Ke Xiao
Joint Fractional Delay and Doppler Frequency Estimator Under Spectrum Wrapping Phenomenon for LEO-ICAN AFDM Signals
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:With the rapid development of low earth orbit (LEO) satellites, the design of integrated communication and navigation (ICAN) signals has attracted increasing attention, especially in the field of vehicle-to-everything (V2X). As a new-generation waveform, Affine Frequency Division Multiplexing (AFDM) features high robustness against Doppler effects, a simple modulation structure, and low pilot overhead, making it a promising candidate for high-dynamic LEO satellite scenarios. However, LEO-ICAN AFDM signals face challenges in fractional delay and Doppler frequency estimation. Existing studies that ignore its inherent spectrum wrapping phenomenon may lead to deviations of varying degrees in model construction. This paper conducts an in-depth derivation of AFDM's input-output relationship under fractional cases, reveals the envelope characteristics of its equivalent channel, and proposes a joint estimation algorithm based on peak-to-sidelobe power ratio (PSPR) detection and early-late gate (ELG) to estimate fractional Doppler frequency and delay. Simulations show that the algorithm has low complexity, low guard interval overhead, and high precision compared with traditional methods.
Towards LLM-enabled autonomous combustion research: A literature-aware agent for self-corrective modeling workflows
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) is transforming artificial intelligence into autonomous research partners, yet a critical gap persists in complex scientific domains such as combustion modeling. Here, practical AI assistance requires the seamless integration of domain literature knowledge with robust execution capabilities for expertise-intensive tools such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD) codes. To bridge this gap, we introduce FlamePilot, an LLM agent designed to empower combustion modeling research through automated and self-corrective CFD workflows. FlamePilot differentiates itself through an architecture that leverages atomic tools to ensure the robust setup and execution of complex simulations in both OpenFOAM and extended frameworks such as DeepFlame. The system is also capable of learning from scientific articles, extracting key information to guide the simulation from initial setup to optimized results. Validation on a public benchmark shows FlamePilot achieved a perfect 1.0 executability score and a 0.438 success rate, surpassing the prior best reported agent scores of 0.625 and 0.250, respectively. Furthermore, a detailed case study on Moderate or Intense Low-oxygen Dilution (MILD) combustion simulation demonstrates its efficacy as a collaborative research copilot, where FlamePilot autonomously translated a research paper into a configured simulation, conducted the simulation, post-processed the results, proposed evidence-based refinements, and managed a multi-step parameter study to convergence under minimal human intervention. By adopting a transparent and interpretable paradigm, FlamePilot establishes a foundational framework for AI-empowered combustion modeling, fostering a collaborative partnership where the agent manages workflow orchestration, freeing the researcher for high-level analysis.
Let It Flow: Agentic Crafting on Rock and Roll, Building the ROME Model within an Open Agentic Learning Ecosystem
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Agentic crafting requires LLMs to operate in real-world environments over multiple turns by taking actions, observing outcomes, and iteratively refining artifacts. Despite its importance, the open-source community lacks a principled, end-to-end ecosystem to streamline agent development. We introduce the Agentic Learning Ecosystem (ALE), a foundational infrastructure that optimizes the production pipeline for agent LLMs. ALE consists of three components: ROLL, a post-training framework for weight optimization; ROCK, a sandbox environment manager for trajectory generation; and iFlow CLI, an agent framework for efficient context engineering. We release ROME (ROME is Obviously an Agentic Model), an open-source agent grounded by ALE and trained on over one million trajectories. Our approach includes data composition protocols for synthesizing complex behaviors and a novel policy optimization algorithm, Interaction-based Policy Alignment (IPA), which assigns credit over semantic interaction chunks rather than individual tokens to improve long-horizon training stability. Empirically, we evaluate ROME within a structured setting and introduce Terminal Bench Pro, a benchmark with improved scale and contamination control. ROME demonstrates strong performance across benchmarks like SWE-bench Verified and Terminal Bench, proving the effectiveness of the ALE infrastructure.
FEMSN: Frequency-Enhanced Multiscale Network for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery under strong noise environments
May 07, 2025Abstract:Rolling bearings are critical components of rotating machinery, and their proper functioning is essential for industrial production. Most existing condition monitoring methods focus on extracting discriminative features from time-domain signals to assess bearing health status. However, under complex operating conditions, periodic impulsive characteristics related to fault information are often obscured by noise interference. Consequently, existing approaches struggle to learn distinctive fault-related features in such scenarios. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel CNN-based model named FEMSN. Specifically, a Fourier Adaptive Denoising Encoder Layer (FADEL) is introduced as an input denoising layer to enhance key features while filtering out irrelevant information. Subsequently, a Multiscale Time-Frequency Fusion (MSTFF) module is employed to extract fused time-frequency features, further improving the model robustness and nonlinear representation capability. Additionally, a distillation layer is incorporated to expand the receptive field. Based on these advancements, a novel deep lightweight CNN model, termed the Frequency-Enhanced Multiscale Network (FEMSN), is developed. The effectiveness of FEMSN and FADEL in machine health monitoring and stability assessment is validated through two case studies.
Machine Learning for Automated Mitral Regurgitation Detection from Cardiac Imaging
Oct 07, 2023Abstract:Mitral regurgitation (MR) is a heart valve disease with potentially fatal consequences that can only be forestalled through timely diagnosis and treatment. Traditional diagnosis methods are expensive, labor-intensive and require clinical expertise, posing a barrier to screening for MR. To overcome this impediment, we propose a new semi-supervised model for MR classification called CUSSP. CUSSP operates on cardiac imaging slices of the 4-chamber view of the heart. It uses standard computer vision techniques and contrastive models to learn from large amounts of unlabeled data, in conjunction with specialized classifiers to establish the first ever automated MR classification system. Evaluated on a test set of 179 labeled -- 154 non-MR and 25 MR -- sequences, CUSSP attains an F1 score of 0.69 and a ROC-AUC score of 0.88, setting the first benchmark result for this new task.
* 12 pages including references and the appendix. 9 Figures, 2 tables. Accepted at MICCAI (Machine Learning for Automated Mitral Regurgitation Detection from Cardiac Imaging) 2023, Link to Springer at https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-43990-2_23
Multi-Resolution Weak Supervision for Sequential Data
Oct 21, 2019
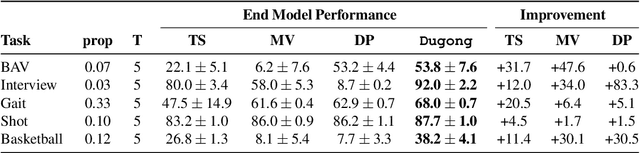
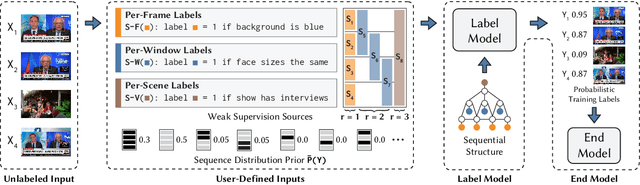

Abstract:Since manually labeling training data is slow and expensive, recent industrial and scientific research efforts have turned to weaker or noisier forms of supervision sources. However, existing weak supervision approaches fail to model multi-resolution sources for sequential data, like video, that can assign labels to individual elements or collections of elements in a sequence. A key challenge in weak supervision is estimating the unknown accuracies and correlations of these sources without using labeled data. Multi-resolution sources exacerbate this challenge due to complex correlations and sample complexity that scales in the length of the sequence. We propose Dugong, the first framework to model multi-resolution weak supervision sources with complex correlations to assign probabilistic labels to training data. Theoretically, we prove that Dugong, under mild conditions, can uniquely recover the unobserved accuracy and correlation parameters and use parameter sharing to improve sample complexity. Our method assigns clinician-validated labels to population-scale biomedical video repositories, helping outperform traditional supervision by 36.8 F1 points and addressing a key use case where machine learning has been severely limited by the lack of expert labeled data. On average, Dugong improves over traditional supervision by 16.0 F1 points and existing weak supervision approaches by 24.2 F1 points across several video and sensor classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge