Longhai Wu
Exploring Simple Siamese Network for High-Resolution Video Quality Assessment
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:In the research of video quality assessment (VQA), two-branch network has emerged as a promising solution. It decouples VQA with separate technical and aesthetic branches to measure the perception of low-level distortions and high-level semantics respectively. However, we argue that while technical and aesthetic perspectives are complementary, the technical perspective itself should be measured in semantic-aware manner. We hypothesize that existing technical branch struggles to perceive the semantics of high-resolution videos, as it is trained on local mini-patches sampled from videos. This issue can be hidden by apparently good results on low-resolution videos, but indeed becomes critical for high-resolution VQA. This work introduces SiamVQA, a simple but effective Siamese network for highre-solution VQA. SiamVQA shares weights between technical and aesthetic branches, enhancing the semantic perception ability of technical branch to facilitate technical-quality representation learning. Furthermore, it integrates a dual cross-attention layer for fusing technical and aesthetic features. SiamVQA achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on high-resolution benchmarks, and competitive results on lower-resolution benchmarks. Codes will be available at: https://github.com/srcn-ivl/SiamVQA
Unified Arbitrary-Time Video Frame Interpolation and Prediction
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Video frame interpolation and prediction aim to synthesize frames in-between and subsequent to existing frames, respectively. Despite being closely-related, these two tasks are traditionally studied with different model architectures, or same architecture but individually trained weights. Furthermore, while arbitrary-time interpolation has been extensively studied, the value of arbitrary-time prediction has been largely overlooked. In this work, we present uniVIP - unified arbitrary-time Video Interpolation and Prediction. Technically, we firstly extend an interpolation-only network for arbitrary-time interpolation and prediction, with a special input channel for task (interpolation or prediction) encoding. Then, we show how to train a unified model on common triplet frames. Our uniVIP provides competitive results for video interpolation, and outperforms existing state-of-the-arts for video prediction. Codes will be available at: https://github.com/srcn-ivl/uniVIP
Dynamic Video Frame Interpolation with integrated Difficulty Pre-Assessment
Apr 25, 2023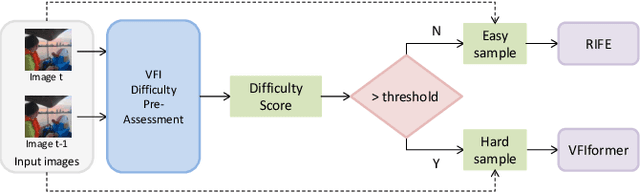
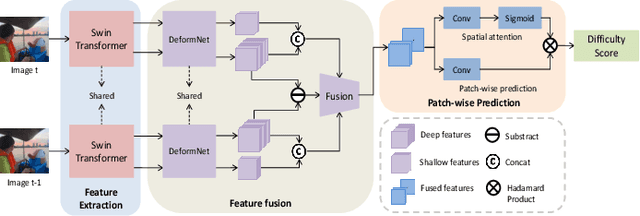
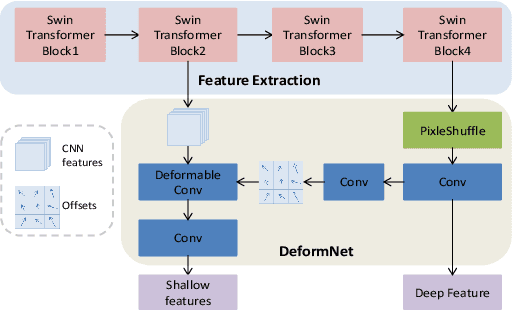
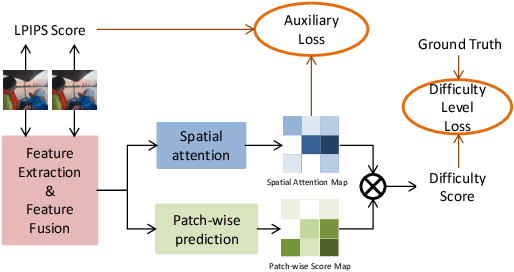
Abstract:Video frame interpolation(VFI) has witnessed great progress in recent years. While existing VFI models still struggle to achieve a good trade-off between accuracy and efficiency: fast models often have inferior accuracy; accurate models typically run slowly. However, easy samples with small motion or clear texture can achieve competitive results with simple models and do not require heavy computation. In this paper, we present an integrated pipeline which combines difficulty assessment with video frame interpolation. Specifically, it firstly leverages a pre-assessment model to measure the interpolation difficulty level of input frames, and then dynamically selects an appropriate VFI model to generate interpolation results. Furthermore, a large-scale VFI difficulty assessment dataset is collected and annotated to train our pre-assessment model. Extensive experiments show that easy samples pass through fast models while difficult samples inference with heavy models, and our proposed pipeline can improve the accuracy-efficiency trade-off for VFI.
A Unified Pyramid Recurrent Network for Video Frame Interpolation
Nov 07, 2022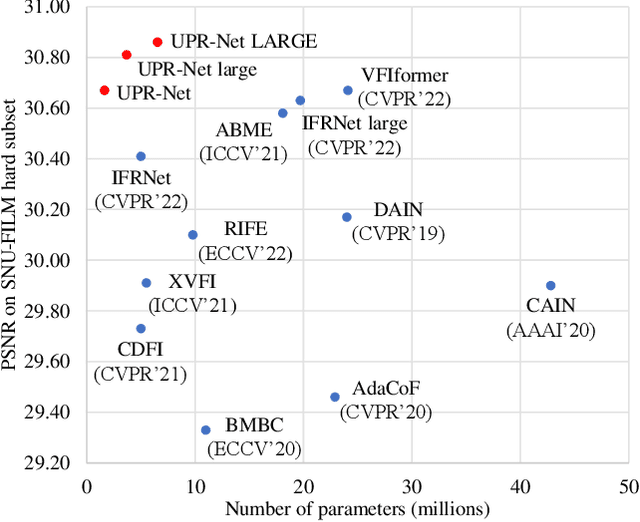
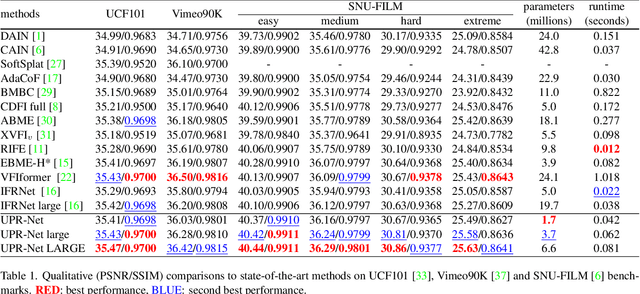
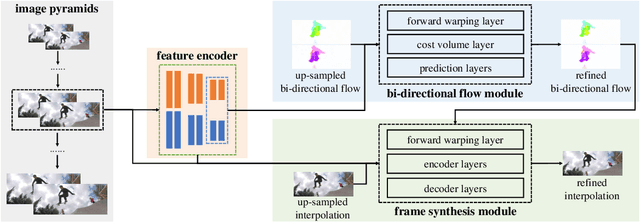
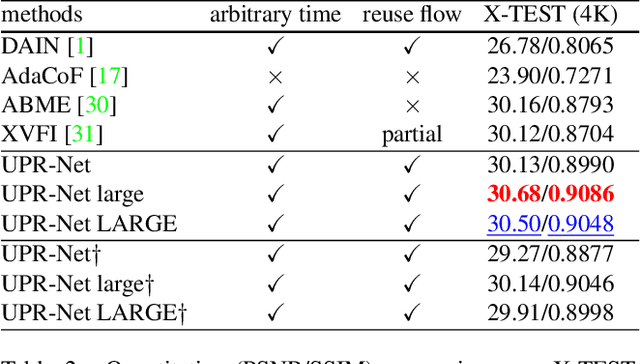
Abstract:Flow-guide synthesis provides a common framework for frame interpolation, where optical flow is typically estimated by a pyramid network, and then leveraged to guide a synthesis network to generate intermediate frames between input frames. In this paper, we present UPR-Net, a novel Unified Pyramid Recurrent Network for frame interpolation. Cast in a flexible pyramid framework, UPR-Net exploits lightweight recurrent modules for both bi-directional flow estimation and intermediate frame synthesis. At each pyramid level, it leverages estimated bi-directional flow to generate forward-warped representations for frame synthesis; across pyramid levels, it enables iterative refinement for both optical flow and intermediate frame. In particular, we show that our iterative synthesis can significantly improve the robustness of frame interpolation on large motion cases. Despite being extremely lightweight (1.7M parameters), UPR-Net achieves excellent performance on a large range of benchmarks. Code will be available soon.
SADRNet: Self-Aligned Dual Face Regression Networks for Robust 3D Dense Face Alignment and Reconstruction
Jun 06, 2021



Abstract:Three-dimensional face dense alignment and reconstruction in the wild is a challenging problem as partial facial information is commonly missing in occluded and large pose face images. Large head pose variations also increase the solution space and make the modeling more difficult. Our key idea is to model occlusion and pose to decompose this challenging task into several relatively more manageable subtasks. To this end, we propose an end-to-end framework, termed as Self-aligned Dual face Regression Network (SADRNet), which predicts a pose-dependent face, a pose-independent face. They are combined by an occlusion-aware self-alignment to generate the final 3D face. Extensive experiments on two popular benchmarks, AFLW2000-3D and Florence, demonstrate that the proposed method achieves significant superior performance over existing state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge