Linrui Gong
EADReg: Probabilistic Correspondence Generation with Efficient Autoregressive Diffusion Model for Outdoor Point Cloud Registration
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have shown the great potential in the point cloud registration (PCR) task, especially for enhancing the robustness to challenging cases. However, existing diffusion-based PCR methods primarily focus on instance-level scenarios and struggle with outdoor LiDAR points, where the sparsity, irregularity, and huge point scale inherent in LiDAR points pose challenges to establishing dense global point-to-point correspondences. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework named EADReg for efficient and robust registration of LiDAR point clouds based on autoregressive diffusion models. EADReg follows a coarse-to-fine registration paradigm. In the coarse stage, we employ a Bi-directional Gaussian Mixture Model (BGMM) to reject outlier points and obtain purified point cloud pairs. BGMM establishes correspondences between the Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) from the source and target frames, enabling reliable coarse registration based on filtered features and geometric information. In the fine stage, we treat diffusion-based PCR as an autoregressive process to generate robust point correspondences, which are then iteratively refined on upper layers. Despite common criticisms of diffusion-based methods regarding inference speed, EADReg achieves runtime comparable to convolutional-based methods. Extensive experiments on the KITTI and NuScenes benchmark datasets highlight the state-of-the-art performance of our proposed method. Codes will be released upon publication.
Precise Knowledge Transfer via Flow Matching
Feb 03, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel knowledge transfer framework that introduces continuous normalizing flows for progressive knowledge transformation and leverages multi-step sampling strategies to achieve precision knowledge transfer. We name this framework Knowledge Transfer with Flow Matching (FM-KT), which can be integrated with a metric-based distillation method with any form (\textit{e.g.} vanilla KD, DKD, PKD and DIST) and a meta-encoder with any available architecture (\textit{e.g.} CNN, MLP and Transformer). By introducing stochastic interpolants, FM-KD is readily amenable to arbitrary noise schedules (\textit{e.g.}, VP-ODE, VE-ODE, Rectified flow) for normalized flow path estimation. We theoretically demonstrate that the training objective of FM-KT is equivalent to minimizing the upper bound of the teacher feature map or logit negative log-likelihood. Besides, FM-KT can be viewed as a unique implicit ensemble method that leads to performance gains. By slightly modifying the FM-KT framework, FM-KT can also be transformed into an online distillation framework OFM-KT with desirable performance gains. Through extensive experiments on CIFAR-100, ImageNet-1k, and MS-COCO datasets, we empirically validate the scalability and state-of-the-art performance of our proposed methods among relevant comparison approaches.
Rethinking Centered Kernel Alignment in Knowledge Distillation
Jan 22, 2024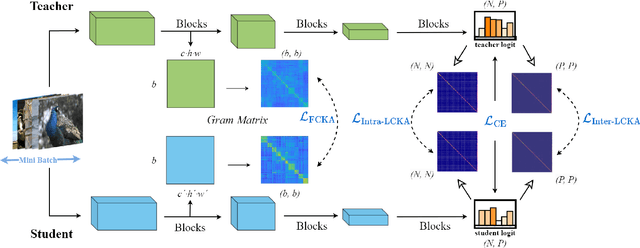
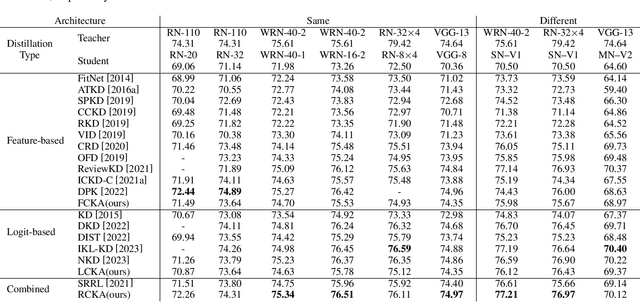
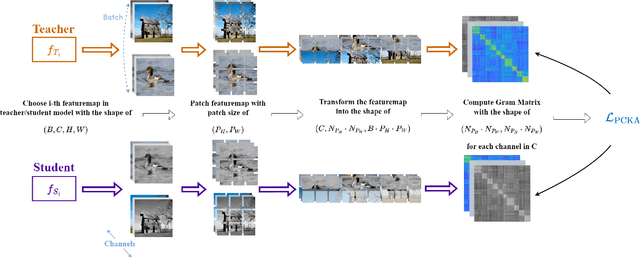
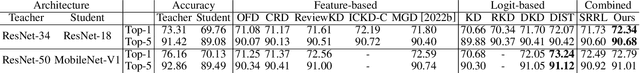
Abstract:Knowledge distillation has emerged as a highly effective method for bridging the representation discrepancy between large-scale models and lightweight models. Prevalent approaches involve leveraging appropriate metrics to minimize the divergence or distance between the knowledge extracted from the teacher model and the knowledge learned by the student model. Centered Kernel Alignment (CKA) is widely used to measure representation similarity and has been applied in several knowledge distillation methods. However, these methods are complex and fail to uncover the essence of CKA, thus not answering the question of how to use CKA to achieve simple and effective distillation properly. This paper first provides a theoretical perspective to illustrate the effectiveness of CKA, which decouples CKA to the upper bound of Maximum Mean Discrepancy~(MMD) and a constant term. Drawing from this, we propose a novel Relation-Centered Kernel Alignment~(RCKA) framework, which practically establishes a connection between CKA and MMD. Furthermore, we dynamically customize the application of CKA based on the characteristics of each task, with less computational source yet comparable performance than the previous methods. The extensive experiments on the CIFAR-100, ImageNet-1k, and MS-COCO demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on almost all teacher-student pairs for image classification and object detection, validating the effectiveness of our approaches.
Learning What You Should Learn
Dec 11, 2022Abstract:In real teaching scenarios, an excellent teacher always teaches what he (or she) is good at but the student is not. This method gives the student the best assistance in making up for his (or her) weaknesses and becoming a good one overall. Enlightened by this, we introduce the approach to the knowledge distillation framework and propose a data-based distillation method named ``Teaching what you Should Teach (TST)''. To be specific, TST contains a neural network-based data augmentation module with the priori bias, which can assist in finding what the teacher is good at while the student are not by learning magnitudes and probabilities to generate suitable samples. By training the data augmentation module and the generalized distillation paradigm in turn, a student model that has excellent generalization ability can be created. To verify the effectiveness of TST, we conducted extensive comparative experiments on object recognition (CIFAR-100 and ImageNet-1k), detection (MS-COCO), and segmentation (Cityscapes) tasks. As experimentally demonstrated, TST achieves state-of-the-art performance on almost all teacher-student pairs. Furthermore, we conduct intriguing studies of TST, including how to solve the performance degradation caused by the stronger teacher and what magnitudes and probabilities are needed for the distillation framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge