Linrui Ma
Diffusion In Diffusion: Reclaiming Global Coherence in Semi-Autoregressive Diffusion
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:One of the most compelling features of global discrete diffusion language models is their global bidirectional contextual capability. However, existing block-based diffusion studies tend to introduce autoregressive priors, which, while offering benefits, can cause models to lose this global coherence at the macro level. To regain global contextual understanding while preserving the advantages of the semi-autoregressive paradigm, we propose Diffusion in Diffusion, a 'draft-then-refine' framework designed to overcome the irreversibility and myopia problems inherent in block diffusion models. Our approach first employs block diffusion to generate rapid drafts using small blocks, then refines these drafts through global bidirectional diffusion with a larger bidirectional receptive field. We utilize snapshot confidence remasking to identify the most critical tokens that require modification, and apply mix-scale training to expand the block diffusion model's global capabilities. Empirical results demonstrate that our approach sets a new benchmark for discrete diffusion models on the OpenWebText dataset. Using only 26% of the fine-tuning budget of baseline models, we reduce generative perplexity from 25.7 to 21.9, significantly narrowing the performance gap with autoregressive models.
Resona: Improving Context Copying in Linear Recurrence Models with Retrieval
Mar 28, 2025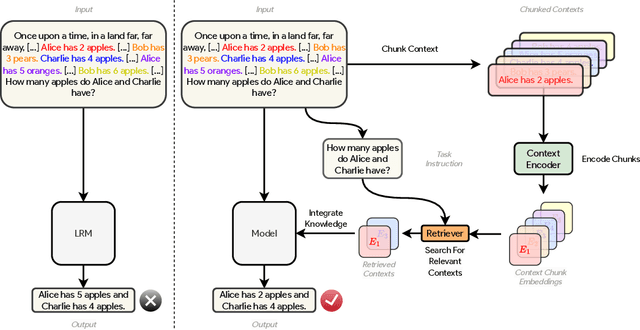

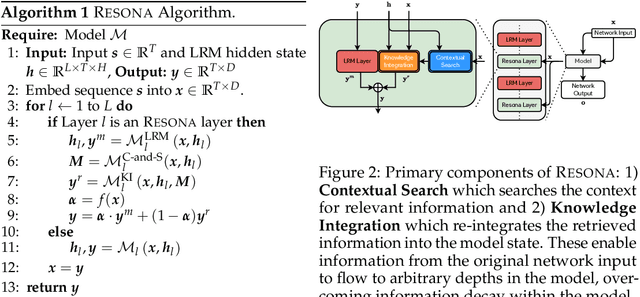
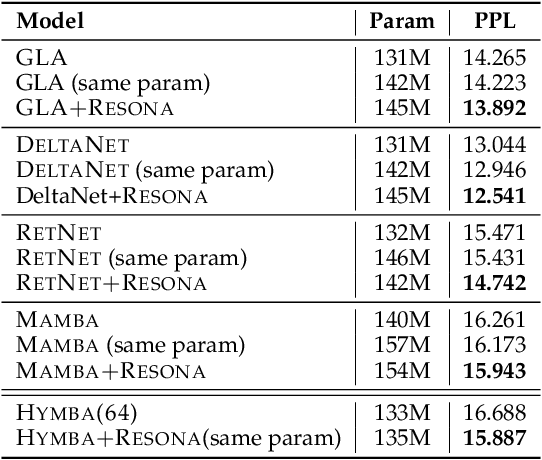
Abstract:Recent shifts in the space of large language model (LLM) research have shown an increasing focus on novel architectures to compete with prototypical Transformer-based models that have long dominated this space. Linear recurrent models have proven to be a viable competitor due to their computational efficiency. However, such models still demonstrate a sizable gap compared to Transformers in terms of in-context learning among other tasks that require recalling information from a context. In this work, we introduce __Resona__, a simple and scalable framework for augmenting linear recurrent models with retrieval. __Resona__~augments models with the ability to integrate retrieved information from the provided input context, enabling tailored behavior to diverse task requirements. Experiments on a variety of linear recurrent models demonstrate that __Resona__-augmented models observe significant performance gains on a variety of synthetic as well as real-world natural language tasks, highlighting its ability to act as a general purpose method to improve the in-context learning and language modeling abilities of linear recurrent LLMs.
BarlowTwins-CXR : Enhancing Chest X-Ray abnormality localization in heterogeneous data with cross-domain self-supervised learning
Feb 09, 2024Abstract:Background: Chest X-ray imaging-based abnormality localization, essential in diagnosing various diseases, faces significant clinical challenges due to complex interpretations and the growing workload of radiologists. While recent advances in deep learning offer promising solutions, there is still a critical issue of domain inconsistency in cross-domain transfer learning, which hampers the efficiency and accuracy of diagnostic processes. This study aims to address the domain inconsistency problem and improve autonomic abnormality localization performance of heterogeneous chest X-ray image analysis, by developing a self-supervised learning strategy called "BarlwoTwins-CXR". Methods: We utilized two publicly available datasets: the NIH Chest X-ray Dataset and the VinDr-CXR. The BarlowTwins-CXR approach was conducted in a two-stage training process. Initially, self-supervised pre-training was performed using an adjusted Barlow Twins algorithm on the NIH dataset with a Resnet50 backbone pre-trained on ImageNet. This was followed by supervised fine-tuning on the VinDr-CXR dataset using Faster R-CNN with Feature Pyramid Network (FPN). Results: Our experiments showed a significant improvement in model performance with BarlowTwins-CXR. The approach achieved a 3% increase in mAP50 accuracy compared to traditional ImageNet pre-trained models. In addition, the Ablation CAM method revealed enhanced precision in localizing chest abnormalities. Conclusion: BarlowTwins-CXR significantly enhances the efficiency and accuracy of chest X-ray image-based abnormality localization, outperforming traditional transfer learning methods and effectively overcoming domain inconsistency in cross-domain scenarios. Our experiment results demonstrate the potential of using self-supervised learning to improve the generalizability of models in medical settings with limited amounts of heterogeneous data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge