Khiem Vuong
AerialMegaDepth: Learning Aerial-Ground Reconstruction and View Synthesis
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:We explore the task of geometric reconstruction of images captured from a mixture of ground and aerial views. Current state-of-the-art learning-based approaches fail to handle the extreme viewpoint variation between aerial-ground image pairs. Our hypothesis is that the lack of high-quality, co-registered aerial-ground datasets for training is a key reason for this failure. Such data is difficult to assemble precisely because it is difficult to reconstruct in a scalable way. To overcome this challenge, we propose a scalable framework combining pseudo-synthetic renderings from 3D city-wide meshes (e.g., Google Earth) with real, ground-level crowd-sourced images (e.g., MegaDepth). The pseudo-synthetic data simulates a wide range of aerial viewpoints, while the real, crowd-sourced images help improve visual fidelity for ground-level images where mesh-based renderings lack sufficient detail, effectively bridging the domain gap between real images and pseudo-synthetic renderings. Using this hybrid dataset, we fine-tune several state-of-the-art algorithms and achieve significant improvements on real-world, zero-shot aerial-ground tasks. For example, we observe that baseline DUSt3R localizes fewer than 5% of aerial-ground pairs within 5 degrees of camera rotation error, while fine-tuning with our data raises accuracy to nearly 56%, addressing a major failure point in handling large viewpoint changes. Beyond camera estimation and scene reconstruction, our dataset also improves performance on downstream tasks like novel-view synthesis in challenging aerial-ground scenarios, demonstrating the practical value of our approach in real-world applications.
WALT3D: Generating Realistic Training Data from Time-Lapse Imagery for Reconstructing Dynamic Objects under Occlusion
Apr 01, 2024



Abstract:Current methods for 2D and 3D object understanding struggle with severe occlusions in busy urban environments, partly due to the lack of large-scale labeled ground-truth annotations for learning occlusion. In this work, we introduce a novel framework for automatically generating a large, realistic dataset of dynamic objects under occlusions using freely available time-lapse imagery. By leveraging off-the-shelf 2D (bounding box, segmentation, keypoint) and 3D (pose, shape) predictions as pseudo-groundtruth, unoccluded 3D objects are identified automatically and composited into the background in a clip-art style, ensuring realistic appearances and physically accurate occlusion configurations. The resulting clip-art image with pseudo-groundtruth enables efficient training of object reconstruction methods that are robust to occlusions. Our method demonstrates significant improvements in both 2D and 3D reconstruction, particularly in scenarios with heavily occluded objects like vehicles and people in urban scenes.
Toward Planet-Wide Traffic Camera Calibration
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Despite the widespread deployment of outdoor cameras, their potential for automated analysis remains largely untapped due, in part, to calibration challenges. The absence of precise camera calibration data, including intrinsic and extrinsic parameters, hinders accurate real-world distance measurements from captured videos. To address this, we present a scalable framework that utilizes street-level imagery to reconstruct a metric 3D model, facilitating precise calibration of in-the-wild traffic cameras. Notably, our framework achieves 3D scene reconstruction and accurate localization of over 100 global traffic cameras and is scalable to any camera with sufficient street-level imagery. For evaluation, we introduce a dataset of 20 fully calibrated traffic cameras, demonstrating our method's significant enhancements over existing automatic calibration techniques. Furthermore, we highlight our approach's utility in traffic analysis by extracting insights via 3D vehicle reconstruction and speed measurement, thereby opening up the potential of using outdoor cameras for automated analysis.
Egocentric Scene Understanding via Multimodal Spatial Rectifier
Jul 14, 2022
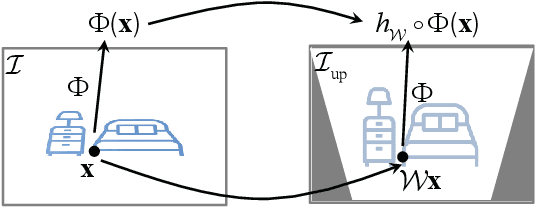


Abstract:In this paper, we study a problem of egocentric scene understanding, i.e., predicting depths and surface normals from an egocentric image. Egocentric scene understanding poses unprecedented challenges: (1) due to large head movements, the images are taken from non-canonical viewpoints (i.e., tilted images) where existing models of geometry prediction do not apply; (2) dynamic foreground objects including hands constitute a large proportion of visual scenes. These challenges limit the performance of the existing models learned from large indoor datasets, such as ScanNet and NYUv2, which comprise predominantly upright images of static scenes. We present a multimodal spatial rectifier that stabilizes the egocentric images to a set of reference directions, which allows learning a coherent visual representation. Unlike unimodal spatial rectifier that often produces excessive perspective warp for egocentric images, the multimodal spatial rectifier learns from multiple directions that can minimize the impact of the perspective warp. To learn visual representations of the dynamic foreground objects, we present a new dataset called EDINA (Egocentric Depth on everyday INdoor Activities) that comprises more than 500K synchronized RGBD frames and gravity directions. Equipped with the multimodal spatial rectifier and the EDINA dataset, our proposed method on single-view depth and surface normal estimation significantly outperforms the baselines not only on our EDINA dataset, but also on other popular egocentric datasets, such as First Person Hand Action (FPHA) and EPIC-KITCHENS.
Deep Multi-view Depth Estimation with Predicted Uncertainty
Nov 19, 2020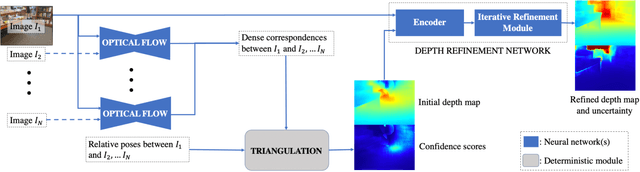
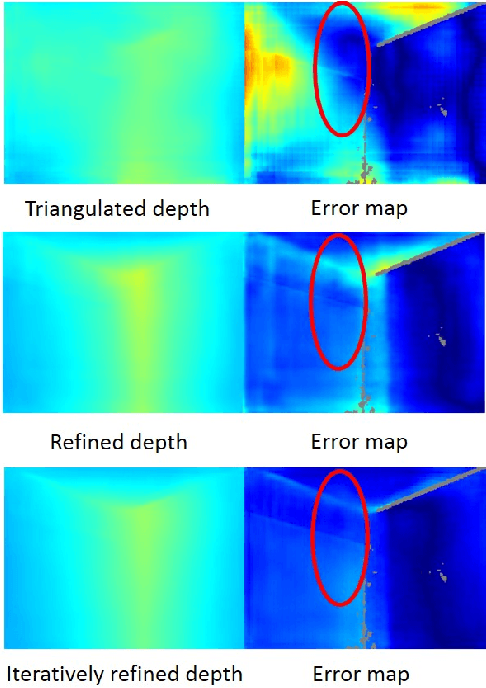
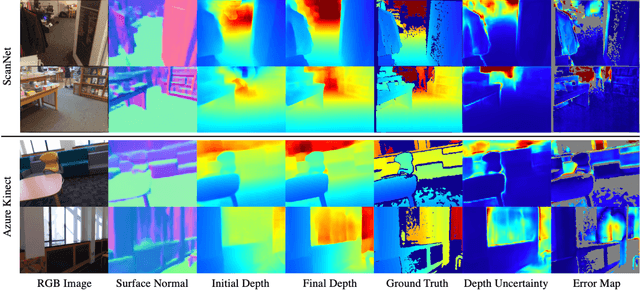
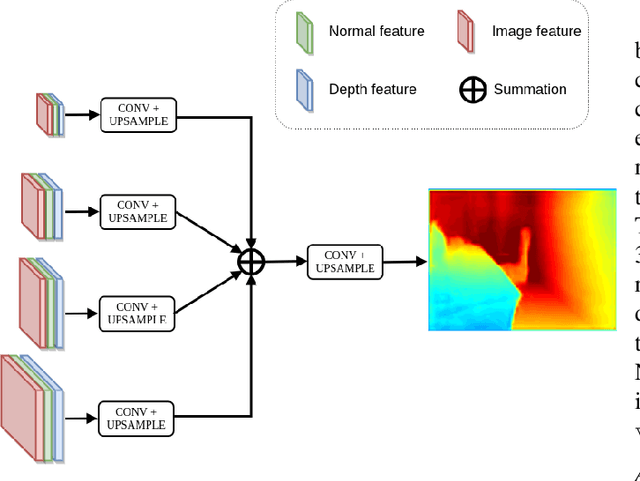
Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of estimating dense depth from a sequence of images using deep neural networks. Specifically, we employ a dense-optical-flow network to compute correspondences and then triangulate the point cloud to obtain an initial depth map. Parts of the point cloud, however, may be less accurate than others due to lack of common observations or small baseline-to-depth ratio. To further increase the triangulation accuracy, we introduce a depth-refinement network (DRN) that optimizes the initial depth map based on the image's contextual cues. In particular, the DRN contains an iterative refinement module (IRM) that improves the depth accuracy over iterations by refining the deep features. Lastly, the DRN also predicts the uncertainty in the refined depths, which is desirable in applications such as measurement selection for scene reconstruction. We show experimentally that our algorithm outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in terms of depth accuracy, and verify that our predicted uncertainty is highly correlated to the actual depth error.
Deep Depth Estimation from Visual-Inertial SLAM
Aug 14, 2020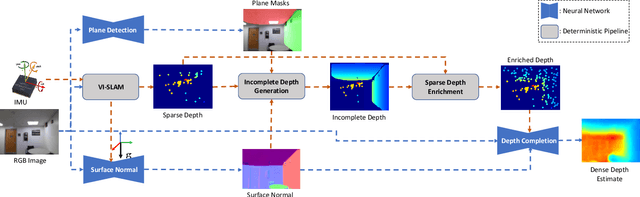

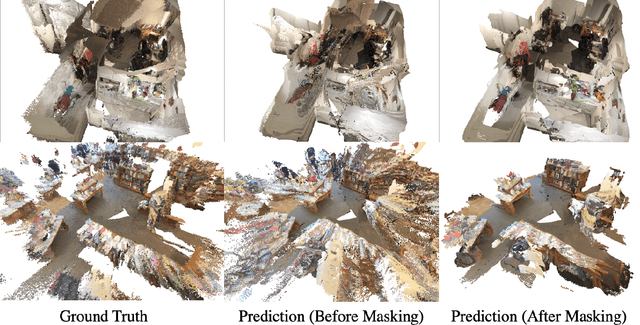
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of learning to complete a scene's depth from sparse depth points and images of indoor scenes. Specifically, we study the case in which the sparse depth is computed from a visual-inertial simultaneous localization and mapping (VI-SLAM) system. The resulting point cloud has low density, it is noisy, and has non-uniform spatial distribution, as compared to the input from active depth sensors, e.g., LiDAR or Kinect. Since the VI-SLAM produces point clouds only over textured areas, we compensate for the missing depth of the low-texture surfaces by leveraging their planar structures and their surface normals which is an important intermediate representation. The pre-trained surface normal network, however, suffers from large performance degradation when there is a significant difference in the viewing direction (especially the roll angle) of the test image as compared to the trained ones. To address this limitation, we use the available gravity estimate from the VI-SLAM to warp the input image to the orientation prevailing in the training dataset. This results in a significant performance gain for the surface normal estimate, and thus the dense depth estimates. Finally, we show that our method outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches both on training (ScanNet and NYUv2) and testing (collected with Azure Kinect) datasets.
Surface Normal Estimation of Tilted Images via Spatial Rectifier
Jul 17, 2020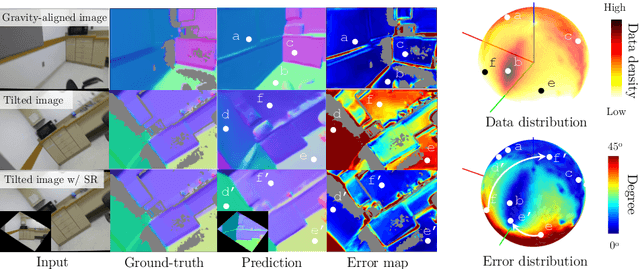
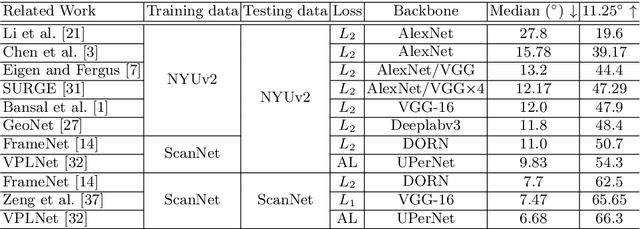
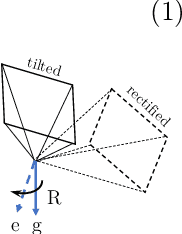
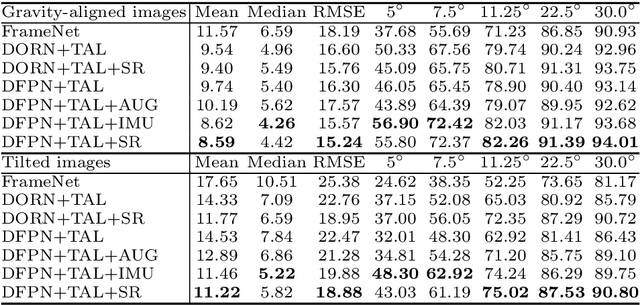
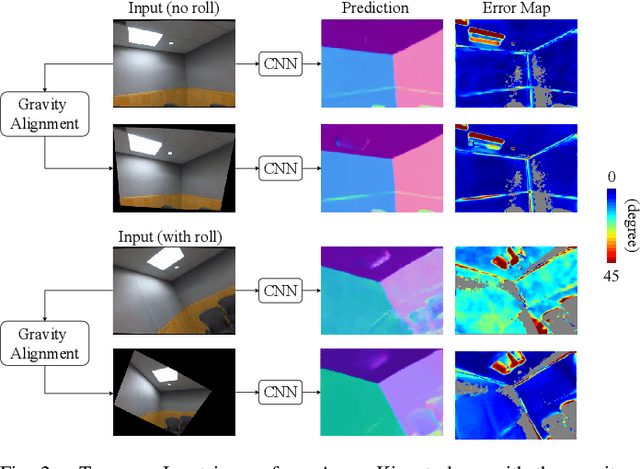
Abstract:In this paper, we present a spatial rectifier to estimate surface normals of tilted images. Tilted images are of particular interest as more visual data are captured by arbitrarily oriented sensors such as body-/robot-mounted cameras. Existing approaches exhibit bounded performance on predicting surface normals because they were trained using gravity-aligned images. Our two main hypotheses are: (1) visual scene layout is indicative of the gravity direction; and (2) not all surfaces are equally represented by a learned estimator due to the structured distribution of the training data, thus, there exists a transformation for each tilted image that is more responsive to the learned estimator than others. We design a spatial rectifier that is learned to transform the surface normal distribution of a tilted image to the rectified one that matches the gravity-aligned training data distribution. Along with the spatial rectifier, we propose a novel truncated angular loss that offers a stronger gradient at smaller angular errors and robustness to outliers. The resulting estimator outperforms the state-of-the-art methods including data augmentation baselines not only on ScanNet and NYUv2 but also on a new dataset called Tilt-RGBD that includes considerable roll and pitch camera motion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge