Kesav Kaza
Task load dependent decision referrals for joint binary classification in human-automation teams
Apr 05, 2025Abstract:We consider the problem of optimal decision referrals in human-automation teams performing binary classification tasks. The automation, which includes a pre-trained classifier, observes data for a batch of independent tasks, analyzes them, and may refer a subset of tasks to a human operator for fresh and final analysis. Our key modeling assumption is that human performance degrades with task load. We model the problem of choosing which tasks to refer as a stochastic optimization problem and show that, for a given task load, it is optimal to myopically refer tasks that yield the largest reduction in expected cost, conditional on the observed data. This provides a ranking scheme and a policy to determine the optimal set of tasks for referral. We evaluate this policy against a baseline through an experimental study with human participants. Using a radar screen simulator, participants made binary target classification decisions under time constraint. They were guided by a decision rule provided to them, but were still prone to errors under time pressure. An initial experiment estimated human performance model parameters, while a second experiment compared two referral policies. Results show statistically significant gains for the proposed optimal referral policy over a blind policy that determines referrals using the automation and human-performance models but not based on the observed data.
An Intent Modeling and Inference Framework for Autonomous and Remotely Piloted Aerial Systems
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:An intent modelling and inference framework is presented to assist the defense planning for protecting a geo-fence against unauthorized flights. First, a novel mathematical definition for the intent of an uncrewed aircraft system (UAS) is presented. The concepts of critical waypoints and critical waypoint patterns are introduced and associated with a motion process to fully characterize an intent. This modelling framework consists of representations of a UAS mission planner, used to plan the aircraft's motion sequence, as well as a defense planner, defined to protect the geo-fence. It is applicable to autonomous, semi-autonomous, and piloted systems in 2D and 3D environments with obstacles. The framework is illustrated by defining a library of intents for a security application. Detection and tracking of the target are presumed for formulating the intent inference problem. Multiple formulations of the decision maker's objective are discussed as part of a deep-learning-based methodology. Further, a multi-modal dynamic model for characterizing the UAS flight is discussed. This is later utilized to extract features using the interacting multiple model (IMM) filter for training the intent classifier. Finally, as part of the simulation study, an attention-based bi-directional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) network for intent inference is presented. The simulation experiments illustrate various aspects of the framework, including trajectory generation, radar measurement simulation, etc., in 2D and 3D environments.
Indexability and Rollout Policy for Multi-State Partially Observable Restless Bandits
Jul 30, 2021



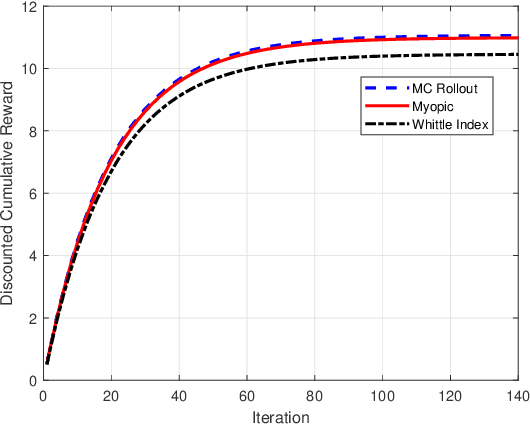
Abstract:Restless multi-armed bandits with partially observable states has applications in communication systems, age of information and recommendation systems. In this paper, we study multi-state partially observable restless bandit models. We consider three different models based on information observable to decision maker -- 1) no information is observable from actions of a bandit 2) perfect information from bandit is observable only for one action on bandit, there is a fixed restart state, i.e., transition occurs from all other states to that state 3) perfect state information is available to decision maker for both actions on a bandit and there are two restart state for two actions. We develop the structural properties. We also show a threshold type policy and indexability for model 2 and 3. We present Monte Carlo (MC) rollout policy. We use it for whittle index computation in case of model 2. We obtain the concentration bound on value function in terms of horizon length and number of trajectories for MC rollout policy. We derive explicit index formula for model 3. We finally describe Monte Carlo rollout policy for model 1 when it is difficult to show indexability. We demonstrate the numerical examples using myopic policy, Monte Carlo rollout policy and Whittle index policy. We observe that Monte Carlo rollout policy is good competitive policy to myopic.
Monte Carlo Rollout Policy for Recommendation Systems with Dynamic User Behavior
Feb 08, 2021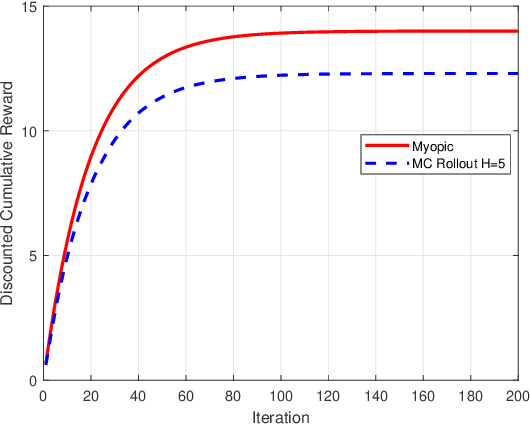
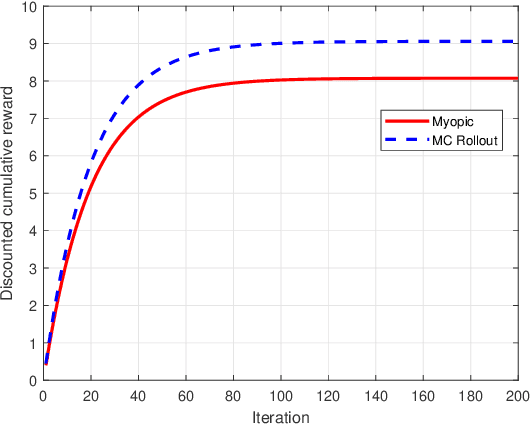

Abstract:We model online recommendation systems using the hidden Markov multi-state restless multi-armed bandit problem. To solve this we present Monte Carlo rollout policy. We illustrate numerically that Monte Carlo rollout policy performs better than myopic policy for arbitrary transition dynamics with no specific structure. But, when some structure is imposed on the transition dynamics, myopic policy performs better than Monte Carlo rollout policy.
Simulation Based Algorithms for Markov Decision Processes and Multi-Action Restless Bandits
Jul 25, 2020


Abstract:We consider multi-dimensional Markov decision processes and formulate a long term discounted reward optimization problem. Two simulation based algorithms---Monte Carlo rollout policy and parallel rollout policy are studied, and various properties for these policies are discussed. We next consider a restless multi-armed bandit (RMAB) with multi-dimensional state space and multi-actions bandit model. A standard RMAB consists of two actions for each arms whereas in multi-actions RMAB, there are more that two actions for each arms. A popular approach for RMAB is Whittle index based heuristic policy. Indexability is an important requirement to use index based policy. Based on this, an RMAB is classified into indexable or non-indexable bandits. Our interest is in the study of Monte-Carlo rollout policy for both indexable and non-indexable restless bandits. We first analyze a standard indexable RMAB (two-action model) and discuss an index based policy approach. We present approximate index computation algorithm using Monte-Carlo rollout policy. This algorithm's convergence is shown using two-timescale stochastic approximation scheme. Later, we analyze multi-actions indexable RMAB, and discuss the index based policy approach. We also study non-indexable RMAB for both standard and multi-actions bandits using Monte-Carlo rollout policy.
Sequential Decision Making under Uncertainty with Dynamic Resource Constraints
Apr 18, 2019



Abstract:This paper studies a class of constrained restless multi-armed bandits. The constraints are in the form of time varying availability of arms. This variation can be either stochastic or semi-deterministic. A fixed number of arms can be chosen to be played in each decision interval. The play of each arm yields a state dependent reward. The current states of arms are partially observable through binary feedback signals from arms that are played. The current availability of arms is fully observable. The objective is to maximize long term cumulative reward. The uncertainty about future availability of arms along with partial state information makes this objective challenging. This optimization problem is analyzed using Whittle's index policy. To this end, a constrained restless single-armed bandit is studied. It is shown to admit a threshold-type optimal policy, and is also indexable. An algorithm to compute Whittle's index is presented. Further, upper bounds on the value function are derived in order to estimate the degree of sub-optimality of various solutions. The simulation study compares the performance of Whittle's index, modified Whittle's index and myopic policies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge