Kai Pak
Enabling Novel Mission Operations and Interactions with ROSA: The Robot Operating System Agent
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:The advancement of robotic systems has revolutionized numerous industries, yet their operation often demands specialized technical knowledge, limiting accessibility for non-expert users. This paper introduces ROSA (Robot Operating System Agent), an AI-powered agent that bridges the gap between the Robot Operating System (ROS) and natural language interfaces. By leveraging state-of-the-art language models and integrating open-source frameworks, ROSA enables operators to interact with robots using natural language, translating commands into actions and interfacing with ROS through well-defined tools. ROSA's design is modular and extensible, offering seamless integration with both ROS1 and ROS2, along with safety mechanisms like parameter validation and constraint enforcement to ensure secure, reliable operations. While ROSA is originally designed for ROS, it can be extended to work with other robotics middle-wares to maximize compatibility across missions. ROSA enhances human-robot interaction by democratizing access to complex robotic systems, empowering users of all expertise levels with multi-modal capabilities such as speech integration and visual perception. Ethical considerations are thoroughly addressed, guided by foundational principles like Asimov's Three Laws of Robotics, ensuring that AI integration promotes safety, transparency, privacy, and accountability. By making robotic technology more user-friendly and accessible, ROSA not only improves operational efficiency but also sets a new standard for responsible AI use in robotics and potentially future mission operations. This paper introduces ROSA's architecture and showcases initial mock-up operations in JPL's Mars Yard, a laboratory, and a simulation using three different robots. The core ROSA library is available as open-source.
Improving Contrastive Learning on Visually Homogeneous Mars Rover Images
Oct 17, 2022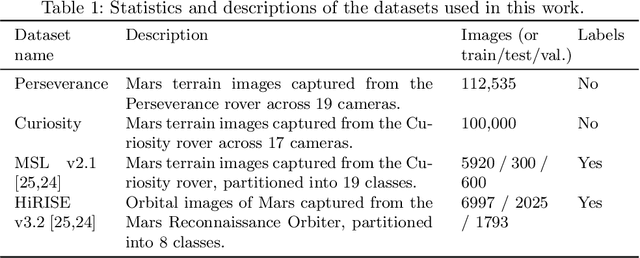

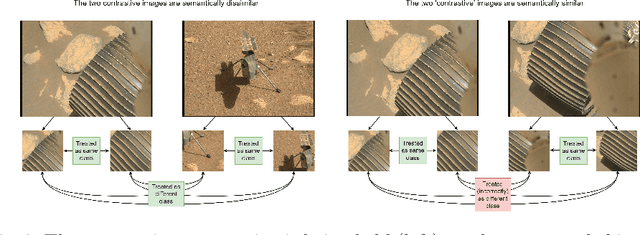

Abstract:Contrastive learning has recently demonstrated superior performance to supervised learning, despite requiring no training labels. We explore how contrastive learning can be applied to hundreds of thousands of unlabeled Mars terrain images, collected from the Mars rovers Curiosity and Perseverance, and from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Such methods are appealing since the vast majority of Mars images are unlabeled as manual annotation is labor intensive and requires extensive domain knowledge. Contrastive learning, however, assumes that any given pair of distinct images contain distinct semantic content. This is an issue for Mars image datasets, as any two pairs of Mars images are far more likely to be semantically similar due to the lack of visual diversity on the planet's surface. Making the assumption that pairs of images will be in visual contrast - when they are in fact not - results in pairs that are falsely considered as negatives, impacting training performance. In this study, we propose two approaches to resolve this: 1) an unsupervised deep clustering step on the Mars datasets, which identifies clusters of images containing similar semantic content and corrects false negative errors during training, and 2) a simple approach which mixes data from different domains to increase visual diversity of the total training dataset. Both cases reduce the rate of false negative pairs, thus minimizing the rate in which the model is incorrectly penalized during contrastive training. These modified approaches remain fully unsupervised end-to-end. To evaluate their performance, we add a single linear layer trained to generate class predictions based on these contrastively-learned features and demonstrate increased performance compared to supervised models; observing an improvement in classification accuracy of 3.06% using only 10% of the labeled data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge