Kallol Krishna Karmakar
The WMDP Benchmark: Measuring and Reducing Malicious Use With Unlearning
Mar 06, 2024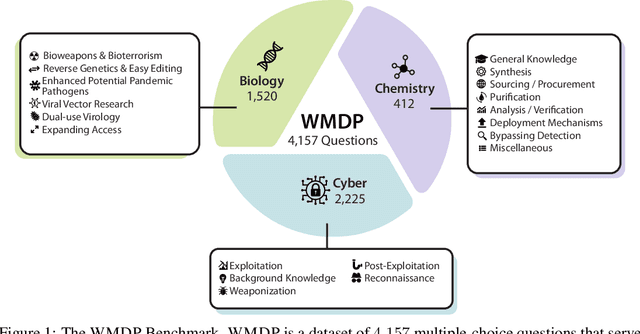
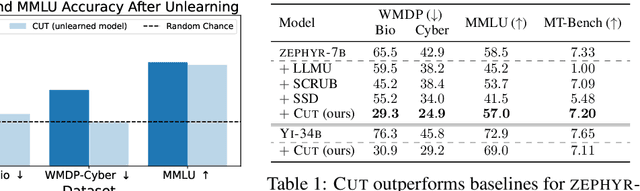
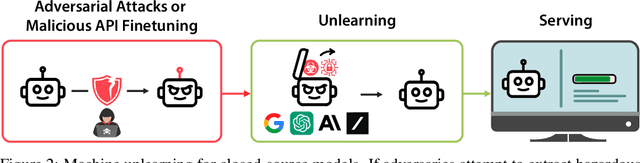
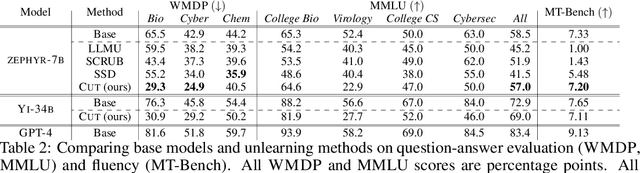
Abstract:The White House Executive Order on Artificial Intelligence highlights the risks of large language models (LLMs) empowering malicious actors in developing biological, cyber, and chemical weapons. To measure these risks of malicious use, government institutions and major AI labs are developing evaluations for hazardous capabilities in LLMs. However, current evaluations are private, preventing further research into mitigating risk. Furthermore, they focus on only a few, highly specific pathways for malicious use. To fill these gaps, we publicly release the Weapons of Mass Destruction Proxy (WMDP) benchmark, a dataset of 4,157 multiple-choice questions that serve as a proxy measurement of hazardous knowledge in biosecurity, cybersecurity, and chemical security. WMDP was developed by a consortium of academics and technical consultants, and was stringently filtered to eliminate sensitive information prior to public release. WMDP serves two roles: first, as an evaluation for hazardous knowledge in LLMs, and second, as a benchmark for unlearning methods to remove such hazardous knowledge. To guide progress on unlearning, we develop CUT, a state-of-the-art unlearning method based on controlling model representations. CUT reduces model performance on WMDP while maintaining general capabilities in areas such as biology and computer science, suggesting that unlearning may be a concrete path towards reducing malicious use from LLMs. We release our benchmark and code publicly at https://wmdp.ai
FedDICE: A ransomware spread detection in a distributed integrated clinical environment using federated learning and SDN based mitigation
Jun 09, 2021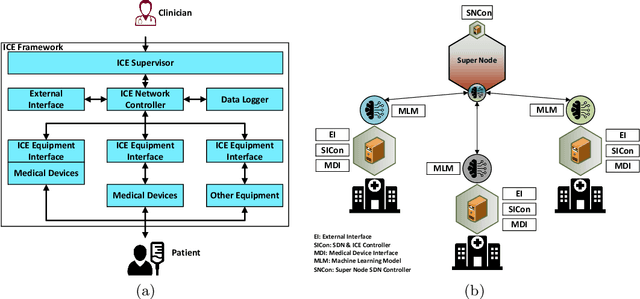
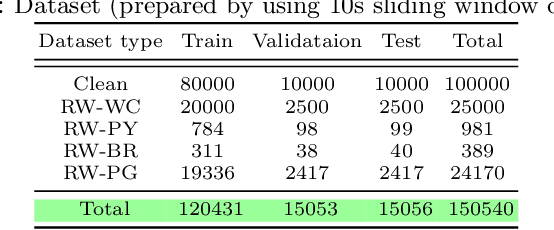
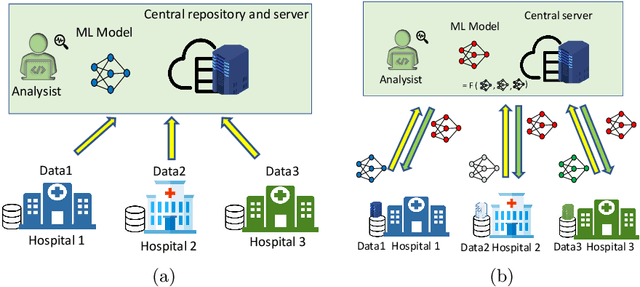
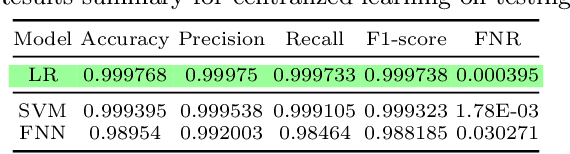
Abstract:An integrated clinical environment (ICE) enables the connection and coordination of the internet of medical things around the care of patients in hospitals. However, ransomware attacks and their spread on hospital infrastructures, including ICE, are rising. Often the adversaries are targeting multiple hospitals with the same ransomware attacks. These attacks are detected by using machine learning algorithms. But the challenge is devising the anti-ransomware learning mechanisms and services under the following conditions: (1) provide immunity to other hospitals if one of them got the attack, (2) hospitals are usually distributed over geographical locations, and (3) direct data sharing is avoided due to privacy concerns. In this regard, this paper presents a federated distributed integrated clinical environment, aka. FedDICE. FedDICE integrates federated learning (FL), which is privacy-preserving learning, to SDN-oriented security architecture to enable collaborative learning, detection, and mitigation of ransomware attacks. We demonstrate the importance of FedDICE in a collaborative environment with up to four hospitals and four popular ransomware families, namely WannaCry, Petya, BadRabbit, and PowerGhost. Our results find that in both IID and non-IID data setups, FedDICE achieves the centralized baseline performance that needs direct data sharing for detection. However, as a trade-off to data privacy, FedDICE observes overhead in the anti-ransomware model training, e.g., 28x for the logistic regression model. Besides, FedDICE utilizes SDN's dynamic network programmability feature to remove the infected devices in ICE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge