Leighton Collins
Learning Robot Swarm Tactics over Complex Adversarial Environments
Sep 13, 2021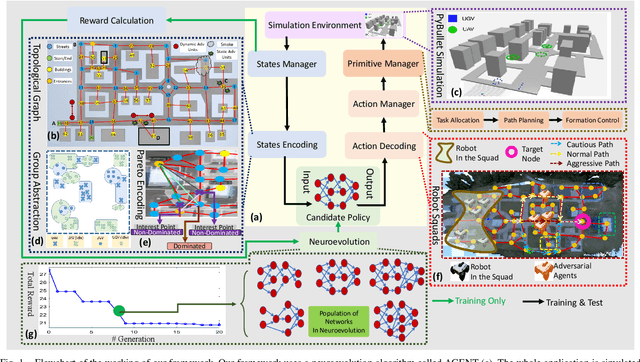
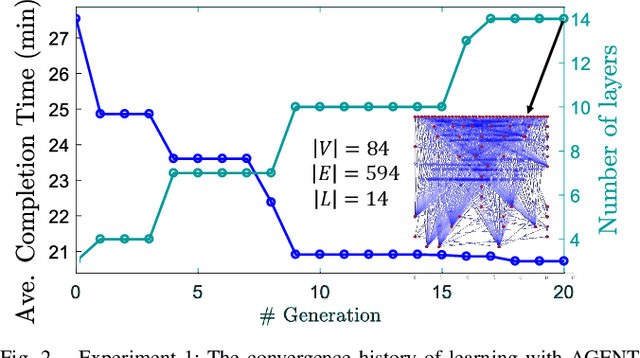
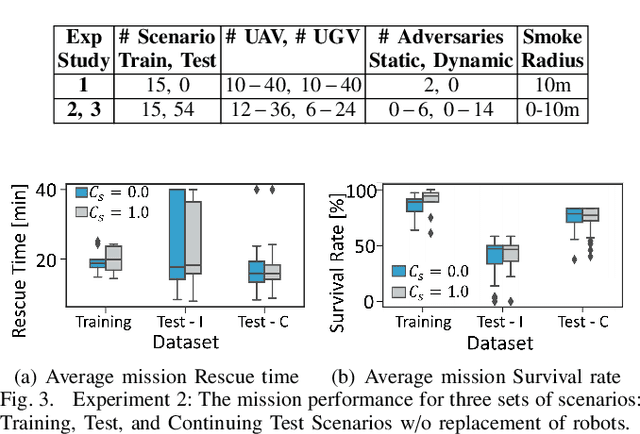
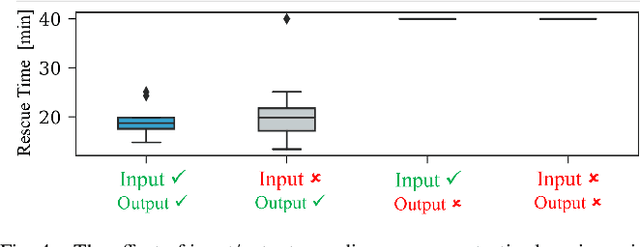
Abstract:To accomplish complex swarm robotic missions in the real world, one needs to plan and execute a combination of single robot behaviors, group primitives such as task allocation, path planning, and formation control, and mission-specific objectives such as target search and group coverage. Most such missions are designed manually by teams of robotics experts. Recent work in automated approaches to learning swarm behavior has been limited to individual primitives with sparse work on learning complete missions. This paper presents a systematic approach to learn tactical mission-specific policies that compose primitives in a swarm to accomplish the mission efficiently using neural networks with special input and output encoding. To learn swarm tactics in an adversarial environment, we employ a combination of 1) map-to-graph abstraction, 2) input/output encoding via Pareto filtering of points of interest and clustering of robots, and 3) learning via neuroevolution and policy gradient approaches. We illustrate this combination as critical to providing tractable learning, especially given the computational cost of simulating swarm missions of this scale and complexity. Successful mission completion outcomes are demonstrated with up to 60 robots. In addition, a close match in the performance statistics in training and testing scenarios shows the potential generalizability of the proposed framework.
Scalable Coverage Path Planning of Multi-Robot Teams for Monitoring Non-Convex Areas
Mar 26, 2021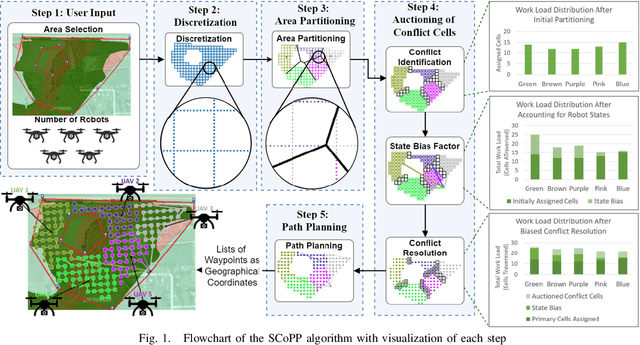


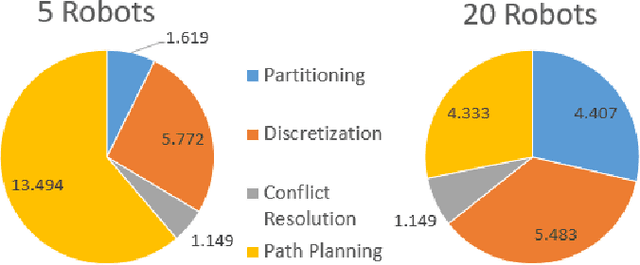
Abstract:This paper presents a novel multi-robot coverage path planning (CPP) algorithm - aka SCoPP - that provides a time-efficient solution, with workload balanced plans for each robot in a multi-robot system, based on their initial states. This algorithm accounts for discontinuities (e.g., no-fly zones) in a specified area of interest, and provides an optimized ordered list of way-points per robot using a discrete, computationally efficient, nearest neighbor path planning algorithm. This algorithm involves five main stages, which include the transformation of the user's input as a set of vertices in geographical coordinates, discretization, load-balanced partitioning, auctioning of conflict cells in a discretized space, and a path planning procedure. To evaluate the effectiveness of the primary algorithm, a multi-unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) post-flood assessment application is considered, and the performance of the algorithm is tested on three test maps of varying sizes. Additionally, our method is compared with a state-of-the-art method created by Guasella et al. Further analyses on scalability and computational time of SCoPP are conducted. The results show that SCoPP is superior in terms of mission completion time; its computing time is found to be under 2 mins for a large map covered by a 150-robot team, thereby demonstrating its computationally scalability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge