Luning Bakke
Co-Design of Rover Wheels and Control using Bayesian Optimization and Rover-Terrain Simulations
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:While simulation is vital for optimizing robotic systems, the cost of modeling deformable terrain has long limited its use in full-vehicle studies of off-road autonomous mobility. For example, Discrete Element Method (DEM) simulations are often confined to single-wheel tests, which obscures coupled wheel-vehicle-controller interactions and prevents joint optimization of mechanical design and control. This paper presents a Bayesian optimization framework that co-designs rover wheel geometry and steering controller parameters using high-fidelity, full-vehicle closed-loop simulations on deformable terrain. Using the efficiency and scalability of a continuum-representation model (CRM) for terramechanics, we evaluate candidate designs on trajectories of varying complexity while towing a fixed load. The optimizer tunes wheel parameters (radius, width, and grouser features) and steering PID gains under a multi-objective formulation that balances traversal speed, tracking error, and energy consumption. We compare two strategies: simultaneous co-optimization of wheel and controller parameters versus a sequential approach that decouples mechanical and control design. We analyze trade-offs in performance and computational cost. Across 3,000 full-vehicle simulations, campaigns finish in five to nine days, versus months with the group's earlier DEM-based workflow. Finally, a preliminary hardware study suggests the simulation-optimized wheel designs preserve relative performance trends on the physical rover. Together, these results show that scalable, high-fidelity simulation can enable practical co-optimization of wheel design and control for off-road vehicles on deformable terrain without relying on prohibitively expensive DEM studies. The simulation infrastructure (scripts and models) is released as open source in a public repository to support reproducibility and further research.
A Study on the Use of Simulation in Synthesizing Path-Following Control Policies for Autonomous Ground Robots
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:We report results obtained and insights gained while answering the following question: how effective is it to use a simulator to establish path following control policies for an autonomous ground robot? While the quality of the simulator conditions the answer to this question, we found that for the simulation platform used herein, producing four control policies for path planning was straightforward once a digital twin of the controlled robot was available. The control policies established in simulation and subsequently demonstrated in the real world are PID control, MPC, and two neural network (NN) based controllers. Training the two NN controllers via imitation learning was accomplished expeditiously using seven simple maneuvers: follow three circles clockwise, follow the same circles counter-clockwise, and drive straight. A test randomization process that employs random micro-simulations is used to rank the ``goodness'' of the four control policies. The policy ranking noted in simulation correlates well with the ranking observed when the control policies were tested in the real world. The simulation platform used is publicly available and BSD3-released as open source; a public Docker image is available for reproducibility studies. It contains a dynamics engine, a sensor simulator, a ROS2 bridge, and a ROS2 autonomy stack the latter employed both in the simulator and the real world experiments.
Zero-Shot Policy Transferability for the Control of a Scale Autonomous Vehicle
Sep 18, 2023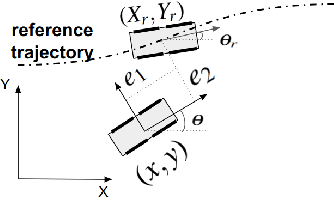
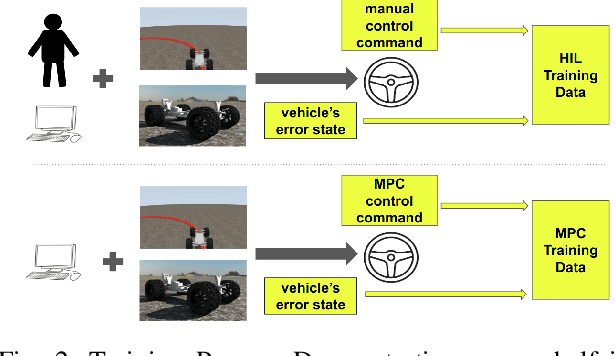
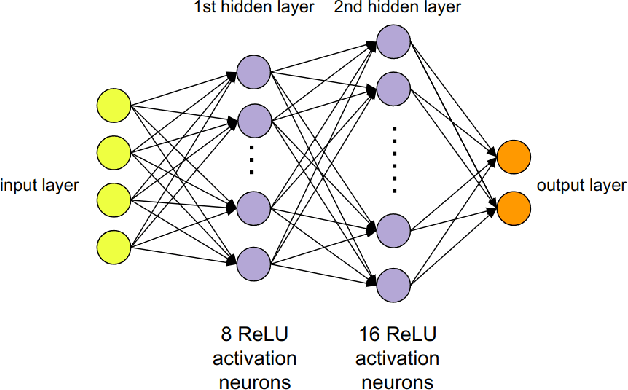
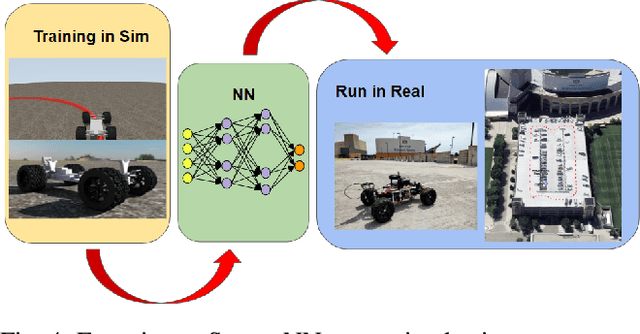
Abstract:We report on a study that employs an in-house developed simulation infrastructure to accomplish zero shot policy transferability for a control policy associated with a scale autonomous vehicle. We focus on implementing policies that require no real world data to be trained (Zero-Shot Transfer), and are developed in-house as opposed to being validated by previous works. We do this by implementing a Neural Network (NN) controller that is trained only on a family of circular reference trajectories. The sensors used are RTK-GPS and IMU, the latter for providing heading. The NN controller is trained using either a human driver (via human in the loop simulation), or a Model Predictive Control (MPC) strategy. We demonstrate these two approaches in conjunction with two operation scenarios: the vehicle follows a waypoint-defined trajectory at constant speed; and the vehicle follows a speed profile that changes along the vehicle's waypoint-defined trajectory. The primary contribution of this work is the demonstration of Zero-Shot Transfer in conjunction with a novel feed-forward NN controller trained using a general purpose, in-house developed simulation platform.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge