Lihao Yin
What Matters For Safety Alignment?
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive empirical study on the safety alignment capabilities. We evaluate what matters for safety alignment in LLMs and LRMs to provide essential insights for developing more secure and reliable AI systems. We systematically investigate and compare the influence of six critical intrinsic model characteristics and three external attack techniques. Our large-scale evaluation is conducted using 32 recent, popular LLMs and LRMs across thirteen distinct model families, spanning a parameter scale from 3B to 235B. The assessment leverages five established safety datasets and probes model vulnerabilities with 56 jailbreak techniques and four CoT attack strategies, resulting in 4.6M API calls. Our key empirical findings are fourfold. First, we identify the LRMs GPT-OSS-20B, Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Thinking, and GPT-OSS-120B as the top-three safest models, which substantiates the significant advantage of integrated reasoning and self-reflection mechanisms for robust safety alignment. Second, post-training and knowledge distillation may lead to a systematic degradation of safety alignment. We thus argue that safety must be treated as an explicit constraint or a core optimization objective during these stages, not merely subordinated to the pursuit of general capability. Third, we reveal a pronounced vulnerability: employing a CoT attack via a response prefix can elevate the attack success rate by 3.34x on average and from 0.6% to 96.3% for Seed-OSS-36B-Instruct. This critical finding underscores the safety risks inherent in text-completion interfaces and features that allow user-defined response prefixes in LLM services, highlighting an urgent need for architectural and deployment safeguards. Fourth, roleplay, prompt injection, and gradient-based search for adversarial prompts are the predominant methodologies for eliciting unaligned behaviors in modern models.
PASER: Post-Training Data Selection for Efficient Pruned Large Language Model Recovery
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Model pruning is an effective approach for compressing large language models. However, this process often leads to significant degradation of model capabilities. While post-training techniques such as instruction tuning are commonly employed to recover model performance, existing methods often overlook the uneven deterioration of model capabilities and incur high computational costs. Moreover, some instruction data irrelevant to model capability recovery may introduce negative effects. To address these challenges, we propose the \textbf{P}ost-training d\textbf{A}ta \textbf{S}election method for \textbf{E}fficient pruned large language model \textbf{R}ecovery (\textbf{PASER}). PASER aims to identify instructions where model capabilities are most severely compromised within a certain recovery data budget. Our approach first applies manifold learning and spectral clustering to group recovery data in the semantic space, revealing capability-specific instruction sets. We then adaptively allocate the data budget to different clusters based on the degrees of model capability degradation. In each cluster, we prioritize data samples where model performance has declined dramatically. To mitigate potential negative transfer, we also detect and filter out conflicting or irrelevant recovery data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PASER significantly outperforms conventional baselines, effectively recovering the general capabilities of pruned LLMs while utilizing merely 4\%-20\% of the original post-training data.
Certifying Language Model Robustness with Fuzzed Randomized Smoothing: An Efficient Defense Against Backdoor Attacks
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:The widespread deployment of pre-trained language models (PLMs) has exposed them to textual backdoor attacks, particularly those planted during the pre-training stage. These attacks pose significant risks to high-reliability applications, as they can stealthily affect multiple downstream tasks. While certifying robustness against such threats is crucial, existing defenses struggle with the high-dimensional, interdependent nature of textual data and the lack of access to original poisoned pre-training data. To address these challenges, we introduce \textbf{F}uzzed \textbf{R}andomized \textbf{S}moothing (\textbf{FRS}), a novel approach for efficiently certifying language model robustness against backdoor attacks. FRS integrates software robustness certification techniques with biphased model parameter smoothing, employing Monte Carlo tree search for proactive fuzzing to identify vulnerable textual segments within the Damerau-Levenshtein space. This allows for targeted and efficient text randomization, while eliminating the need for access to poisoned training data during model smoothing. Our theoretical analysis demonstrates that FRS achieves a broader certified robustness radius compared to existing methods. Extensive experiments across various datasets, model configurations, and attack strategies validate FRS's superiority in terms of defense efficiency, accuracy, and robustness.
SoLA: Solver-Layer Adaption of LLM for Better Logic Reasoning
Feb 19, 2024



Abstract:Considering the challenges faced by large language models (LLMs) on logical reasoning, prior efforts have sought to transform problem-solving through tool learning. While progress has been made on small-scale problems, solving industrial cases remains difficult due to their large scale and intricate expressions. In this paper, we propose a novel solver-layer adaptation (SoLA) method, where we introduce a solver as a new layer of the LLM to differentially guide solutions towards satisfiability. In SoLA, LLM aims to comprehend the search space described in natural language and identify local solutions of the highest quality, while the solver layer focuses solely on constraints not satisfied by the initial solution. Leveraging MaxSAT as a bridge, we define forward and backward transfer gradients, enabling the final model to converge to a satisfied solution or prove unsatisfiability. The backdoor theory ensures that SoLA can obtain accurate solutions within polynomial loops. We evaluate the performance of SoLA on various datasets and empirically demonstrate its consistent outperformance against existing symbolic solvers (including Z3 and Kissat) and tool-learning methods in terms of efficiency in large-scale problem-solving.
Row-clustering of a Point Process-valued Matrix
Oct 04, 2021
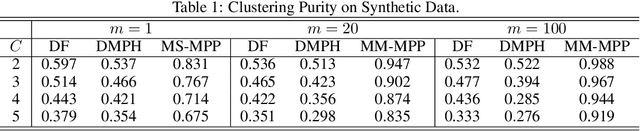

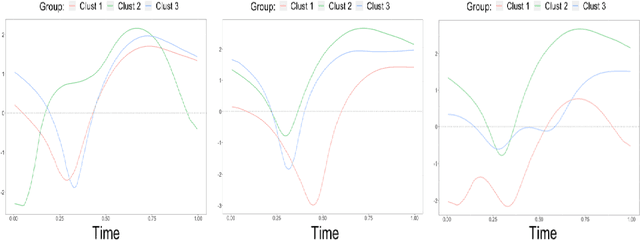
Abstract:Structured point process data harvested from various platforms poses new challenges to the machine learning community. By imposing a matrix structure to repeatedly observed marked point processes, we propose a novel mixture model of multi-level marked point processes for identifying potential heterogeneity in the observed data. Specifically, we study a matrix whose entries are marked log-Gaussian Cox processes and cluster rows of such a matrix. An efficient semi-parametric Expectation-Solution (ES) algorithm combined with functional principal component analysis (FPCA) of point processes is proposed for model estimation. The effectiveness of the proposed framework is demonstrated through simulation studies and a real data analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge