Keisuke Okumura
Pairwise is Not Enough: Hypergraph Neural Networks for Multi-Agent Pathfinding
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) is a representative multi-agent coordination problem, where multiple agents are required to navigate to their respective goals without collisions. Solving MAPF optimally is known to be NP-hard, leading to the adoption of learning-based approaches to alleviate the online computational burden. Prevailing approaches, such as Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), are typically constrained to pairwise message passing between agents. However, this limitation leads to suboptimal behaviours and critical issues, such as attention dilution, particularly in dense environments where group (i.e. beyond just two agents) coordination is most critical. Despite the importance of such higher-order interactions, existing approaches have not been able to fully explore them. To address this representational bottleneck, we introduce HMAGAT (Hypergraph Multi-Agent Attention Network), a novel architecture that leverages attentional mechanisms over directed hypergraphs to explicitly capture group dynamics. Empirically, HMAGAT establishes a new state-of-the-art among learning-based MAPF solvers: e.g., despite having just 1M parameters and being trained on 100$\times$ less data, it outperforms the current SoTA 85M parameter model. Through detailed analysis of HMAGAT's attention values, we demonstrate how hypergraph representations mitigate the attention dilution inherent in GNNs and capture complex interactions where pairwise methods fail. Our results illustrate that appropriate inductive biases are often more critical than the training data size or sheer parameter count for multi-agent problems.
Local Guidance for Configuration-Based Multi-Agent Pathfinding
Oct 21, 2025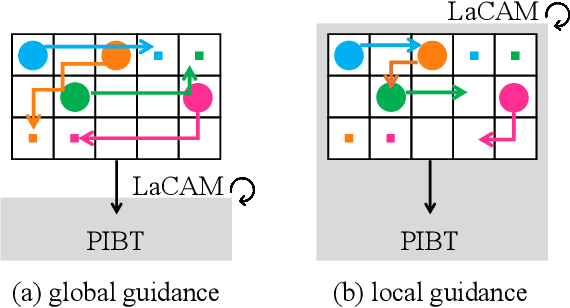
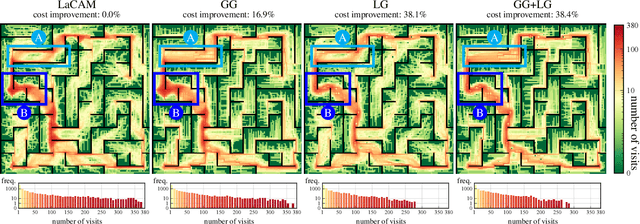
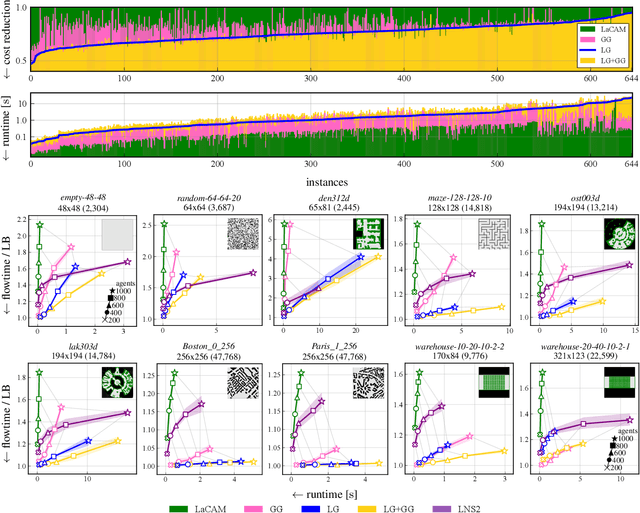
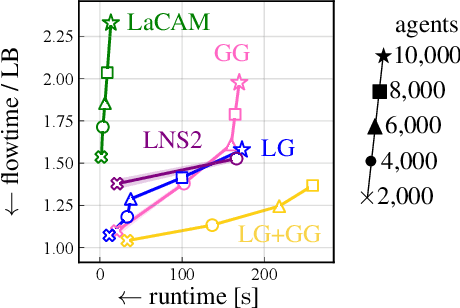
Abstract:Guidance is an emerging concept that improves the empirical performance of real-time, sub-optimal multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF) methods. It offers additional information to MAPF algorithms to mitigate congestion on a global scale by considering the collective behavior of all agents across the entire workspace. This global perspective helps reduce agents' waiting times, thereby improving overall coordination efficiency. In contrast, this study explores an alternative approach: providing local guidance in the vicinity of each agent. While such localized methods involve recomputation as agents move and may appear computationally demanding, we empirically demonstrate that supplying informative spatiotemporal cues to the planner can significantly improve solution quality without exceeding a moderate time budget. When applied to LaCAM, a leading configuration-based solver, this form of guidance establishes a new performance frontier for MAPF.
LF: Online Multi-Robot Path Planning Meets Optimal Trajectory Control
Jul 15, 2025Abstract:We propose a multi-robot control paradigm to solve point-to-point navigation tasks for a team of holonomic robots with access to the full environment information. The framework invokes two processes asynchronously at high frequency: (i) a centralized, discrete, and full-horizon planner for computing collision- and deadlock-free paths rapidly, leveraging recent advances in multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF), and (ii) dynamics-aware, robot-wise optimal trajectory controllers that ensure all robots independently follow their assigned paths reliably. This hierarchical shift in planning representation from (i) discrete and coupled to (ii) continuous and decoupled domains enables the framework to maintain long-term scalable motion synthesis. As an instantiation of this idea, we present LF, which combines a fast state-of-the-art MAPF solver (LaCAM), and a robust feedback control stack (Freyja) for executing agile robot maneuvers. LF provides a robust and versatile mechanism for lifelong multi-robot navigation even under asynchronous and partial goal updates, and adapts to dynamic workspaces simply by quick replanning. We present various multirotor and ground robot demonstrations, including the deployment of 15 real multirotors with random, consecutive target updates while a person walks through the operational workspace.
Lightweight and Effective Preference Construction in PIBT for Large-Scale Multi-Agent Pathfinding
May 19, 2025Abstract:PIBT is a computationally lightweight algorithm that can be applied to a variety of multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF) problems, generating the next collision-free locations of agents given another. Because of its simplicity and scalability, it is becoming a popular underlying scheme for recent large-scale MAPF methods involving several hundreds or thousands of agents. Vanilla PIBT makes agents behave greedily towards their assigned goals, while agents typically have multiple best actions, since the graph shortest path is not always unique. Consequently, tiebreaking about how to choose between these actions significantly affects resulting solutions. This paper studies two simple yet effective techniques for tiebreaking in PIBT, without compromising its computational advantage. The first technique allows an agent to intelligently dodge another, taking into account whether each action will hinder the progress of the next timestep. The second technique is to learn, through multiple PIBT runs, how an action causes regret in others and to use this information to minimise regret collectively. Our empirical results demonstrate that these techniques can reduce the solution cost of one-shot MAPF and improve the throughput of lifelong MAPF. For instance, in densely populated one-shot cases, the combined use of these tiebreaks achieves improvements of around 10-20% in sum-of-costs, without significantly compromising the speed of a PIBT-based planner.
D4orm: Multi-Robot Trajectories with Dynamics-aware Diffusion Denoised Deformations
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:This work presents an optimization method for generating kinodynamically feasible and collision-free multi-robot trajectories that exploits an incremental denoising scheme in diffusion models. Our key insight is that high-quality trajectories can be discovered merely by denoising noisy trajectories sampled from a distribution. This approach has no learning component, relying instead on only two ingredients: a dynamical model of the robots to obtain feasible trajectories via rollout, and a score function to guide denoising with Monte Carlo gradient approximation. The proposed framework iteratively optimizes the deformation from the previous round with this denoising process, allows \textit{anytime} refinement as time permits, supports different dynamics, and benefits from GPU acceleration. Our evaluations for differential-drive and holonomic teams with up to 16 robots in 2D and 3D worlds show its ability to discover high-quality solutions faster than other black-box optimization methods such as MPPI, approximately three times faster in a 3D holonomic case with 16 robots. As evidence for feasibility, we demonstrate zero-shot deployment of the planned trajectories on eight multirotors.
Pathfinding with Lazy Successor Generation
Aug 27, 2024



Abstract:We study a pathfinding problem where only locations (i.e., vertices) are given, and edges are implicitly defined by an oracle answering the connectivity of two locations. Despite its simple structure, this problem becomes non-trivial with a massive number of locations, due to posing a huge branching factor for search algorithms. Limiting the number of successors, such as with nearest neighbors, can reduce search efforts but compromises completeness. Instead, we propose a novel LaCAS* algorithm, which does not generate successors all at once but gradually generates successors as the search progresses. This scheme is implemented with k-nearest neighbors search on a k-d tree. LaCAS* is a complete and anytime algorithm that eventually converges to the optima. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the efficacy of LaCAS*, e.g., solving complex pathfinding instances quickly, where conventional methods falter.
Engineering LaCAM$^\ast$: Towards Real-Time, Large-Scale, and Near-Optimal Multi-Agent Pathfinding
Aug 08, 2023

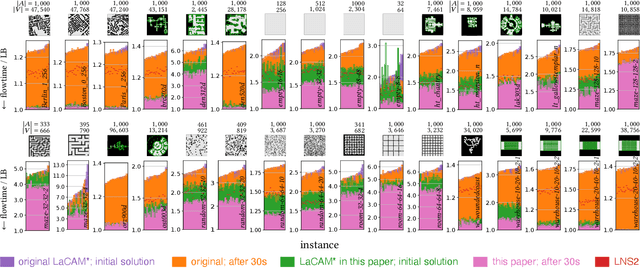
Abstract:This paper addresses the challenges of real-time, large-scale, and near-optimal multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF) through enhancements to the recently proposed LaCAM* algorithm. LaCAM* is a scalable search-based algorithm that guarantees the eventual finding of optimal solutions for cumulative transition costs. While it has demonstrated remarkable planning success rates, surpassing various state-of-the-art MAPF methods, its initial solution quality is far from optimal, and its convergence speed to the optimum is slow. To overcome these limitations, this paper introduces several improvement techniques, partly drawing inspiration from other MAPF methods. We provide empirical evidence that the fusion of these techniques significantly improves the solution quality of LaCAM*, thus further pushing the boundaries of MAPF algorithms.
Improving LaCAM for Scalable Eventually Optimal Multi-Agent Pathfinding
May 05, 2023Abstract:This study extends the recently-developed LaCAM algorithm for multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF). LaCAM is a sub-optimal search-based algorithm that uses lazy successor generation to dramatically reduce the planning effort. We present two enhancements. First, we propose its anytime version, called LaCAM*, which eventually converges to optima, provided that solution costs are accumulated transition costs. Second, we improve the successor generation to quickly obtain initial solutions. Exhaustive experiments demonstrate their utility. For instance, LaCAM* sub-optimally solved 99% of the instances retrieved from the MAPF benchmark, where the number of agents varied up to a thousand, within ten seconds on a standard desktop PC, while ensuring eventual convergence to optima; developing a new horizon of MAPF algorithms.
Fault-Tolerant Offline Multi-Agent Path Planning
Nov 25, 2022Abstract:We study a novel graph path planning problem for multiple agents that may crash at runtime, and block part of the workspace. In our setting, agents can detect neighboring crashed agents, and change followed paths at runtime. The objective is then to prepare a set of paths and switching rules for each agent, ensuring that all correct agents reach their destinations without collisions or deadlocks, despite unforeseen crashes of other agents. Such planning is attractive to build reliable multi-robot systems. We present problem formalization, theoretical analysis such as computational complexities, and how to solve this offline planning problem.
LaCAM: Search-Based Algorithm for Quick Multi-Agent Pathfinding
Nov 24, 2022
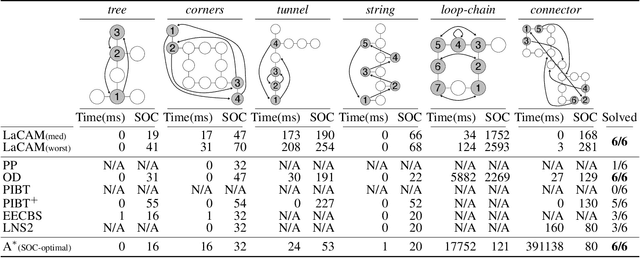

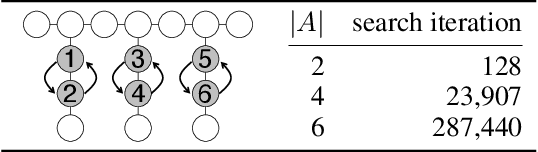
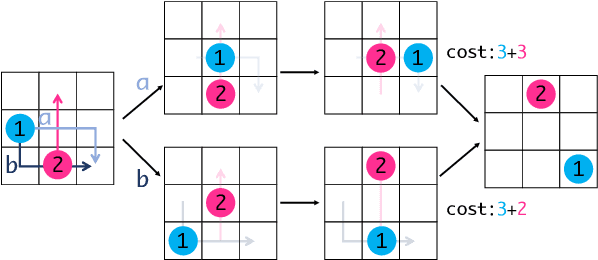
Abstract:We propose a novel complete algorithm for multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF) called lazy constraints addition search for MAPF (LaCAM). MAPF is a problem of finding collision-free paths for multiple agents on graphs and is the foundation of multi-robot coordination. LaCAM uses a two-level search to find solutions quickly, even with hundreds of agents or more. At the low-level, it searches constraints about agents' locations. At the high-level, it searches a sequence of all agents' locations, following the constraints specified by the low-level. Our exhaustive experiments reveal that LaCAM is comparable to or outperforms state-of-the-art sub-optimal MAPF algorithms in a variety of scenarios, regarding success rate, planning time, and solution quality of sum-of-costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge