Kenan Erdogan
iLCM - A Virtual Research Infrastructure for Large-Scale Qualitative Data
May 11, 2018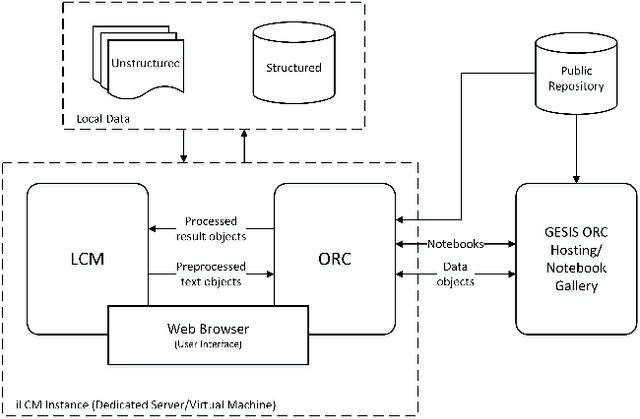
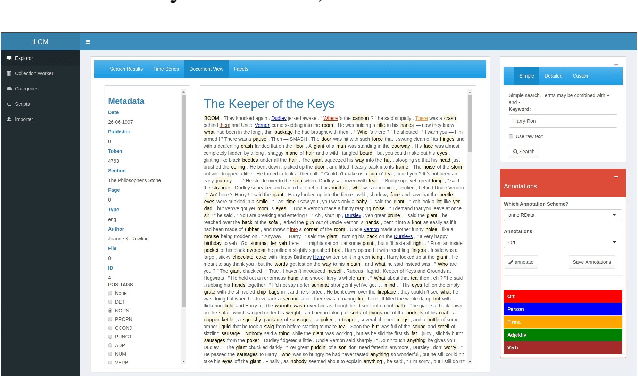
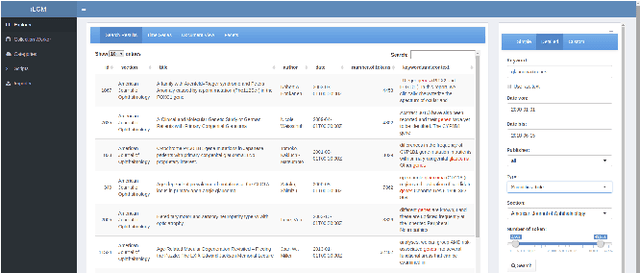
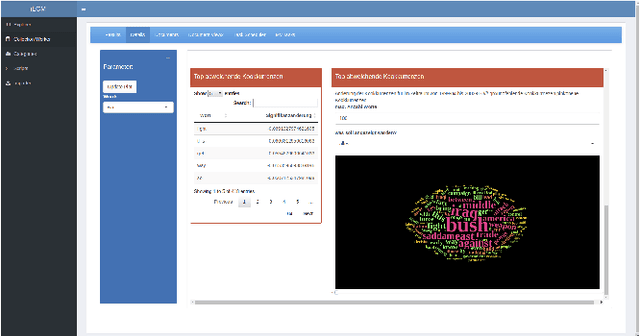
Abstract:The iLCM project pursues the development of an integrated research environment for the analysis of structured and unstructured data in a "Software as a Service" architecture (SaaS). The research environment addresses requirements for the quantitative evaluation of large amounts of qualitative data with text mining methods as well as requirements for the reproducibility of data-driven research designs in the social sciences. For this, the iLCM research environment comprises two central components. First, the Leipzig Corpus Miner (LCM), a decentralized SaaS application for the analysis of large amounts of news texts developed in a previous Digital Humanities project. Second, the text mining tools implemented in the LCM are extended by an "Open Research Computing" (ORC) environment for executable script documents, so-called "notebooks". This novel integration allows to combine generic, high-performance methods to process large amounts of unstructured text data and with individual program scripts to address specific research requirements in computational social science and digital humanities.
TokTrack: A Complete Token Provenance and Change Tracking Dataset for the English Wikipedia
Mar 23, 2017



Abstract:We present a dataset that contains every instance of all tokens (~ words) ever written in undeleted, non-redirect English Wikipedia articles until October 2016, in total 13,545,349,787 instances. Each token is annotated with (i) the article revision it was originally created in, and (ii) lists with all the revisions in which the token was ever deleted and (potentially) re-added and re-deleted from its article, enabling a complete and straightforward tracking of its history. This data would be exceedingly hard to create by an average potential user as it is (i) very expensive to compute and as (ii) accurately tracking the history of each token in revisioned documents is a non-trivial task. Adapting a state-of-the-art algorithm, we have produced a dataset that allows for a range of analyses and metrics, already popular in research and going beyond, to be generated on complete-Wikipedia scale; ensuring quality and allowing researchers to forego expensive text-comparison computation, which so far has hindered scalable usage. We show how this data enables, on token-level, computation of provenance, measuring survival of content over time, very detailed conflict metrics, and fine-grained interactions of editors like partial reverts, re-additions and other metrics, in the process gaining several novel insights.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge