Luya Gao
Pushing the Frontier of Audiovisual Perception with Large-Scale Multimodal Correspondence Learning
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:We introduce Perception Encoder Audiovisual, PE-AV, a new family of encoders for audio and video understanding trained with scaled contrastive learning. Built on PE, PE-AV makes several key contributions to extend representations to audio, and natively support joint embeddings across audio-video, audio-text, and video-text modalities. PE-AV's unified cross-modal embeddings enable novel tasks such as speech retrieval, and set a new state of the art across standard audio and video benchmarks. We unlock this by building a strong audiovisual data engine that synthesizes high-quality captions for O(100M) audio-video pairs, enabling large-scale supervision consistent across modalities. Our audio data includes speech, music, and general sound effects-avoiding single-domain limitations common in prior work. We exploit ten pairwise contrastive objectives, showing that scaling cross-modality and caption-type pairs strengthens alignment and improves zero-shot performance. We further develop PE-A-Frame by fine-tuning PE-AV with frame-level contrastive objectives, enabling fine-grained audio-frame-to-text alignment for tasks such as sound event detection.
SAM Audio: Segment Anything in Audio
Dec 19, 2025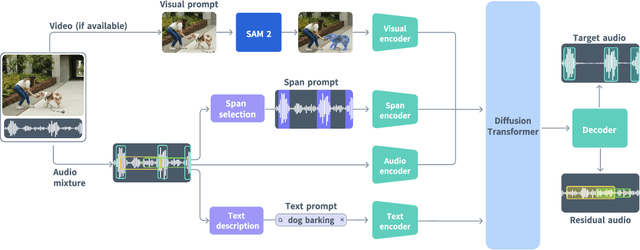
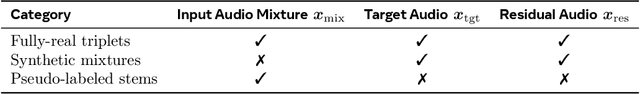
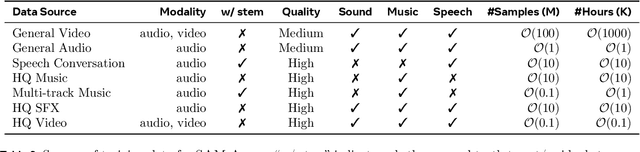
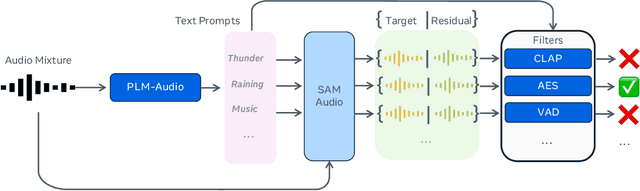
Abstract:General audio source separation is a key capability for multimodal AI systems that can perceive and reason about sound. Despite substantial progress in recent years, existing separation models are either domain-specific, designed for fixed categories such as speech or music, or limited in controllability, supporting only a single prompting modality such as text. In this work, we present SAM Audio, a foundation model for general audio separation that unifies text, visual, and temporal span prompting within a single framework. Built on a diffusion transformer architecture, SAM Audio is trained with flow matching on large-scale audio data spanning speech, music, and general sounds, and can flexibly separate target sources described by language, visual masks, or temporal spans. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance across a diverse suite of benchmarks, including general sound, speech, music, and musical instrument separation in both in-the-wild and professionally produced audios, substantially outperforming prior general-purpose and specialized systems. Furthermore, we introduce a new real-world separation benchmark with human-labeled multimodal prompts and a reference-free evaluation model that correlates strongly with human judgment.
Movie Gen: A Cast of Media Foundation Models
Oct 17, 2024
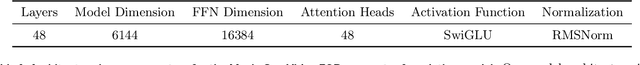
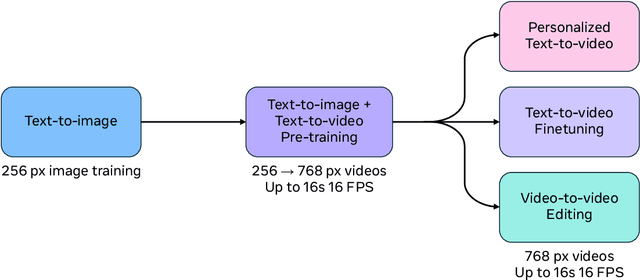
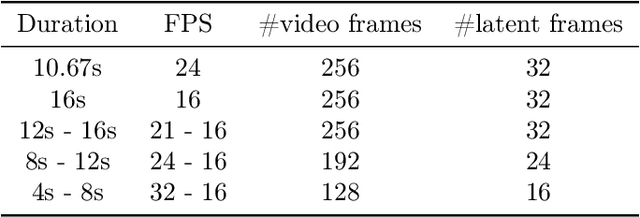
Abstract:We present Movie Gen, a cast of foundation models that generates high-quality, 1080p HD videos with different aspect ratios and synchronized audio. We also show additional capabilities such as precise instruction-based video editing and generation of personalized videos based on a user's image. Our models set a new state-of-the-art on multiple tasks: text-to-video synthesis, video personalization, video editing, video-to-audio generation, and text-to-audio generation. Our largest video generation model is a 30B parameter transformer trained with a maximum context length of 73K video tokens, corresponding to a generated video of 16 seconds at 16 frames-per-second. We show multiple technical innovations and simplifications on the architecture, latent spaces, training objectives and recipes, data curation, evaluation protocols, parallelization techniques, and inference optimizations that allow us to reap the benefits of scaling pre-training data, model size, and training compute for training large scale media generation models. We hope this paper helps the research community to accelerate progress and innovation in media generation models. All videos from this paper are available at https://go.fb.me/MovieGenResearchVideos.
UnsupervisedR&R: Unsupervised Point Cloud Registration via Differentiable Rendering
Feb 23, 2021



Abstract:Aligning partial views of a scene into a single whole is essential to understanding one's environment and is a key component of numerous robotics tasks such as SLAM and SfM. Recent approaches have proposed end-to-end systems that can outperform traditional methods by leveraging pose supervision. However, with the rising prevalence of cameras with depth sensors, we can expect a new stream of raw RGB-D data without the annotations needed for supervision. We propose UnsupervisedR&R: an end-to-end unsupervised approach to learning point cloud registration from raw RGB-D video. The key idea is to leverage differentiable alignment and rendering to enforce photometric and geometric consistency between frames. We evaluate our approach on indoor scene datasets and find that we outperform existing traditional approaches with classic and learned descriptors while being competitive with supervised geometric point cloud registration approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge