Kanghee Lee
SpatialMosaic: A Multiview VLM Dataset for Partial Visibility
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has unlocked the potential for enhanced 3D scene understanding and spatial reasoning. However, existing approaches often rely on pre-constructed 3D representations or off-the-shelf reconstruction pipelines, which constrain scalability and real-world applicability. A recent line of work explores learning spatial reasoning directly from multi-view images, enabling Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to understand 3D scenes without explicit 3D reconstructions. Nevertheless, key challenges that frequently arise in real-world environments, such as partial visibility, occlusion, and low-overlap conditions that require spatial reasoning from fragmented visual cues, remain under-explored. To address these limitations, we propose a scalable multi-view data generation and annotation pipeline that constructs realistic spatial reasoning QAs, resulting in SpatialMosaic, a comprehensive instruction-tuning dataset featuring 2M QA pairs. We further introduce SpatialMosaic-Bench, a challenging benchmark for evaluating multi-view spatial reasoning under realistic and challenging scenarios, consisting of 1M QA pairs across 6 tasks. In addition, we present SpatialMosaicVLM, a hybrid framework that integrates 3D reconstruction models as geometry encoders within VLMs for robust spatial reasoning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed dataset and VQA tasks effectively enhance spatial reasoning under challenging multi-view conditions, validating the effectiveness of our data generation pipeline in constructing realistic and diverse QA pairs. Code and dataset will be available soon.
BUFFER-X: Towards Zero-Shot Point Cloud Registration in Diverse Scenes
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning-based point cloud registration have improved generalization, yet most methods still require retraining or manual parameter tuning for each new environment. In this paper, we identify three key factors limiting generalization: (a) reliance on environment-specific voxel size and search radius, (b) poor out-of-domain robustness of learning-based keypoint detectors, and (c) raw coordinate usage, which exacerbates scale discrepancies. To address these issues, we present a zero-shot registration pipeline called BUFFER-X by (a) adaptively determining voxel size/search radii, (b) using farthest point sampling to bypass learned detectors, and (c) leveraging patch-wise scale normalization for consistent coordinate bounds. In particular, we present a multi-scale patch-based descriptor generation and a hierarchical inlier search across scales to improve robustness in diverse scenes. We also propose a novel generalizability benchmark using 11 datasets that cover various indoor/outdoor scenarios and sensor modalities, demonstrating that BUFFER-X achieves substantial generalization without prior information or manual parameter tuning for the test datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/MIT-SPARK/BUFFER-X.
3D Geometric Shape Assembly via Efficient Point Cloud Matching
Jul 15, 2024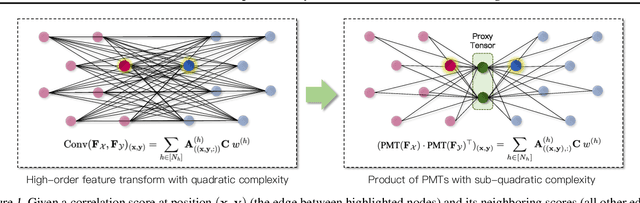
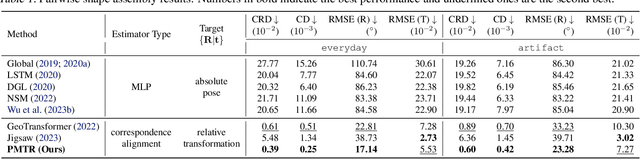
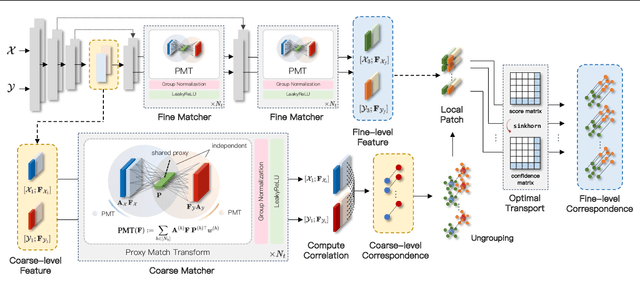
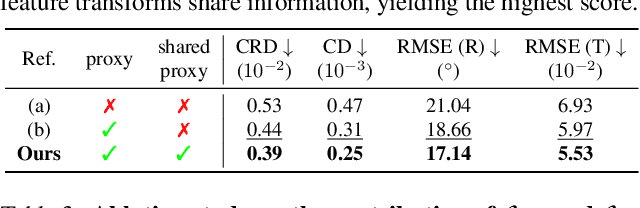
Abstract:Learning to assemble geometric shapes into a larger target structure is a pivotal task in various practical applications. In this work, we tackle this problem by establishing local correspondences between point clouds of part shapes in both coarse- and fine-levels. To this end, we introduce Proxy Match Transform (PMT), an approximate high-order feature transform layer that enables reliable matching between mating surfaces of parts while incurring low costs in memory and computation. Building upon PMT, we introduce a new framework, dubbed Proxy Match TransformeR (PMTR), for the geometric assembly task. We evaluate the proposed PMTR on the large-scale 3D geometric shape assembly benchmark dataset of Breaking Bad and demonstrate its superior performance and efficiency compared to state-of-the-art methods. Project page: https://nahyuklee.github.io/pmtr.
Learning to Register Unbalanced Point Pairs
Jul 09, 2022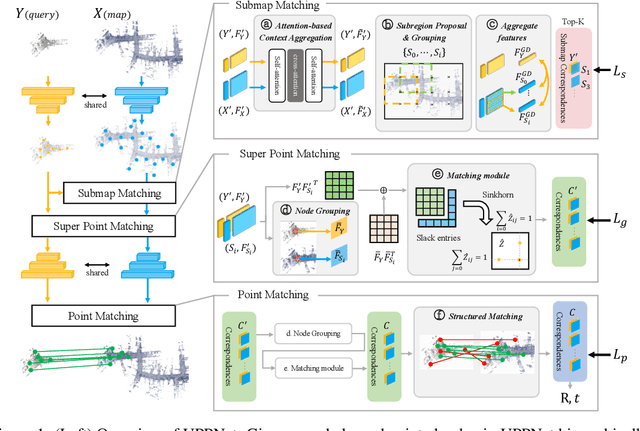
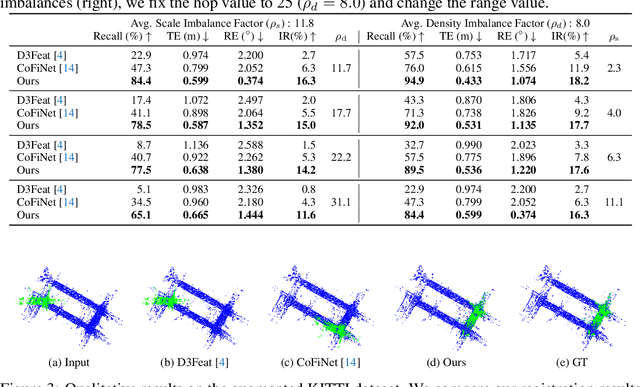

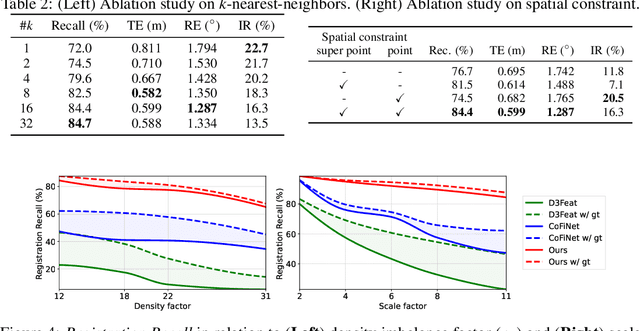
Abstract:Recent 3D registration methods can effectively handle large-scale or partially overlapping point pairs. However, despite its practicality, matching the unbalanced pairs in terms of spatial scale and density has been overlooked. We present a novel 3D registration method, called UPPNet, for the unbalanced point pairs. We propose a hierarchical framework to find inlier correspondences effectively by gradually reducing search space. Our method predicts the subregions of the target points likely to be overlapped with the query points. The following super-point matching module and fine-grained refinement module estimate accurate inlier correspondences between two point clouds. Furthermore, we apply geometric constraints to refine the correspondences that satisfy spatial compatibility. Correspondence prediction is trained end-to-end, and our approach can predict the proper rigid transformation with a single forward pass given unbalanced point cloud pairs. To validate the efficacy of the proposed method, we create a KITTI-UPP dataset by augmenting the KITTI LiDAR dataset. Experiments on this dataset reveal that the proposed approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art pairwise point cloud registration methods by a large margin, resulting in 78% improvement in Registration Recall when the target point cloud is about 10$\times$ spatially larger and about 10$\times$ times denser than the query point cloud.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge