Keyang Yu
Categorizing Flight Paths using Data Visualization and Clustering Methodologies
Oct 01, 2023Abstract:This work leverages the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration's Traffic Flow Management System dataset and DV8, a recently developed tool for highly interactive visualization of air traffic data, to develop clustering algorithms for categorizing air traffic by their varying flight paths. Two clustering methodologies, a spatial-based geographic distance model, and a vector-based cosine similarity model, are demonstrated and compared for their clustering effectiveness. Examples of their applications reveal successful, realistic clustering based on automated clustering result determination and human-in-the-loop processes, with geographic distance algorithms performing better for enroute portions of flight paths and cosine similarity algorithms performing better for near-terminal operations, such as arrival paths. A point extraction technique is applied to improve computation efficiency.
* Published in the 9th International Conference on Research in Air Transportation (ICRAT'20): https://www.icrat.org/previous-conferences/9th-international-conference/papers/
Learning Weakly Supervised Audio-Visual Violence Detection in Hyperbolic Space
Jun 02, 2023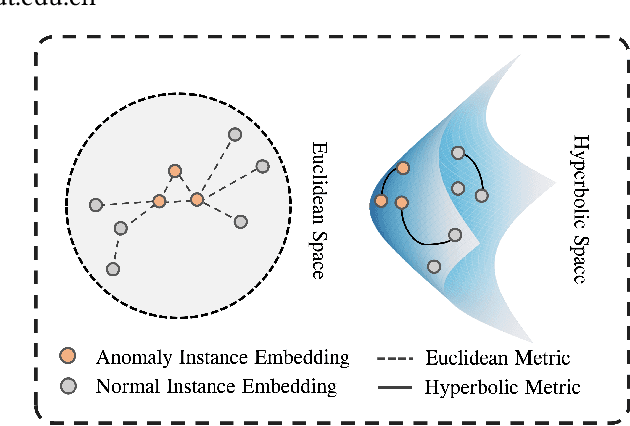
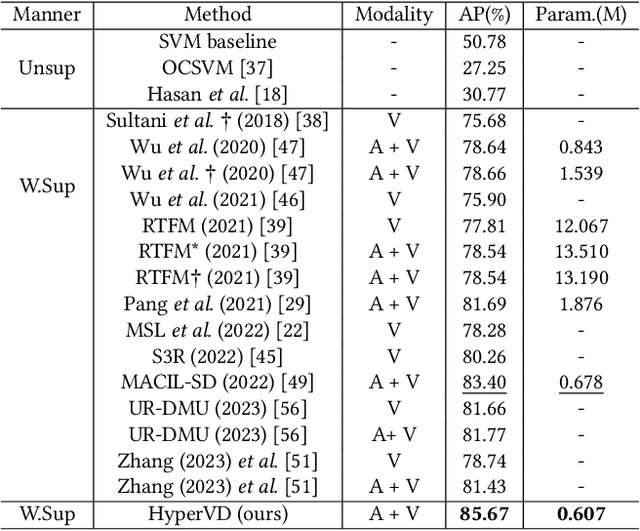
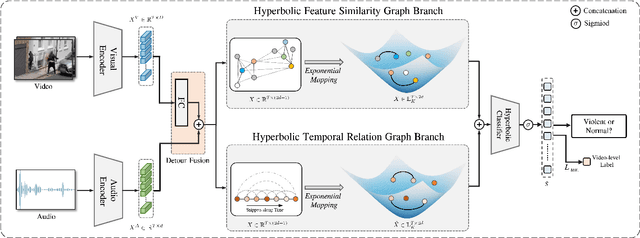
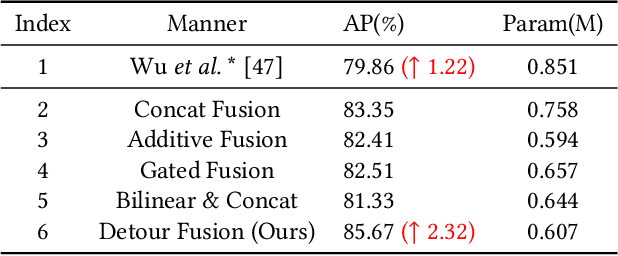
Abstract:In recent years, the task of weakly supervised audio-visual violence detection has gained considerable attention. The goal of this task is to identify violent segments within multimodal data based on video-level labels. Despite advances in this field, traditional Euclidean neural networks, which have been used in prior research, encounter difficulties in capturing highly discriminative representations due to limitations of the feature space. To overcome this, we propose HyperVD, a novel framework that learns snippet embeddings in hyperbolic space to improve model discrimination. Our framework comprises a detour fusion module for multimodal fusion, effectively alleviating modality inconsistency between audio and visual signals. Additionally, we contribute two branches of fully hyperbolic graph convolutional networks that excavate feature similarities and temporal relationships among snippets in hyperbolic space. By learning snippet representations in this space, the framework effectively learns semantic discrepancies between violent and normal events. Extensive experiments on the XD-Violence benchmark demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a sizable margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge