Ludwig Kürzinger
JTubeSpeech: corpus of Japanese speech collected from YouTube for speech recognition and speaker verification
Dec 17, 2021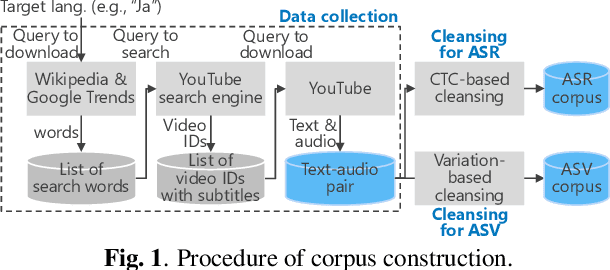

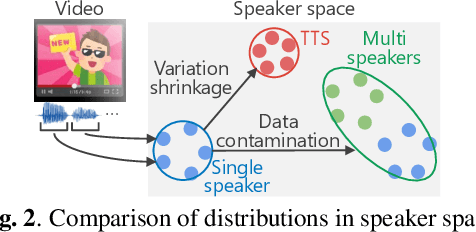
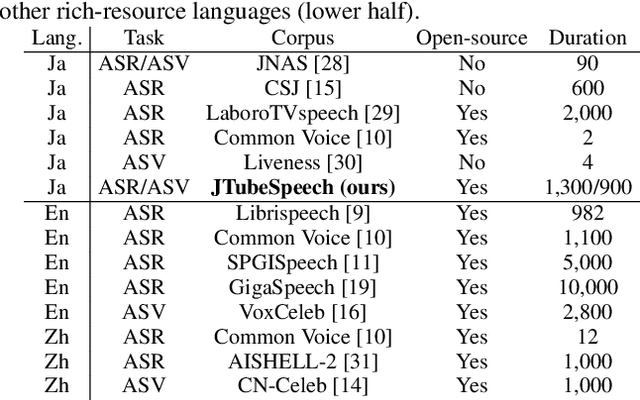
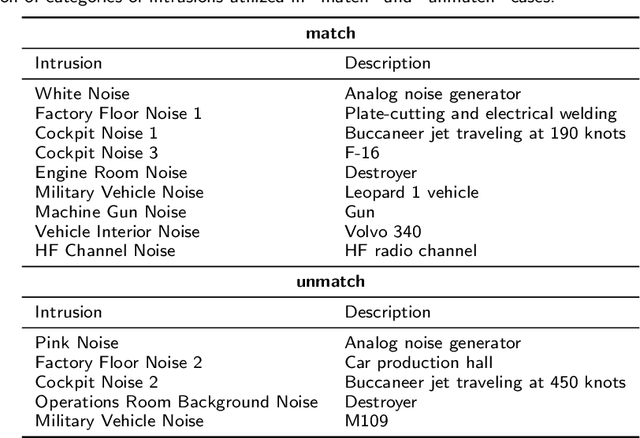
Abstract:In this paper, we construct a new Japanese speech corpus called "JTubeSpeech." Although recent end-to-end learning requires large-size speech corpora, open-sourced such corpora for languages other than English have not yet been established. In this paper, we describe the construction of a corpus from YouTube videos and subtitles for speech recognition and speaker verification. Our method can automatically filter the videos and subtitles with almost no language-dependent processes. We consistently employ Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC)-based techniques for automatic speech recognition (ASR) and a speaker variation-based method for automatic speaker verification (ASV). We build 1) a large-scale Japanese ASR benchmark with more than 1,300 hours of data and 2) 900 hours of data for Japanese ASV.
Adversarial Joint Training with Self-Attention Mechanism for Robust End-to-End Speech Recognition
Apr 03, 2021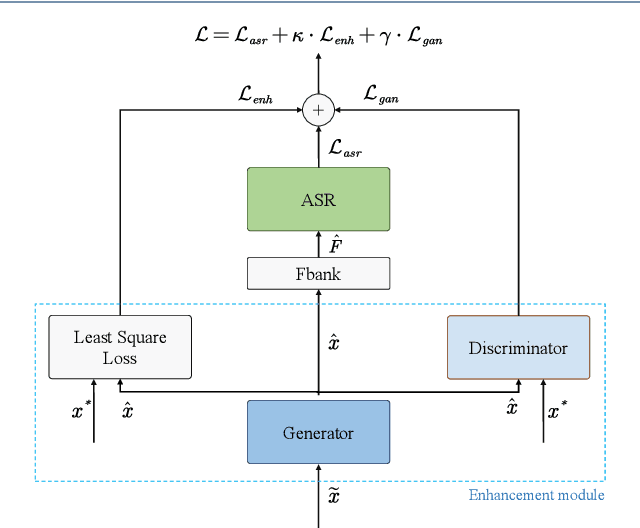
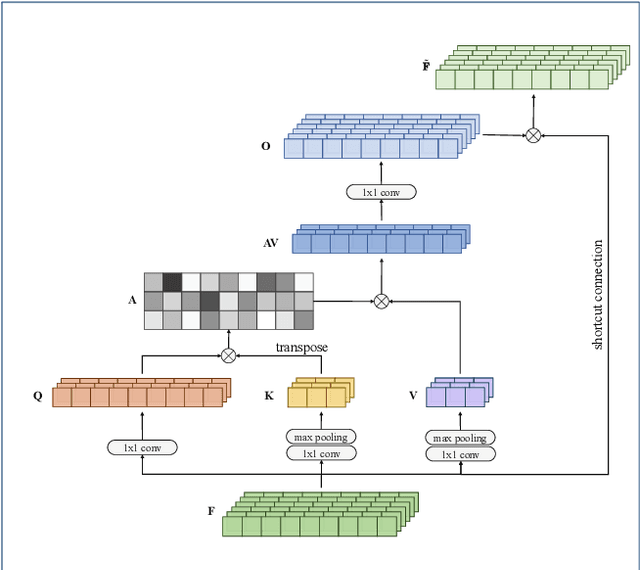
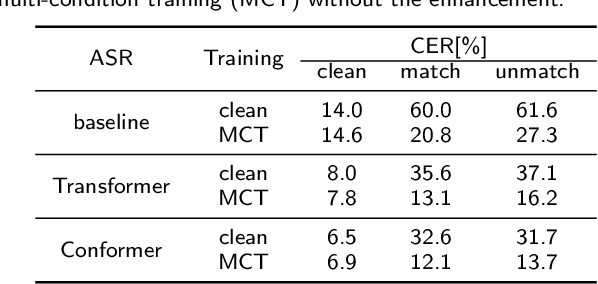
Abstract:Lately, the self-attention mechanism has marked a new milestone in the field of automatic speech recognition (ASR). Nevertheless, its performance is susceptible to environmental intrusions as the system predicts the next output symbol depending on the full input sequence and the previous predictions. Inspired by the extensive applications of the generative adversarial networks (GANs) in speech enhancement and ASR tasks, we propose an adversarial joint training framework with the self-attention mechanism to boost the noise robustness of the ASR system. Generally, it consists of a self-attention speech enhancement GAN and a self-attention end-to-end ASR model. There are two highlights which are worth noting in this proposed framework. One is that it benefits from the advancement of both self-attention mechanism and GANs; while the other is that the discriminator of GAN plays the role of the global discriminant network in the stage of the adversarial joint training, which guides the enhancement front-end to capture more compatible structures for the subsequent ASR module and thereby offsets the limitation of the separate training and handcrafted loss functions. With the adversarial joint optimization, the proposed framework is expected to learn more robust representations suitable for the ASR task. We execute systematic experiments on the corpus AISHELL-1, and the experimental results show that on the artificial noisy test set, the proposed framework achieves the relative improvements of 66% compared to the ASR model trained by clean data solely, 35.1% compared to the speech enhancement & ASR scheme without joint training, and 5.3% compared to multi-condition training.
Regularized Forward-Backward Decoder for Attention Models
Jun 15, 2020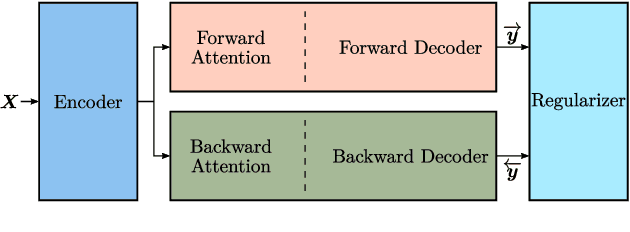
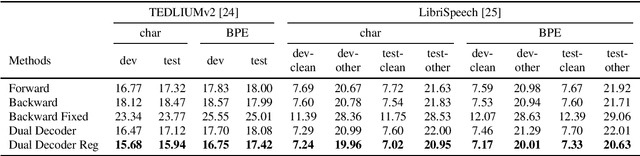
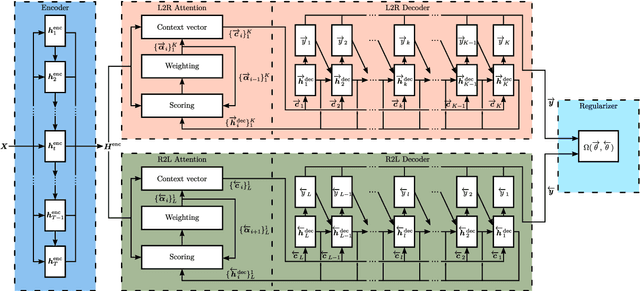
Abstract:Nowadays, attention models are one of the popular candidates for speech recognition. So far, many studies mainly focus on the encoder structure or the attention module to enhance the performance of these models. However, mostly ignore the decoder. In this paper, we propose a novel regularization technique incorporating a second decoder during the training phase. This decoder is optimized on time-reversed target labels beforehand and supports the standard decoder during training by adding knowledge from future context. Since it is only added during training, we are not changing the basic structure of the network or adding complexity during decoding. We evaluate our approach on the smaller TEDLIUMv2 and the larger LibriSpeech dataset, achieving consistent improvements on both of them.
Small-Footprint Keyword Spotting on Raw Audio Data with Sinc-Convolutions
Nov 05, 2019
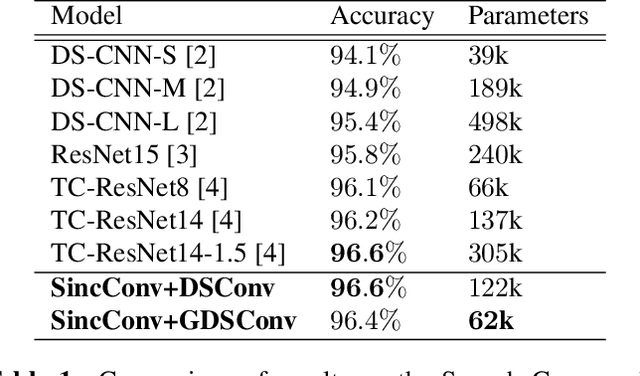
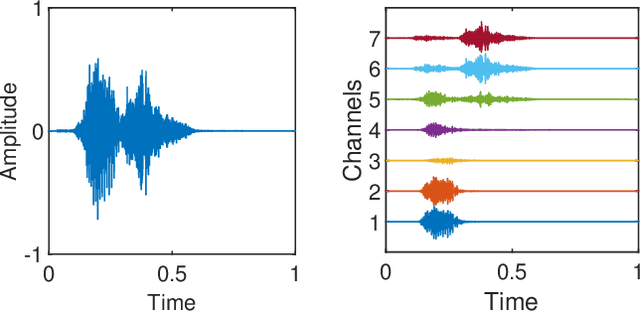

Abstract:Keyword Spotting (KWS) enables speech-based user interaction on smart devices. Always-on and battery-powered application scenarios for smart devices put constraints on hardware resources and power consumption, while also demanding high accuracy as well as real-time capability. Previous architectures first extracted acoustic features and then applied a neural network to classify keyword probabilities, optimizing towards memory footprint and execution time. Compared to previous publications, we took additional steps to reduce power and memory consumption without reducing classification accuracy. Power-consuming audio preprocessing and data transfer steps are eliminated by directly classifying from raw audio. For this, our end-to-end architecture extracts spectral features using parametrized Sinc-convolutions. Its memory footprint is further reduced by grouping depthwise separable convolutions. Our network achieves the competitive accuracy of 96.4% on Google's Speech Commands test set with only 62k parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge