Lucie Lévêque
UNIV GUSTAVE EIFFEL
Objective quality assessment of medical images and videos: Review and challenges
Dec 14, 2022Abstract:Quality assessment is a key element for the evaluation of hardware and software involved in image and video acquisition, processing, and visualization. In the medical field, user-based quality assessment is still considered more reliable than objective methods, which allow the implementation of automated and more efficient solutions. Regardless of increasing research in this topic in the last decade, defining quality standards for medical content remains a non-trivial task, as the focus should be on the diagnostic value assessed from expert viewers rather than the perceived quality from na\"{i}ve viewers, and objective quality metrics should aim at estimating the first rather than the latter. In this paper, we present a survey of methodologies used for the objective quality assessment of medical images and videos, dividing them into visual quality-based and task-based approaches. Visual quality based methods compute a quality index directly from visual attributes, while task-based methods, being increasingly explored, measure the impact of quality impairments on the performance of a specific task. A discussion on the limitations of state-of-the-art research on this topic is also provided, along with future challenges to be addressed.
Cuid: A new study of perceived image quality and its subjective assessment
Sep 28, 2020
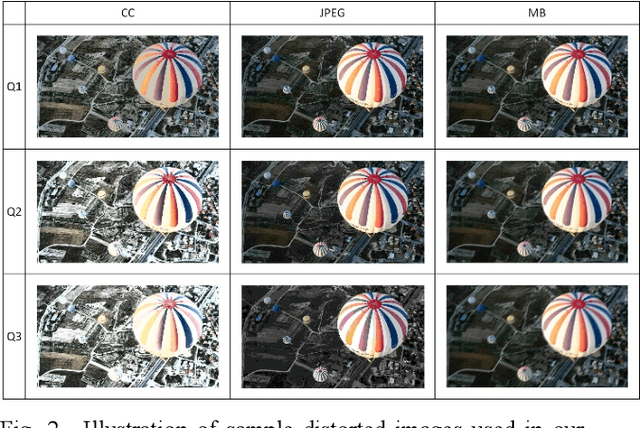


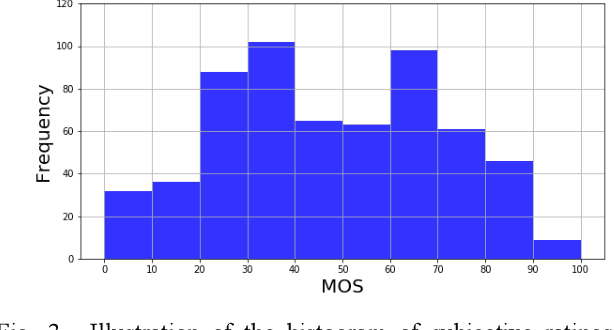
Abstract:Research on image quality assessment (IQA) remains limited mainly due to our incomplete knowledge about human visual perception. Existing IQA algorithms have been designed or trained with insufficient subjective data with a small degree of stimulus variability. This has led to challenges for those algorithms to handle complexity and diversity of real-world digital content. Perceptual evidence from human subjects serves as a grounding for the development of advanced IQA algorithms. It is thus critical to acquire reliable subjective data with controlled perception experiments that faithfully reflect human behavioural responses to distortions in visual signals. In this paper, we present a new study of image quality perception where subjective ratings were collected in a controlled lab environment. We investigate how quality perception is affected by a combination of different categories of images and different types and levels of distortions. The database will be made publicly available to facilitate calibration and validation of IQA algorithms.
Subjective Quality Assessment of Ground-based Camera Images
Dec 16, 2019



Abstract:Image quality assessment is critical to control and maintain the perceived quality of visual content. Both subjective and objective evaluations can be utilised, however, subjective image quality assessment is currently considered the most reliable approach. Databases containing distorted images and mean opinion scores are needed in the field of atmospheric research with a view to improve the current state-of-the-art methodologies. In this paper, we focus on using ground-based sky camera images to understand the atmospheric events. We present a new image quality assessment dataset containing original and distorted nighttime images of sky/cloud from SWINSEG database. Subjective quality assessment was carried out in controlled conditions, as recommended by the ITU. Statistical analyses of the subjective scores showed the impact of noise type and distortion level on the perceived quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge