Junxian Liu
ST-BCP: Tightening Coverage Bound for Backward Conformal Prediction via Non-Conformity Score Transformation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Conformal Prediction (CP) provides a statistical framework for uncertainty quantification that constructs prediction sets with coverage guarantees. While CP yields uncontrolled prediction set sizes, Backward Conformal Prediction (BCP) inverts this paradigm by enforcing a predefined upper bound on set size and estimating the resulting coverage guarantee. However, the looseness induced by Markov's inequality within the BCP framework causes a significant gap between the estimated coverage bound and the empirical coverage. In this work, we introduce ST-BCP, a novel method that introduces a data-dependent transformation of nonconformity scores to narrow the coverage gap. In particular, we develop a computable transformation and prove that it outperforms the baseline identity transformation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, reducing the average coverage gap from 4.20\% to 1.12\% on common benchmarks.
GMC-IQA: Exploiting Global-correlation and Mean-opinion Consistency for No-reference Image Quality Assessment
Jan 19, 2024
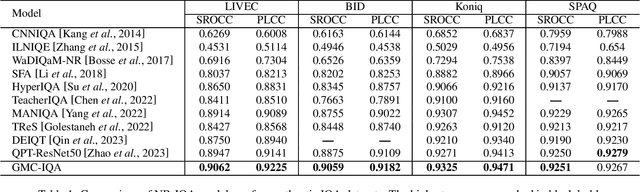
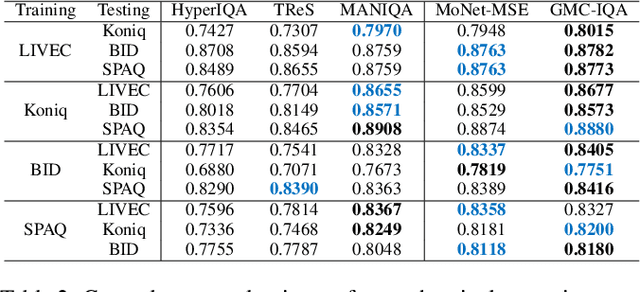
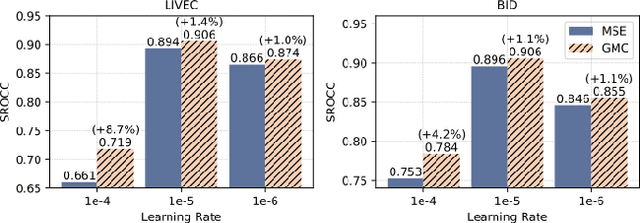
Abstract:Due to the subjective nature of image quality assessment (IQA), assessing which image has better quality among a sequence of images is more reliable than assigning an absolute mean opinion score for an image. Thus, IQA models are evaluated by global correlation consistency (GCC) metrics like PLCC and SROCC, rather than mean opinion consistency (MOC) metrics like MAE and MSE. However, most existing methods adopt MOC metrics to define their loss functions, due to the infeasible computation of GCC metrics during training. In this work, we construct a novel loss function and network to exploit Global-correlation and Mean-opinion Consistency, forming a GMC-IQA framework. Specifically, we propose a novel GCC loss by defining a pairwise preference-based rank estimation to solve the non-differentiable problem of SROCC and introducing a queue mechanism to reserve previous data to approximate the global results of the whole data. Moreover, we propose a mean-opinion network, which integrates diverse opinion features to alleviate the randomness of weight learning and enhance the model robustness. Experiments indicate that our method outperforms SOTA methods on multiple authentic datasets with higher accuracy and generalization. We also adapt the proposed loss to various networks, which brings better performance and more stable training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge