Lingfeng Dai
Diverse and Vivid Sound Generation from Text Descriptions
May 03, 2023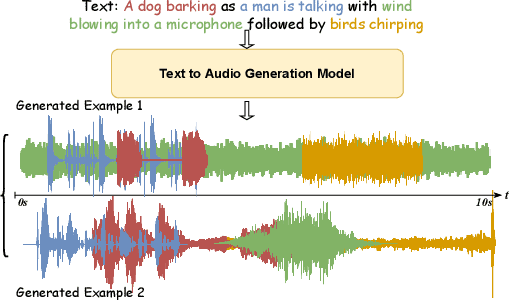
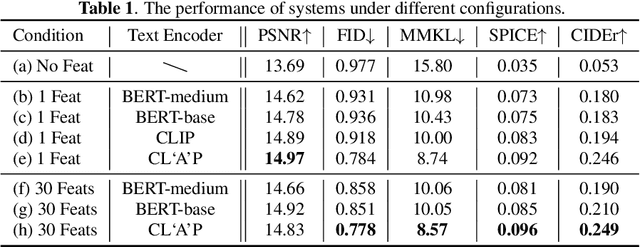
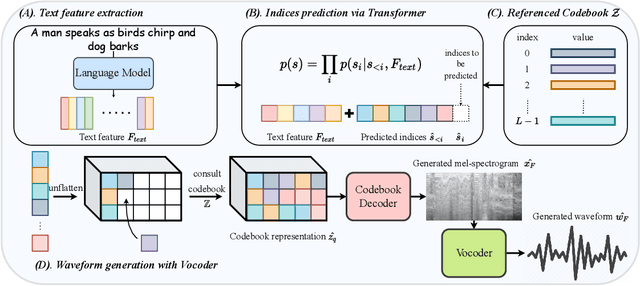
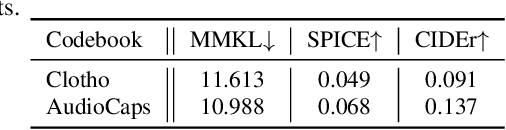
Abstract:Previous audio generation mainly focuses on specified sound classes such as speech or music, whose form and content are greatly restricted. In this paper, we go beyond specific audio generation by using natural language description as a clue to generate broad sounds. Unlike visual information, a text description is concise by its nature but has rich hidden meanings beneath, which poses a higher possibility and complexity on the audio to be generated. A Variation-Quantized GAN is used to train a codebook learning discrete representations of spectrograms. For a given text description, its pre-trained embedding is fed to a Transformer to sample codebook indices to decode a spectrogram to be further transformed into waveform by a melgan vocoder. The generated waveform has high quality and fidelity while excellently corresponding to the given text. Experiments show that our proposed method is capable of generating natural, vivid audios, achieving superb quantitative and qualitative results.
D4: a Chinese Dialogue Dataset for Depression-Diagnosis-Oriented Chat
May 24, 2022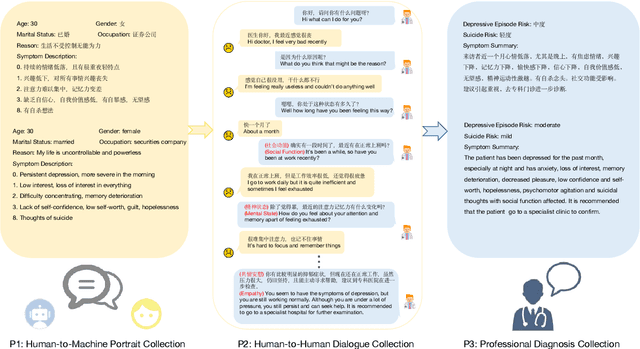
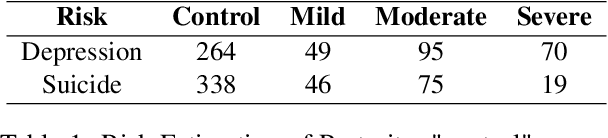
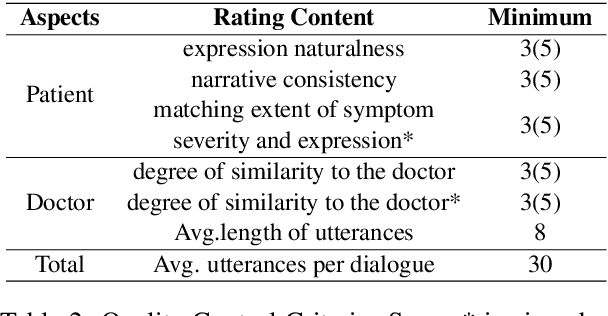
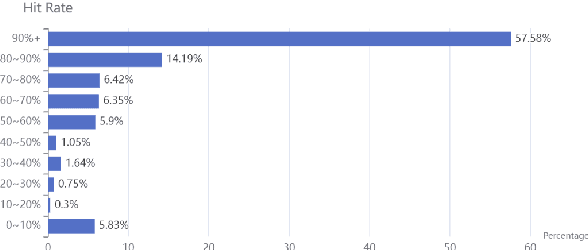
Abstract:In a depression-diagnosis-directed clinical session, doctors initiate a conversation with ample emotional support that guides the patients to expose their symptoms based on clinical diagnosis criteria. Such a dialog is a combination of task-oriented and chitchat, different from traditional single-purpose human-machine dialog systems. However, due to the social stigma associated with mental illness, the dialogue data related to depression consultation and diagnosis are rarely disclosed. Though automatic dialogue-based diagnosis foresees great application potential, data sparsity has become one of the major bottlenecks restricting research on such task-oriented chat dialogues. Based on clinical depression diagnostic criteria ICD-11 and DSM-5, we construct the D$^4$: a Chinese Dialogue Dataset for Depression-Diagnosis-Oriented Chat which simulates the dialogue between doctors and patients during the diagnosis of depression, including diagnosis results and symptom summary given by professional psychiatrists for each dialogue.Finally, we finetune on state-of-the-art pre-training models and respectively present our dataset baselines on four tasks including response generation, topic prediction, dialog summary, and severity classification of depressive episode and suicide risk. Multi-scale evaluation results demonstrate that a more empathy-driven and diagnostic-accurate consultation dialogue system trained on our dataset can be achieved compared to rule-based bots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge