Kamrun Naher Keya
Bias: Friend or Foe? User Acceptance of Gender Stereotypes in Automated Career Recommendations
Jun 13, 2021



Abstract:Currently, there is a surge of interest in fair Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) research which aims to mitigate discriminatory bias in AI algorithms, e.g. along lines of gender, age, and race. While most research in this domain focuses on developing fair AI algorithms, in this work, we show that a fair AI algorithm on its own may be insufficient to achieve its intended results in the real world. Using career recommendation as a case study, we build a fair AI career recommender by employing gender debiasing machine learning techniques. Our offline evaluation showed that the debiased recommender makes fairer career recommendations without sacrificing its accuracy. Nevertheless, an online user study of more than 200 college students revealed that participants on average prefer the original biased system over the debiased system. Specifically, we found that perceived gender disparity is a determining factor for the acceptance of a recommendation. In other words, our results demonstrate we cannot fully address the gender bias issue in AI recommendations without addressing the gender bias in humans.
Fair Representation Learning for Heterogeneous Information Networks
Apr 18, 2021



Abstract:Recently, much attention has been paid to the societal impact of AI, especially concerns regarding its fairness. A growing body of research has identified unfair AI systems and proposed methods to debias them, yet many challenges remain. Representation learning for Heterogeneous Information Networks (HINs), a fundamental building block used in complex network mining, has socially consequential applications such as automated career counseling, but there have been few attempts to ensure that it will not encode or amplify harmful biases, e.g. sexism in the job market. To address this gap, in this paper we propose a comprehensive set of de-biasing methods for fair HINs representation learning, including sampling-based, projection-based, and graph neural networks (GNNs)-based techniques. We systematically study the behavior of these algorithms, especially their capability in balancing the trade-off between fairness and prediction accuracy. We evaluate the performance of the proposed methods in an automated career counseling application where we mitigate gender bias in career recommendation. Based on the evaluation results on two datasets, we identify the most effective fair HINs representation learning techniques under different conditions.
Equitable Allocation of Healthcare Resources with Fair Cox Models
Oct 14, 2020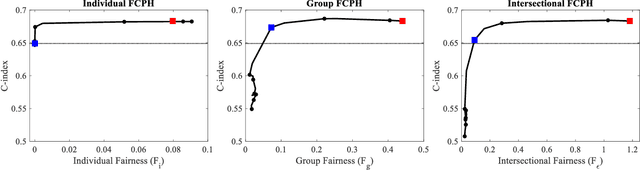

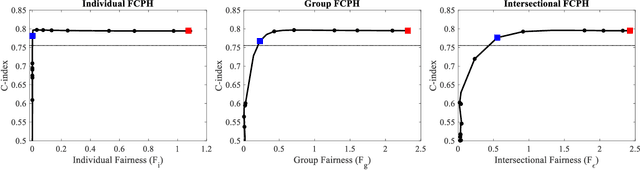
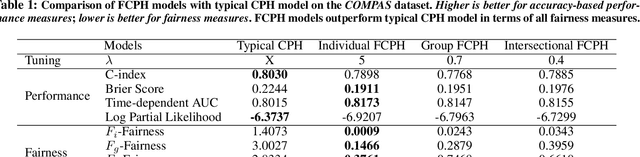
Abstract:Healthcare programs such as Medicaid provide crucial services to vulnerable populations, but due to limited resources, many of the individuals who need these services the most languish on waiting lists. Survival models, e.g. the Cox proportional hazards model, can potentially improve this situation by predicting individuals' levels of need, which can then be used to prioritize the waiting lists. Providing care to those in need can prevent institutionalization for those individuals, which both improves quality of life and reduces overall costs. While the benefits of such an approach are clear, care must be taken to ensure that the prioritization process is fair or independent of demographic information-based harmful stereotypes. In this work, we develop multiple fairness definitions for survival models and corresponding fair Cox proportional hazards models to ensure equitable allocation of healthcare resources. We demonstrate the utility of our methods in terms of fairness and predictive accuracy on two publicly available survival datasets.
Neural Fair Collaborative Filtering
Sep 02, 2020



Abstract:A growing proportion of human interactions are digitized on social media platforms and subjected to algorithmic decision-making, and it has become increasingly important to ensure fair treatment from these algorithms. In this work, we investigate gender bias in collaborative-filtering recommender systems trained on social media data. We develop neural fair collaborative filtering (NFCF), a practical framework for mitigating gender bias in recommending sensitive items (e.g. jobs, academic concentrations, or courses of study) using a pre-training and fine-tuning approach to neural collaborative filtering, augmented with bias correction techniques. We show the utility of our methods for gender de-biased career and college major recommendations on the MovieLens dataset and a Facebook dataset, respectively, and achieve better performance and fairer behavior than several state-of-the-art models.
Neural Embedding Allocation: Distributed Representations of Topic Models
Sep 10, 2019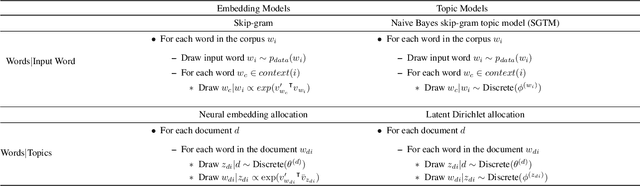
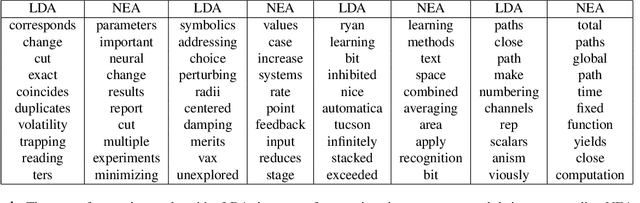
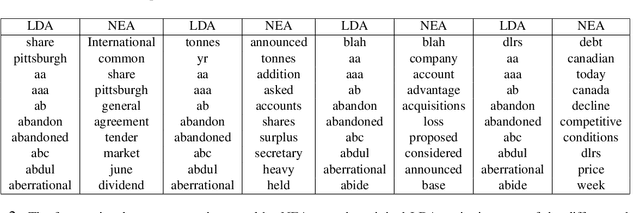
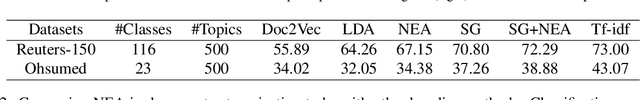
Abstract:Word embedding models such as the skip-gram learn vector representations of words' semantic relationships, and document embedding models learn similar representations for documents. On the other hand, topic models provide latent representations of the documents' topical themes. To get the benefits of these representations simultaneously, we propose a unifying algorithm, called neural embedding allocation (NEA), which deconstructs topic models into interpretable vector-space embeddings of words, topics, documents, authors, and so on, by learning neural embeddings to mimic the topic models. We showcase NEA's effectiveness and generality on LDA, author-topic models and the recently proposed mixed membership skip gram topic model and achieve better performance with the embeddings compared to several state-of-the-art models. Furthermore, we demonstrate that using NEA to smooth out the topics improves coherence scores over the original topic models when the number of topics is large.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge