Kanghoon Lee
Priority-Aware Multi-Robot Coverage Path Planning
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Multi-robot systems are widely used for coverage tasks that require efficient coordination across large environments. In Multi-Robot Coverage Path Planning (MCPP), the objective is typically to minimize the makespan by generating non-overlapping paths for full-area coverage. However, most existing methods assume uniform importance across regions, limiting their effectiveness in scenarios where some zones require faster attention. We introduce the Priority-Aware MCPP (PA-MCPP) problem, where a subset of the environment is designated as prioritized zones with associated weights. The goal is to minimize, in lexicographic order, the total priority-weighted latency of zone coverage and the overall makespan. To address this, we propose a scalable two-phase framework combining (1) greedy zone assignment with local search, spanning-tree-based path planning, and (2) Steiner-tree-guided residual coverage. Experiments across diverse scenarios demonstrate that our method significantly reduces priority-weighted latency compared to standard MCPP baselines, while maintaining competitive makespan. Sensitivity analyses further show that the method scales well with the number of robots and that zone coverage behavior can be effectively controlled by adjusting priority weights.
TrajEvo: Trajectory Prediction Heuristics Design via LLM-driven Evolution
Aug 07, 2025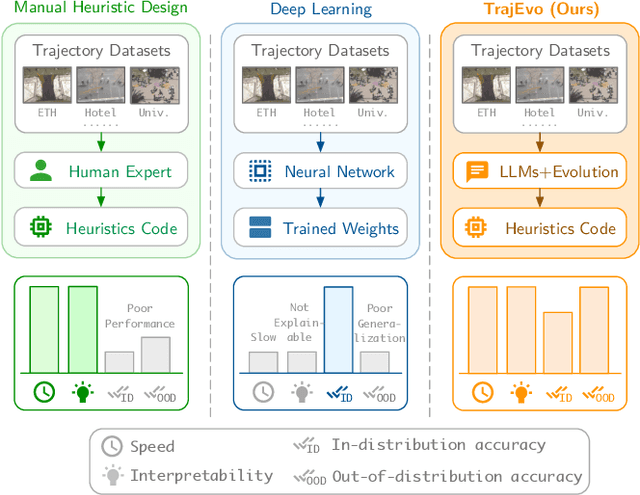
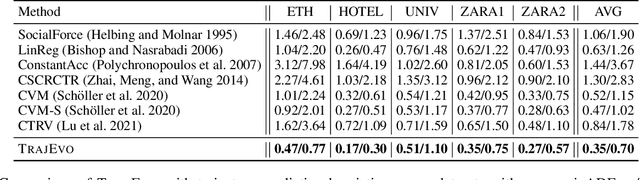
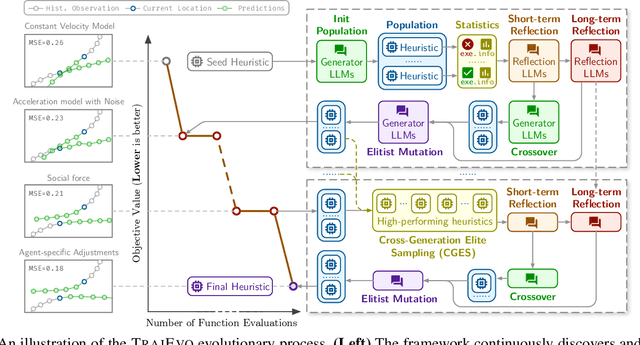
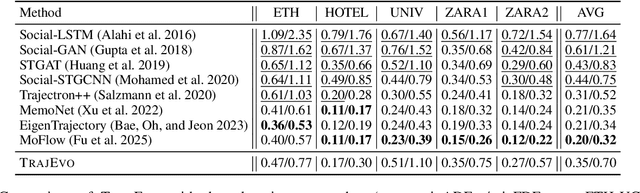
Abstract:Trajectory prediction is a critical task in modeling human behavior, especially in safety-critical domains such as social robotics and autonomous vehicle navigation. Traditional heuristics based on handcrafted rules often lack accuracy and generalizability. Although deep learning approaches offer improved performance, they typically suffer from high computational cost, limited explainability, and, importantly, poor generalization to out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios. In this paper, we introduce TrajEvo, a framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to automatically design trajectory prediction heuristics. TrajEvo employs an evolutionary algorithm to generate and refine prediction heuristics from past trajectory data. We propose two key innovations: Cross-Generation Elite Sampling to encourage population diversity, and a Statistics Feedback Loop that enables the LLM to analyze and improve alternative predictions. Our evaluations demonstrate that TrajEvo outperforms existing heuristic methods across multiple real-world datasets, and notably surpasses both heuristic and deep learning methods in generalizing to an unseen OOD real-world dataset. TrajEvo marks a promising step toward the automated design of fast, explainable, and generalizable trajectory prediction heuristics. We release our source code to facilitate future research at https://github.com/ai4co/trajevo.
TrajEvo: Designing Trajectory Prediction Heuristics via LLM-driven Evolution
May 07, 2025



Abstract:Trajectory prediction is a crucial task in modeling human behavior, especially in fields as social robotics and autonomous vehicle navigation. Traditional heuristics based on handcrafted rules often lack accuracy, while recently proposed deep learning approaches suffer from computational cost, lack of explainability, and generalization issues that limit their practical adoption. In this paper, we introduce TrajEvo, a framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to automatically design trajectory prediction heuristics. TrajEvo employs an evolutionary algorithm to generate and refine prediction heuristics from past trajectory data. We introduce a Cross-Generation Elite Sampling to promote population diversity and a Statistics Feedback Loop allowing the LLM to analyze alternative predictions. Our evaluations show TrajEvo outperforms previous heuristic methods on the ETH-UCY datasets, and remarkably outperforms both heuristics and deep learning methods when generalizing to the unseen SDD dataset. TrajEvo represents a first step toward automated design of fast, explainable, and generalizable trajectory prediction heuristics. We make our source code publicly available to foster future research at https://github.com/ai4co/trajevo.
Human Implicit Preference-Based Policy Fine-tuning for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning in USV Swarm
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) has shown promise in solving complex problems involving cooperation and competition among agents, such as an Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USV) swarm used in search and rescue, surveillance, and vessel protection. However, aligning system behavior with user preferences is challenging due to the difficulty of encoding expert intuition into reward functions. To address the issue, we propose a Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) approach for MARL that resolves credit-assignment challenges through an Agent-Level Feedback system categorizing feedback into intra-agent, inter-agent, and intra-team types. To overcome the challenges of direct human feedback, we employ a Large Language Model (LLM) evaluator to validate our approach using feedback scenarios such as region constraints, collision avoidance, and task allocation. Our method effectively refines USV swarm policies, addressing key challenges in multi-agent systems while maintaining fairness and performance consistency.
An Offline Meta Black-box Optimization Framework for Adaptive Design of Urban Traffic Light Management Systems
Aug 14, 2024Abstract:Complex urban road networks with high vehicle occupancy frequently face severe traffic congestion. Designing an effective strategy for managing multiple traffic lights plays a crucial role in managing congestion. However, most current traffic light management systems rely on human-crafted decisions, which may not adapt well to diverse traffic patterns. In this paper, we delve into two pivotal design components of the traffic light management system that can be dynamically adjusted to various traffic conditions: phase combination and phase time allocation. While numerous studies have sought an efficient strategy for managing traffic lights, most of these approaches consider a fixed traffic pattern and are limited to relatively small road networks. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel and practical framework to formulate the optimization of such design components using an offline meta black-box optimization. We then present a simple yet effective method to efficiently find a solution for the aforementioned problem. In our framework, we first collect an offline meta dataset consisting of pairs of design choices and corresponding congestion measures from various traffic patterns. After collecting the dataset, we employ the Attentive Neural Process (ANP) to predict the impact of the proposed design on congestion across various traffic patterns with well-calibrated uncertainty. Finally, Bayesian optimization, with ANP as a surrogate model, is utilized to find an optimal design for unseen traffic patterns through limited online simulations. Our experiment results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on complex road networks in terms of the number of waiting vehicles. Surprisingly, the deployment of our method into a real-world traffic system was able to improve traffic throughput by 4.80\% compared to the original strategy.
ELA: Exploited Level Augmentation for Offline Learning in Zero-Sum Games
Feb 28, 2024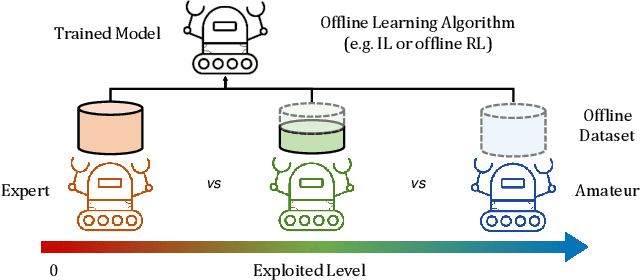


Abstract:Offline learning has become widely used due to its ability to derive effective policies from offline datasets gathered by expert demonstrators without interacting with the environment directly. Recent research has explored various ways to enhance offline learning efficiency by considering the characteristics (e.g., expertise level or multiple demonstrators) of the dataset. However, a different approach is necessary in the context of zero-sum games, where outcomes vary significantly based on the strategy of the opponent. In this study, we introduce a novel approach that uses unsupervised learning techniques to estimate the exploited level of each trajectory from the offline dataset of zero-sum games made by diverse demonstrators. Subsequently, we incorporate the estimated exploited level into the offline learning to maximize the influence of the dominant strategy. Our method enables interpretable exploited level estimation in multiple zero-sum games and effectively identifies dominant strategy data. Also, our exploited level augmented offline learning significantly enhances the original offline learning algorithms including imitation learning and offline reinforcement learning for zero-sum games.
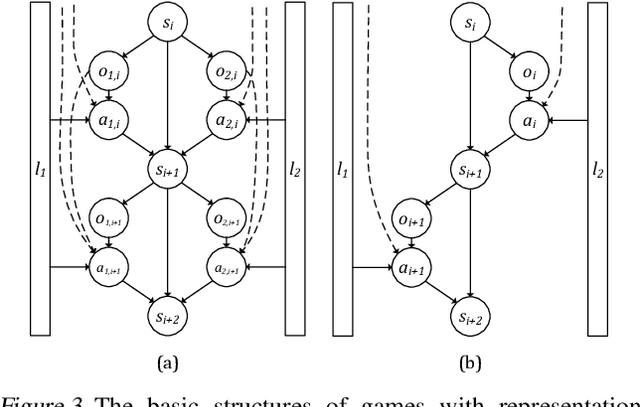
Interactive Autonomous Navigation with Internal State Inference and Interactivity Estimation
Nov 27, 2023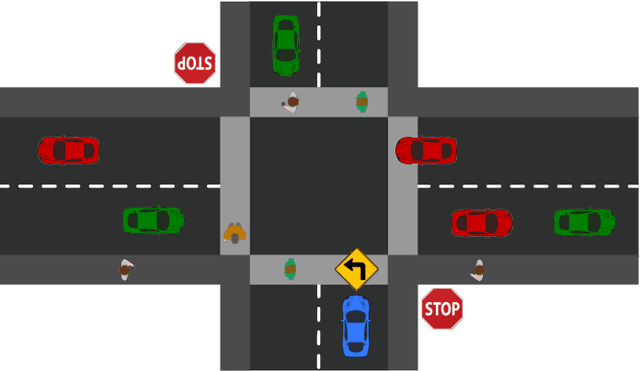
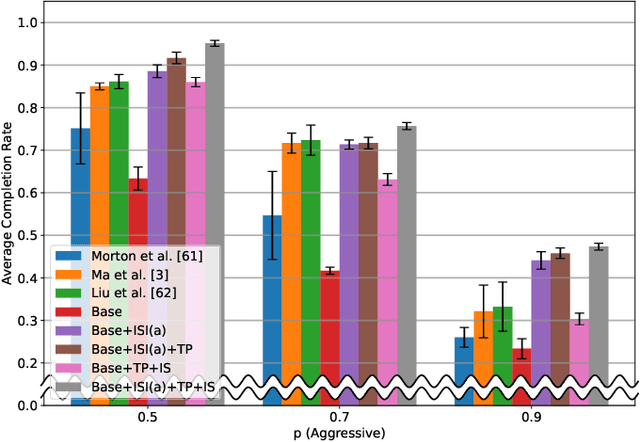
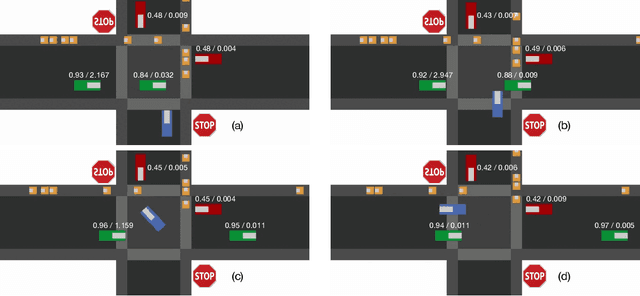
Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) provides a promising way for intelligent agents (e.g., autonomous vehicles) to learn to navigate complex scenarios. However, DRL with neural networks as function approximators is typically considered a black box with little explainability and often suffers from suboptimal performance, especially for autonomous navigation in highly interactive multi-agent environments. To address these issues, we propose three auxiliary tasks with spatio-temporal relational reasoning and integrate them into the standard DRL framework, which improves the decision making performance and provides explainable intermediate indicators. We propose to explicitly infer the internal states (i.e., traits and intentions) of surrounding agents (e.g., human drivers) as well as to predict their future trajectories in the situations with and without the ego agent through counterfactual reasoning. These auxiliary tasks provide additional supervision signals to infer the behavior patterns of other interactive agents. Multiple variants of framework integration strategies are compared. We also employ a spatio-temporal graph neural network to encode relations between dynamic entities, which enhances both internal state inference and decision making of the ego agent. Moreover, we propose an interactivity estimation mechanism based on the difference between predicted trajectories in these two situations, which indicates the degree of influence of the ego agent on other agents. To validate the proposed method, we design an intersection driving simulator based on the Intelligent Intersection Driver Model (IIDM) that simulates vehicles and pedestrians. Our approach achieves robust and state-of-the-art performance in terms of standard evaluation metrics and provides explainable intermediate indicators (i.e., internal states, and interactivity scores) for decision making.
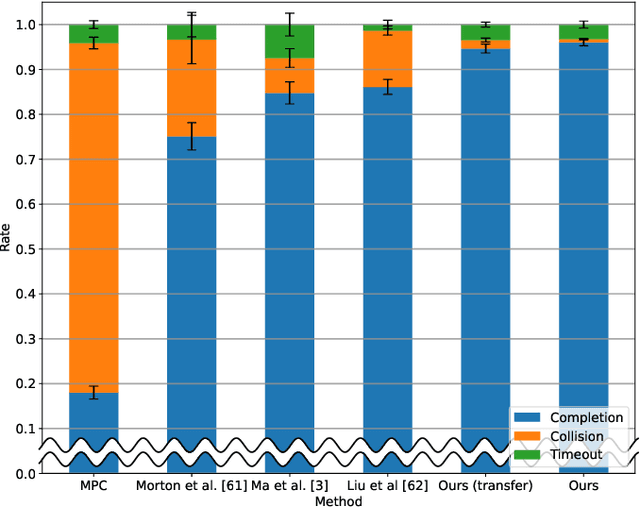
Robust Driving Policy Learning with Guided Meta Reinforcement Learning
Jul 19, 2023



Abstract:Although deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has shown promising results for autonomous navigation in interactive traffic scenarios, existing work typically adopts a fixed behavior policy to control social vehicles in the training environment. This may cause the learned driving policy to overfit the environment, making it difficult to interact well with vehicles with different, unseen behaviors. In this work, we introduce an efficient method to train diverse driving policies for social vehicles as a single meta-policy. By randomizing the interaction-based reward functions of social vehicles, we can generate diverse objectives and efficiently train the meta-policy through guiding policies that achieve specific objectives. We further propose a training strategy to enhance the robustness of the ego vehicle's driving policy using the environment where social vehicles are controlled by the learned meta-policy. Our method successfully learns an ego driving policy that generalizes well to unseen situations with out-of-distribution (OOD) social agents' behaviors in a challenging uncontrolled T-intersection scenario.
Stochastic Doubly Robust Gradient
Dec 21, 2018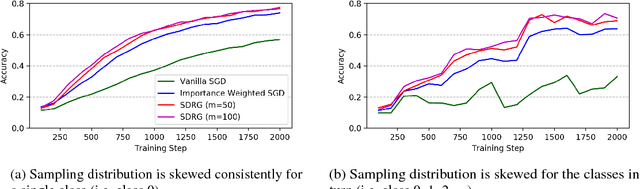
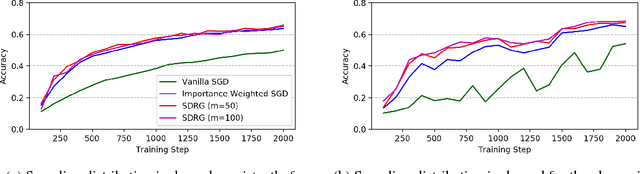
Abstract:When training a machine learning model with observational data, it is often encountered that some values are systemically missing. Learning from the incomplete data in which the missingness depends on some covariates may lead to biased estimation of parameters and even harm the fairness of decision outcome. This paper proposes how to adjust the causal effect of covariates on the missingness when training models using stochastic gradient descent (SGD). Inspired by the design of doubly robust estimator and its theoretical property of double robustness, we introduce stochastic doubly robust gradient (SDRG) consisting of two models: weight-corrected gradients for inverse propensity score weighting and per-covariate control variates for regression adjustment. Also, we identify the connection between double robustness and variance reduction in SGD by demonstrating the SDRG algorithm with a unifying framework for variance reduced SGD. The performance of our approach is empirically tested by showing the convergence in training image classifiers with several examples of missing data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge