Justus C. Will
Progressive Compression with Universally Quantized Diffusion Models
Dec 14, 2024Abstract:Diffusion probabilistic models have achieved mainstream success in many generative modeling tasks, from image generation to inverse problem solving. A distinct feature of these models is that they correspond to deep hierarchical latent variable models optimizing a variational evidence lower bound (ELBO) on the data likelihood. Drawing on a basic connection between likelihood modeling and compression, we explore the potential of diffusion models for progressive coding, resulting in a sequence of bits that can be incrementally transmitted and decoded with progressively improving reconstruction quality. Unlike prior work based on Gaussian diffusion or conditional diffusion models, we propose a new form of diffusion model with uniform noise in the forward process, whose negative ELBO corresponds to the end-to-end compression cost using universal quantization. We obtain promising first results on image compression, achieving competitive rate-distortion and rate-realism results on a wide range of bit-rates with a single model, bringing neural codecs a step closer to practical deployment.
Understanding and Visualizing Droplet Distributions in Simulations of Shallow Clouds
Oct 31, 2023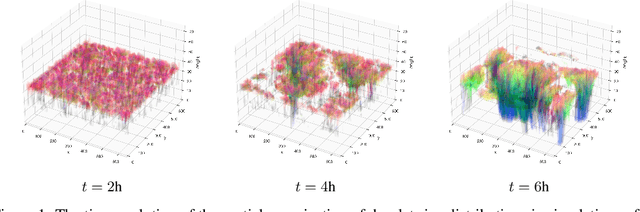
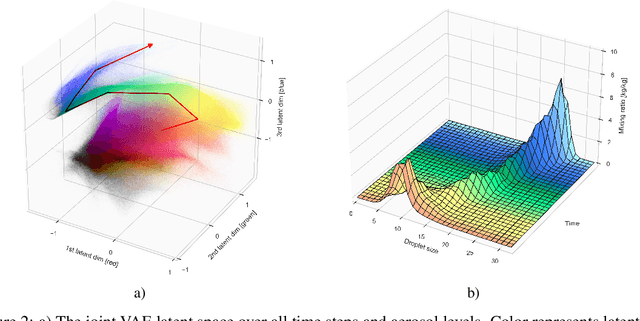
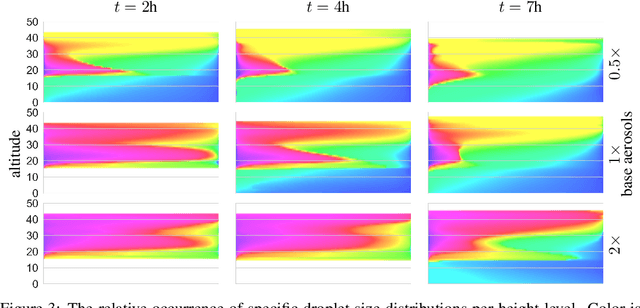
Abstract:Thorough analysis of local droplet-level interactions is crucial to better understand the microphysical processes in clouds and their effect on the global climate. High-accuracy simulations of relevant droplet size distributions from Large Eddy Simulations (LES) of bin microphysics challenge current analysis techniques due to their high dimensionality involving three spatial dimensions, time, and a continuous range of droplet sizes. Utilizing the compact latent representations from Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), we produce novel and intuitive visualizations for the organization of droplet sizes and their evolution over time beyond what is possible with clustering techniques. This greatly improves interpretation and allows us to examine aerosol-cloud interactions by contrasting simulations with different aerosol concentrations. We find that the evolution of the droplet spectrum is similar across aerosol levels but occurs at different paces. This similarity suggests that precipitation initiation processes are alike despite variations in onset times.
ClimSim: An open large-scale dataset for training high-resolution physics emulators in hybrid multi-scale climate simulators
Jun 16, 2023Abstract:Modern climate projections lack adequate spatial and temporal resolution due to computational constraints. A consequence is inaccurate and imprecise prediction of critical processes such as storms. Hybrid methods that combine physics with machine learning (ML) have introduced a new generation of higher fidelity climate simulators that can sidestep Moore's Law by outsourcing compute-hungry, short, high-resolution simulations to ML emulators. However, this hybrid ML-physics simulation approach requires domain-specific treatment and has been inaccessible to ML experts because of lack of training data and relevant, easy-to-use workflows. We present ClimSim, the largest-ever dataset designed for hybrid ML-physics research. It comprises multi-scale climate simulations, developed by a consortium of climate scientists and ML researchers. It consists of 5.7 billion pairs of multivariate input and output vectors that isolate the influence of locally-nested, high-resolution, high-fidelity physics on a host climate simulator's macro-scale physical state. The dataset is global in coverage, spans multiple years at high sampling frequency, and is designed such that resulting emulators are compatible with downstream coupling into operational climate simulators. We implement a range of deterministic and stochastic regression baselines to highlight the ML challenges and their scoring. The data (https://huggingface.co/datasets/LEAP/ClimSim_high-res) and code (https://leap-stc.github.io/ClimSim) are released openly to support the development of hybrid ML-physics and high-fidelity climate simulations for the benefit of science and society.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge