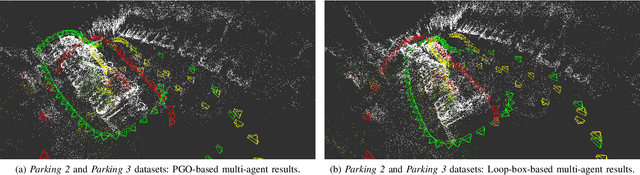


Abstract:In this paper, we present a multi-agent framework for real-time large-scale 3D reconstruction applications. In SLAM, researchers usually build and update a 3D map after applying non-linear pose graph optimization techniques. Moreover, many multi-agent systems are prevalently using odometry information from additional sensors. These methods generally involve intensive computer vision algorithms and are tightly coupled with various sensors. We develop a generic method for the keychallenging scenarios in multi-agent 3D mapping based on different camera systems. The proposed framework performs actively in terms of localizing each agent after the first loop closure between them. It is shown that the proposed system only uses monocular cameras to yield real-time multi-agent large-scale localization and 3D global mapping. Based on the initial matching, our system can calculate the optimal scale difference between multiple 3D maps and then estimate an accurate relative pose transformation for large-scale global mapping.
* Material related to this work is available at https://usmanmaqbool.github.io/loop-box
Multiple Lane Detection Algorithm Based on Optimised Dense Disparity Map Estimation
Aug 28, 2018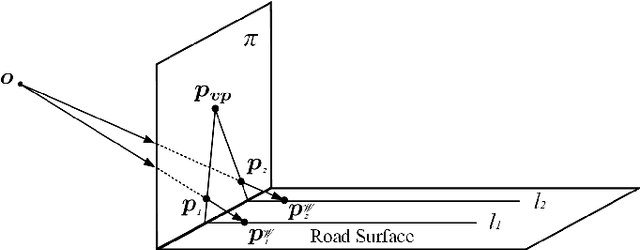
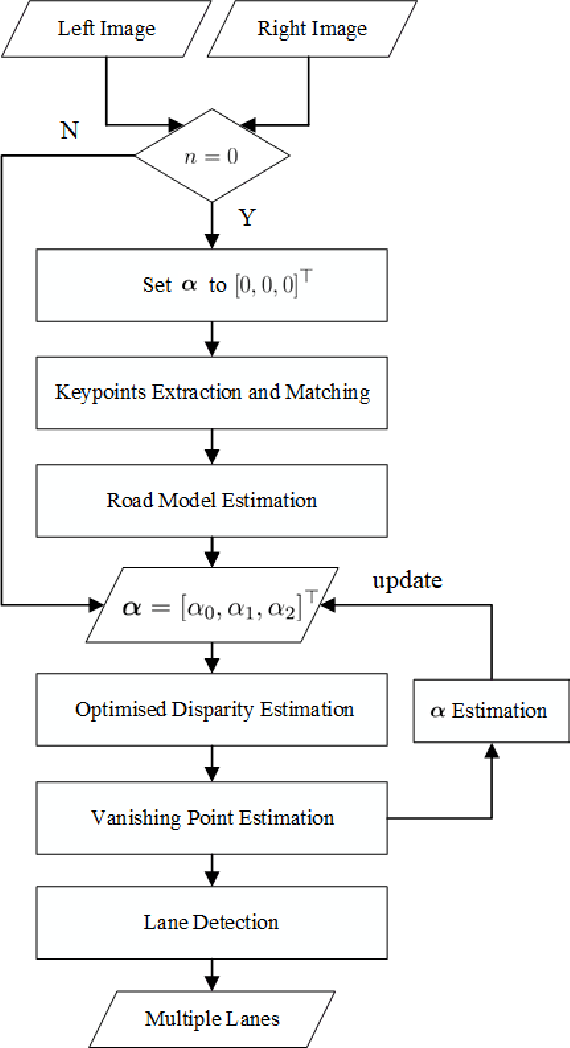

Abstract:Lane detection is very important for self-driving vehicles. In recent years, computer stereo vision has been prevalently used to enhance the accuracy of the lane detection systems. This paper mainly presents a multiple lane detection algorithm developed based on optimised dense disparity map estimation, where the disparity information obtained at time t_{n} is utilised to optimise the process of disparity estimation at time t_{n+1}. This is achieved by estimating the road model at time t_{n} and then controlling the search range for the disparity estimation at time t_{n+1}. The lanes are then detected using our previously published algorithm, where the vanishing point information is used to model the lanes. The experimental results illustrate that the runtime of the disparity estimation is reduced by around 37% and the accuracy of the lane detection is about 99%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge