Lucas Rafael Stefanel Gris
Evaluating OpenAI's Whisper ASR for Punctuation Prediction and Topic Modeling of life histories of the Museum of the Person
May 26, 2023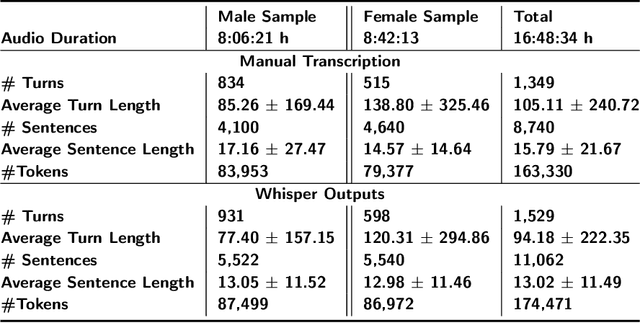
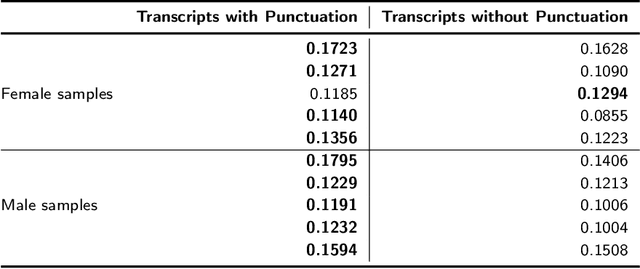
Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems play a key role in applications involving human-machine interactions. Despite their importance, ASR models for the Portuguese language proposed in the last decade have limitations in relation to the correct identification of punctuation marks in automatic transcriptions, which hinder the use of transcriptions by other systems, models, and even by humans. However, recently Whisper ASR was proposed by OpenAI, a general-purpose speech recognition model that has generated great expectations in dealing with such limitations. This chapter presents the first study on the performance of Whisper for punctuation prediction in the Portuguese language. We present an experimental evaluation considering both theoretical aspects involving pausing points (comma) and complete ideas (exclamation, question, and fullstop), as well as practical aspects involving transcript-based topic modeling - an application dependent on punctuation marks for promising performance. We analyzed experimental results from videos of Museum of the Person, a virtual museum that aims to tell and preserve people's life histories, thus discussing the pros and cons of Whisper in a real-world scenario. Although our experiments indicate that Whisper achieves state-of-the-art results, we conclude that some punctuation marks require improvements, such as exclamation, semicolon and colon.
Interpretability Analysis of Deep Models for COVID-19 Detection
Nov 25, 2022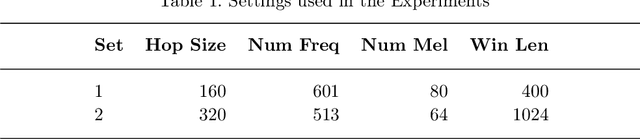
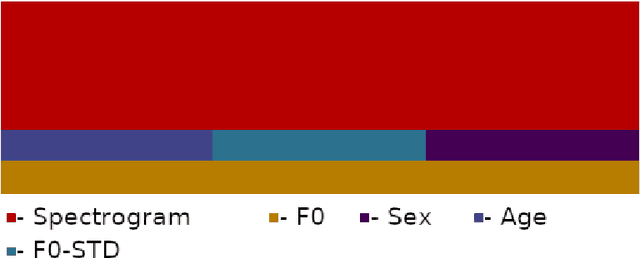
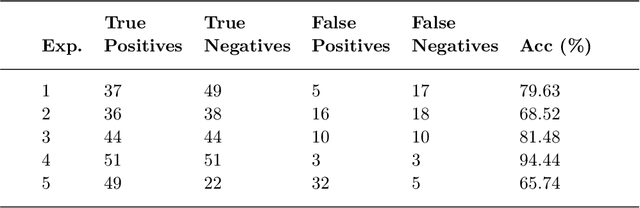
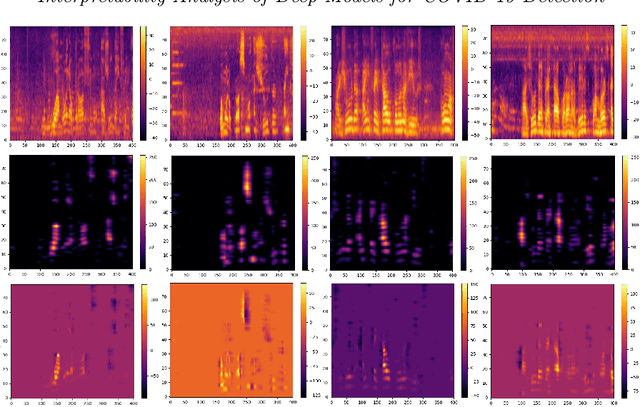
Abstract:During the outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic, several research areas joined efforts to mitigate the damages caused by SARS-CoV-2. In this paper we present an interpretability analysis of a convolutional neural network based model for COVID-19 detection in audios. We investigate which features are important for model decision process, investigating spectrograms, F0, F0 standard deviation, sex and age. Following, we analyse model decisions by generating heat maps for the trained models to capture their attention during the decision process. Focusing on a explainable Inteligence Artificial approach, we show that studied models can taken unbiased decisions even in the presence of spurious data in the training set, given the adequate preprocessing steps. Our best model has 94.44% of accuracy in detection, with results indicating that models favors spectrograms for the decision process, particularly, high energy areas in the spectrogram related to prosodic domains, while F0 also leads to efficient COVID-19 detection.
Bringing NURC/SP to Digital Life: the Role of Open-source Automatic Speech Recognition Models
Oct 14, 2022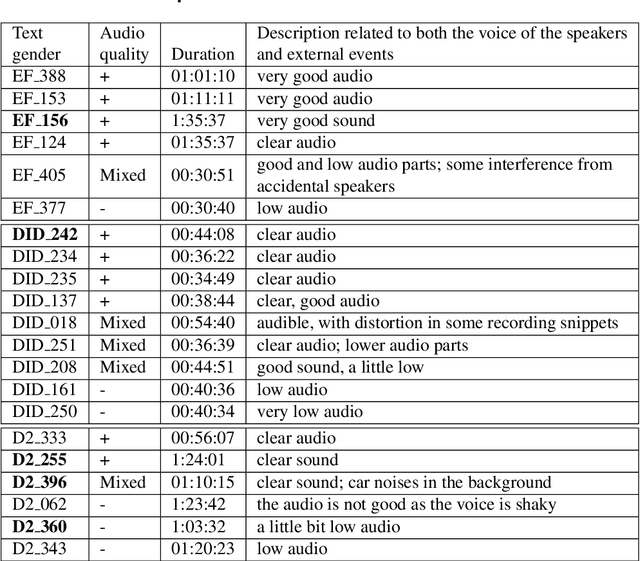
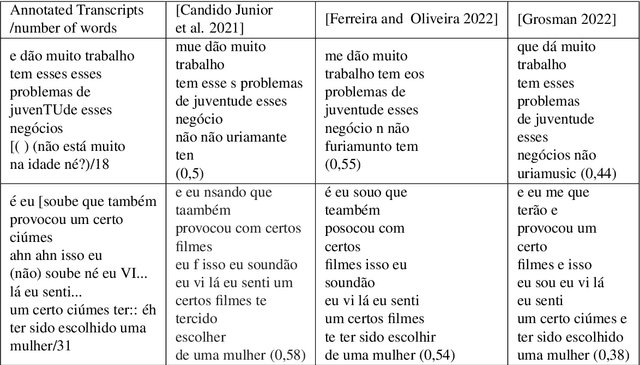
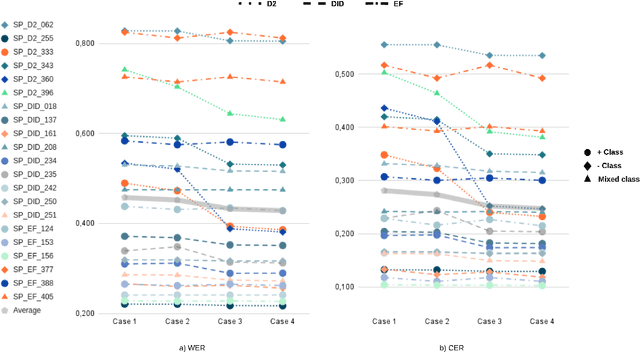
Abstract:The NURC Project that started in 1969 to study the cultured linguistic urban norm spoken in five Brazilian capitals, was responsible for compiling a large corpus for each capital. The digitized NURC/SP comprises 375 inquiries in 334 hours of recordings taken in S\~ao Paulo capital. Although 47 inquiries have transcripts, there was no alignment between the audio-transcription, and 328 inquiries were not transcribed. This article presents an evaluation and error analysis of three automatic speech recognition models trained with spontaneous speech in Portuguese and one model trained with prepared speech. The evaluation allowed us to choose the best model, using WER and CER metrics, in a manually aligned sample of NURC/SP, to automatically transcribe 284 hours.
CORAA: a large corpus of spontaneous and prepared speech manually validated for speech recognition in Brazilian Portuguese
Oct 14, 2021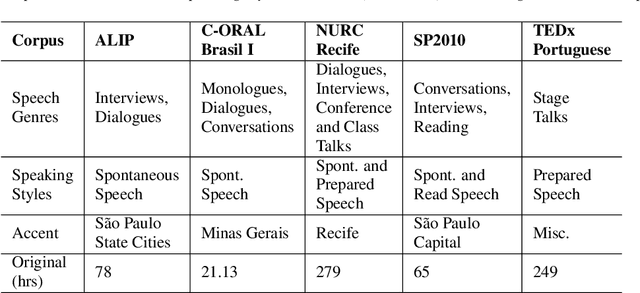
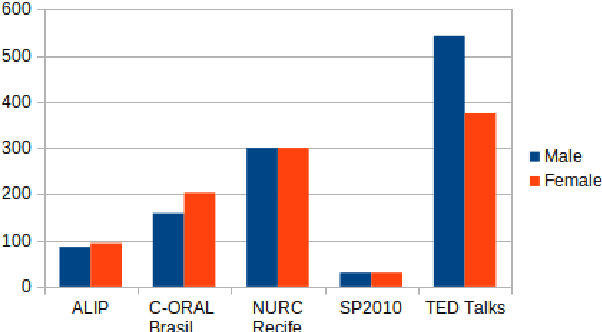
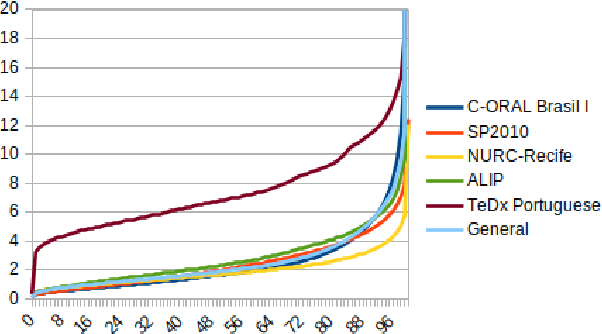
Abstract:Automatic Speech recognition (ASR) is a complex and challenging task. In recent years, there have been significant advances in the area. In particular, for the Brazilian Portuguese (BP) language, there were about 376 hours public available for ASR task until the second half of 2020. With the release of new datasets in early 2021, this number increased to 574 hours. The existing resources, however, are composed of audios containing only read and prepared speech. There is a lack of datasets including spontaneous speech, which are essential in different ASR applications. This paper presents CORAA (Corpus of Annotated Audios) v1. with 291 hours, a publicly available dataset for ASR in BP containing validated pairs (audio-transcription). CORAA also contains European Portuguese audios (4.69 hours). We also present two public ASR models based on Wav2Vec 2.0 XLSR-53 and fine-tuned over CORAA. Our best model achieved a Word Error Rate of 27.35% on CORAA test set and 16.01% on Common Voice test set. When measuring the Character Error Rate, we obtained 14.26% and 5.45% for CORAA and Common Voice, respectively. CORAA corpora were assembled to both improve ASR models in BP with phenomena from spontaneous speech and motivate young researchers to start their studies on ASR for Portuguese. All the corpora are publicly available at https://github.com/nilc-nlp/CORAA under the CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license.
Brazilian Portuguese Speech Recognition Using Wav2vec 2.0
Jul 23, 2021
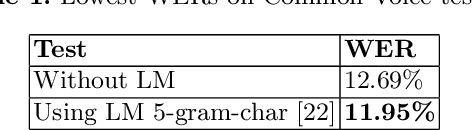

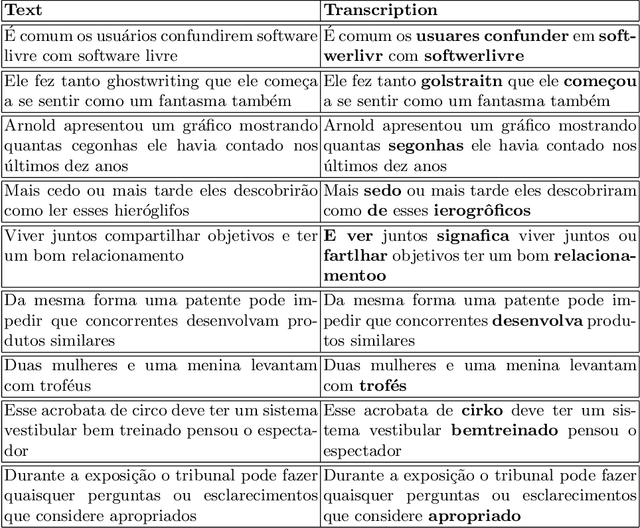
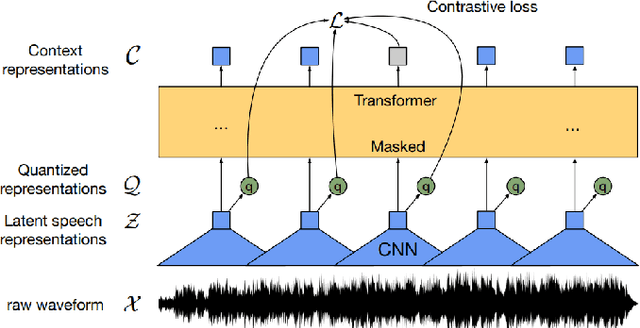
Abstract:Deep learning techniques have been shown to be efficient in various tasks, especially in the development of speech recognition systems, that is, systems that aim to transcribe a sentence in audio in a sequence of words. Despite the progress in the area, speech recognition can still be considered difficult, especially for languages lacking available data, as Brazilian Portuguese. In this sense, this work presents the development of an public Automatic Speech Recognition system using only open available audio data, from the fine-tuning of the Wav2vec 2.0 XLSR-53 model pre-trained in many languages over Brazilian Portuguese data. The final model presents a Word Error Rate of 11.95% (Common Voice Dataset). This corresponds to 13% less than the best open Automatic Speech Recognition model for Brazilian Portuguese available according to our best knowledge, which is a promising result for the language. In general, this work validates the use of self-supervising learning techniques, in special, the use of the Wav2vec 2.0 architecture in the development of robust systems, even for languages having few available data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge