Konrad Wagstyl
Robust and Generalisable Segmentation of Subtle Epilepsy-causing Lesions: a Graph Convolutional Approach
Jun 05, 2023



Abstract:Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) is a leading cause of drug-resistant focal epilepsy, which can be cured by surgery. These lesions are extremely subtle and often missed even by expert neuroradiologists. "Ground truth" manual lesion masks are therefore expensive, limited and have large inter-rater variability. Existing FCD detection methods are limited by high numbers of false positive predictions, primarily due to vertex- or patch-based approaches that lack whole-brain context. Here, we propose to approach the problem as semantic segmentation using graph convolutional networks (GCN), which allows our model to learn spatial relationships between brain regions. To address the specific challenges of FCD identification, our proposed model includes an auxiliary loss to predict distance from the lesion to reduce false positives and a weak supervision classification loss to facilitate learning from uncertain lesion masks. On a multi-centre dataset of 1015 participants with surface-based features and manual lesion masks from structural MRI data, the proposed GCN achieved an AUC of 0.74, a significant improvement against a previously used vertex-wise multi-layer perceptron (MLP) classifier (AUC 0.64). With sensitivity thresholded at 67%, the GCN had a specificity of 71% in comparison to 49% when using the MLP. This improvement in specificity is vital for clinical integration of lesion-detection tools into the radiological workflow, through increasing clinical confidence in the use of AI radiological adjuncts and reducing the number of areas requiring expert review.
Convolutional Neural Networks for cytoarchitectonic brain mapping at large scale
Nov 25, 2020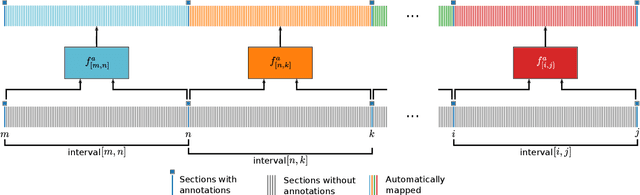

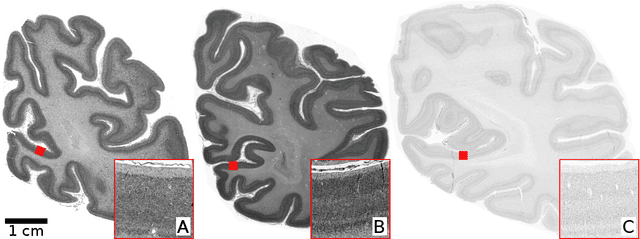
Abstract:Human brain atlases provide spatial reference systems for data characterizing brain organization at different levels, coming from different brains. Cytoarchitecture is a basic principle of the microstructural organization of the brain, as regional differences in the arrangement and composition of neuronal cells are indicators of changes in connectivity and function. Automated scanning procedures and observer-independent methods are prerequisites to reliably identify cytoarchitectonic areas, and to achieve reproducible models of brain segregation. Time becomes a key factor when moving from the analysis of single regions of interest towards high-throughput scanning of large series of whole-brain sections. Here we present a new workflow for mapping cytoarchitectonic areas in large series of cell-body stained histological sections of human postmortem brains. It is based on a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), which is trained on a pair of section images with annotations, with a large number of un-annotated sections in between. The model learns to create all missing annotations in between with high accuracy, and faster than our previous workflow based on observer-independent mapping. The new workflow does not require preceding 3D-reconstruction of sections, and is robust against histological artefacts. It processes large data sets with sizes in the order of multiple Terabytes efficiently. The workflow was integrated into a web interface, to allow access without expertise in deep learning and batch computing. Applying deep neural networks for cytoarchitectonic mapping opens new perspectives to enable high-resolution models of brain areas, introducing CNNs to identify borders of brain areas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge