Kun Yin
Youtu-Parsing: Perception, Structuring and Recognition via High-Parallelism Decoding
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:This paper presents Youtu-Parsing, an efficient and versatile document parsing model designed for high-performance content extraction. The architecture employs a native Vision Transformer (ViT) featuring a dynamic-resolution visual encoder to extract shared document features, coupled with a prompt-guided Youtu-LLM-2B language model for layout analysis and region-prompted decoding. Leveraging this decoupled and feature-reusable framework, we introduce a high-parallelism decoding strategy comprising two core components: token parallelism and query parallelism. The token parallelism strategy concurrently generates up to 64 candidate tokens per inference step, which are subsequently validated through a verification mechanism. This approach yields a 5--11x speedup over traditional autoregressive decoding and is particularly well-suited for highly structured scenarios, such as table recognition. To further exploit the advantages of region-prompted decoding, the query parallelism strategy enables simultaneous content prediction for multiple bounding boxes (up to five), providing an additional 2x acceleration while maintaining output quality equivalent to standard decoding. Youtu-Parsing encompasses a diverse range of document elements, including text, formulas, tables, charts, seals, and hierarchical structures. Furthermore, the model exhibits strong robustness when handling rare characters, multilingual text, and handwritten content. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that Youtu-Parsing achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on both the OmniDocBench and olmOCR-bench benchmarks. Overall, Youtu-Parsing demonstrates significant experimental value and practical utility for large-scale document intelligence applications.
Youtu-VL: Unleashing Visual Potential via Unified Vision-Language Supervision
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Despite the significant advancements represented by Vision-Language Models (VLMs), current architectures often exhibit limitations in retaining fine-grained visual information, leading to coarse-grained multimodal comprehension. We attribute this deficiency to a suboptimal training paradigm inherent in prevailing VLMs, which exhibits a text-dominant optimization bias by conceptualizing visual signals merely as passive conditional inputs rather than supervisory targets. To mitigate this, we introduce Youtu-VL, a framework leveraging the Vision-Language Unified Autoregressive Supervision (VLUAS) paradigm, which fundamentally shifts the optimization objective from ``vision-as-input'' to ``vision-as-target.'' By integrating visual tokens directly into the prediction stream, Youtu-VL applies unified autoregressive supervision to both visual details and linguistic content. Furthermore, we extend this paradigm to encompass vision-centric tasks, enabling a standard VLM to perform vision-centric tasks without task-specific additions. Extensive empirical evaluations demonstrate that Youtu-VL achieves competitive performance on both general multimodal tasks and vision-centric tasks, establishing a robust foundation for the development of comprehensive generalist visual agents.
TACO: Think-Answer Consistency for Optimized Long-Chain Reasoning and Efficient Data Learning via Reinforcement Learning in LVLMs
May 27, 2025Abstract:DeepSeek R1 has significantly advanced complex reasoning for large language models (LLMs). While recent methods have attempted to replicate R1's reasoning capabilities in multimodal settings, they face limitations, including inconsistencies between reasoning and final answers, model instability and crashes during long-chain exploration, and low data learning efficiency. To address these challenges, we propose TACO, a novel reinforcement learning algorithm for visual reasoning. Building on Generalized Reinforcement Policy Optimization (GRPO), TACO introduces Think-Answer Consistency, which tightly couples reasoning with answer consistency to ensure answers are grounded in thoughtful reasoning. We also introduce the Rollback Resample Strategy, which adaptively removes problematic samples and reintroduces them to the sampler, enabling stable long-chain exploration and future learning opportunities. Additionally, TACO employs an adaptive learning schedule that focuses on moderate difficulty samples to optimize data efficiency. Furthermore, we propose the Test-Time-Resolution-Scaling scheme to address performance degradation due to varying resolutions during reasoning while balancing computational overhead. Extensive experiments on in-distribution and out-of-distribution benchmarks for REC and VQA tasks show that fine-tuning LVLMs leads to significant performance improvements.
HRVDA: High-Resolution Visual Document Assistant
Apr 10, 2024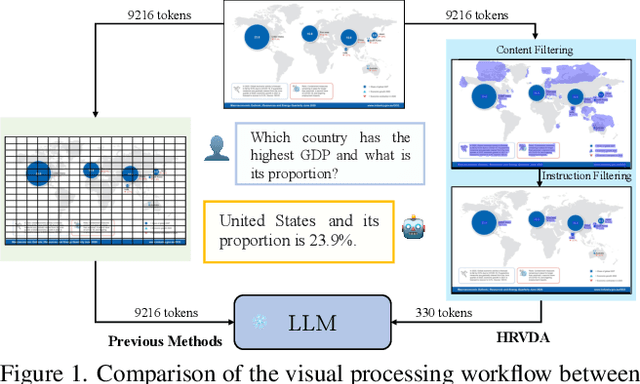
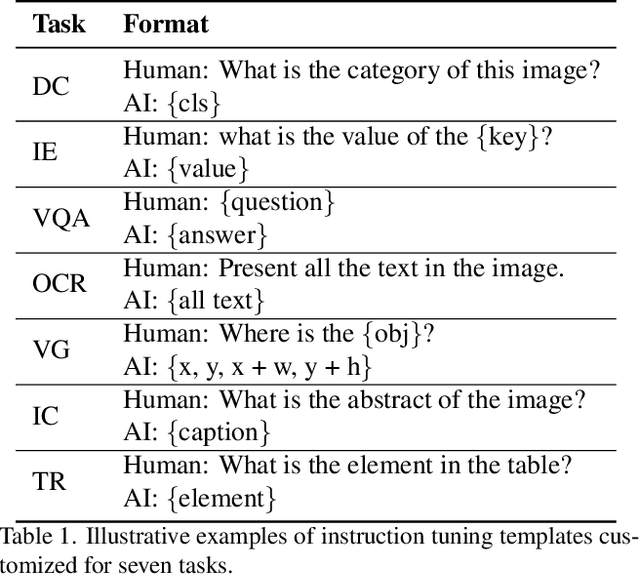
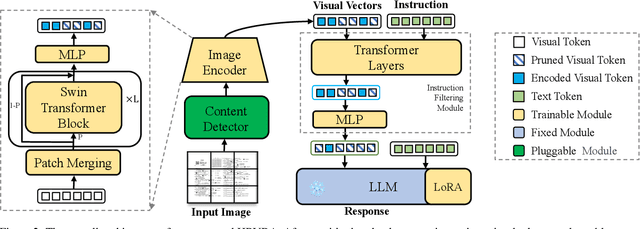
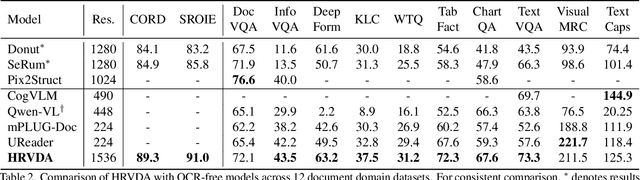
Abstract:Leveraging vast training data, multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated formidable general visual comprehension capabilities and achieved remarkable performance across various tasks. However, their performance in visual document understanding still leaves much room for improvement. This discrepancy is primarily attributed to the fact that visual document understanding is a fine-grained prediction task. In natural scenes, MLLMs typically use low-resolution images, leading to a substantial loss of visual information. Furthermore, general-purpose MLLMs do not excel in handling document-oriented instructions. In this paper, we propose a High-Resolution Visual Document Assistant (HRVDA), which bridges the gap between MLLMs and visual document understanding. This model employs a content filtering mechanism and an instruction filtering module to separately filter out the content-agnostic visual tokens and instruction-agnostic visual tokens, thereby achieving efficient model training and inference for high-resolution images. In addition, we construct a document-oriented visual instruction tuning dataset and apply a multi-stage training strategy to enhance the model's document modeling capabilities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple document understanding datasets, while maintaining training efficiency and inference speed comparable to low-resolution models.
Attention Where It Matters: Rethinking Visual Document Understanding with Selective Region Concentration
Sep 03, 2023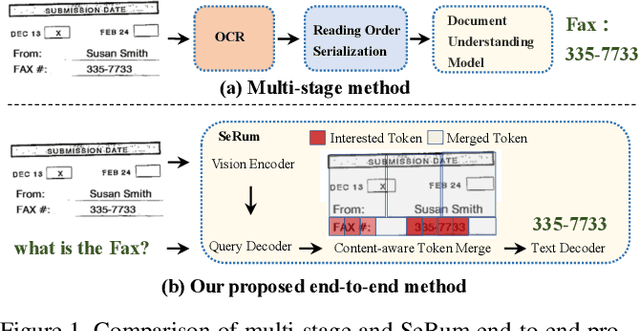
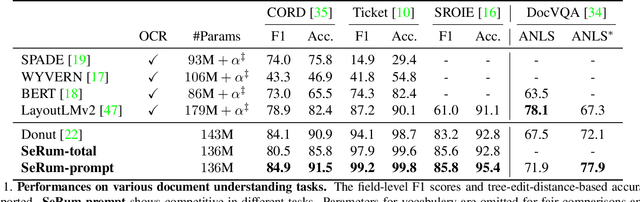
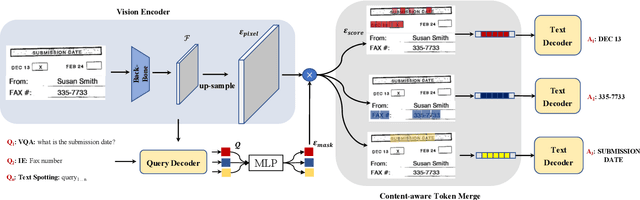
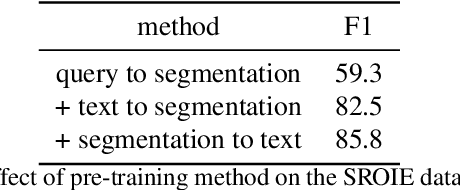
Abstract:We propose a novel end-to-end document understanding model called SeRum (SElective Region Understanding Model) for extracting meaningful information from document images, including document analysis, retrieval, and office automation. Unlike state-of-the-art approaches that rely on multi-stage technical schemes and are computationally expensive, SeRum converts document image understanding and recognition tasks into a local decoding process of the visual tokens of interest, using a content-aware token merge module. This mechanism enables the model to pay more attention to regions of interest generated by the query decoder, improving the model's effectiveness and speeding up the decoding speed of the generative scheme. We also designed several pre-training tasks to enhance the understanding and local awareness of the model. Experimental results demonstrate that SeRum achieves state-of-the-art performance on document understanding tasks and competitive results on text spotting tasks. SeRum represents a substantial advancement towards enabling efficient and effective end-to-end document understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge