Linhan Zhang
Exploiting Correlations Between Contexts and Definitions with Multiple Definition Modeling
May 24, 2023Abstract:Definition modeling is an important task in advanced natural language applications such as understanding and conversation. Since its introduction, it focus on generating one definition for a target word or phrase in a given context, which we refer to as Single Definition Modeling (SDM). However, this approach does not adequately model the correlations and patterns among different contexts and definitions of words. In addition, the creation of a training dataset for SDM requires significant human expertise and effort. In this paper, we carefully design a new task called Multiple Definition Modeling (MDM) that pool together all contexts and definition of target words. We demonstrate the ease of creating a model as well as multiple training sets automatically. % In the experiments, we demonstrate and analyze the benefits of MDM, including improving SDM's performance by using MDM as the pretraining task and its comparable performance in the zero-shot setting.
Weighted Sampling for Masked Language Modeling
Feb 28, 2023
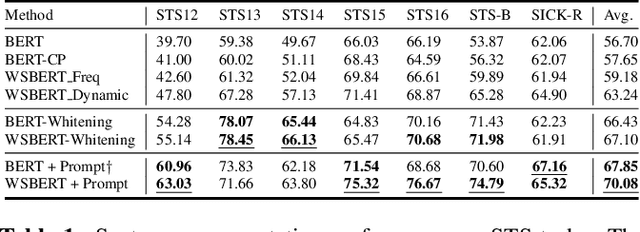
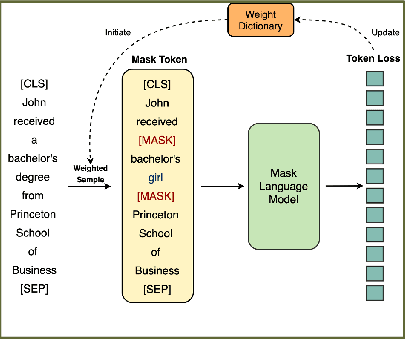
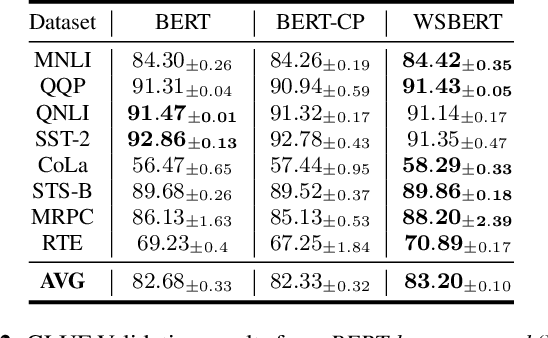
Abstract:Masked Language Modeling (MLM) is widely used to pretrain language models. The standard random masking strategy in MLM causes the pre-trained language models (PLMs) to be biased toward high-frequency tokens. Representation learning of rare tokens is poor and PLMs have limited performance on downstream tasks. To alleviate this frequency bias issue, we propose two simple and effective Weighted Sampling strategies for masking tokens based on the token frequency and training loss. We apply these two strategies to BERT and obtain Weighted-Sampled BERT (WSBERT). Experiments on the Semantic Textual Similarity benchmark (STS) show that WSBERT significantly improves sentence embeddings over BERT. Combining WSBERT with calibration methods and prompt learning further improves sentence embeddings. We also investigate fine-tuning WSBERT on the GLUE benchmark and show that Weighted Sampling also improves the transfer learning capability of the backbone PLM. We further analyze and provide insights into how WSBERT improves token embeddings.
* 6 pages, 2 figures
Global and Local Hierarchy-aware Contrastive Framework for Implicit Discourse Relation Recognition
Nov 25, 2022Abstract:Due to the absence of explicit connectives, implicit discourse relation recognition (IDRR) remains a challenging task in discourse analysis. The critical step for IDRR is to learn high-quality discourse relation representations between two arguments. Recent methods tend to integrate the whole hierarchical information of senses into discourse relation representations for multi-level sense recognition. Nevertheless, they insufficiently incorporate the static hierarchical structure containing all senses (defined as global hierarchy), and ignore the hierarchical sense label sequence corresponding to each instance (defined as local hierarchy). For the purpose of sufficiently exploiting global and local hierarchies of senses to learn better discourse relation representations, we propose a novel GLobal and LOcal Hierarchy-aware Contrastive Framework (GLOF), to model two kinds of hierarchies with the aid of contrastive learning. Experimental results on the PDTB dataset demonstrate that our method remarkably outperforms the current state-of-the-art model at all hierarchical levels.
MDERank: A Masked Document Embedding Rank Approach for Unsupervised Keyphrase Extraction
Oct 13, 2021
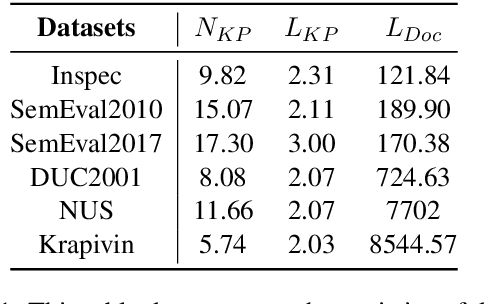
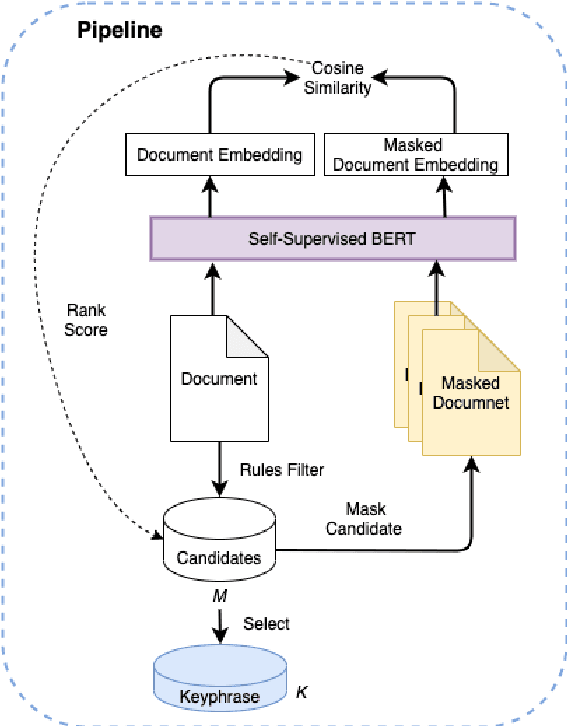
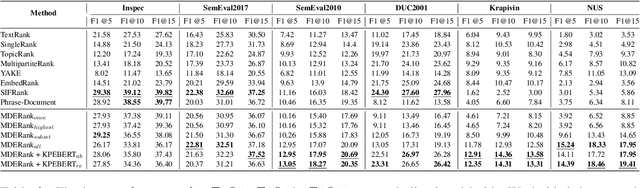
Abstract:Keyphrases are phrases in a document providing a concise summary of core content, helping readers to understand what the article is talking about in a minute. However, existing unsupervised works are not robust enough to handle various types of documents owing to the mismatch of sequence length for comparison. In this paper, we propose a novel unsupervised keyword extraction method by leveraging the BERT-based model to select and rank candidate keyphrases with a MASK strategy. In addition, we further enhance the model, denoted as Keyphrases Extraction BERT (KPEBERT), via designing a compatible self-supervised task and conducting a contrast learning. We conducted extensive experimental evaluation to demonstrate the superiority and robustness of the proposed method as well as the effectiveness of KPEBERT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge