Junil Choi
Hybrid Federated Learning for Noise-Robust Training
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Federated learning (FL) and federated distillation (FD) are distributed learning paradigms that train UE models with enhanced privacy, each offering different trade-offs between noise robustness and learning speed. To mitigate their respective weaknesses, we propose a hybrid federated learning (HFL) framework in which each user equipment (UE) transmits either gradients or logits, and the base station (BS) selects the per-round weights of FL and FD updates. We derive convergence of HFL framework and introduce two methods to exploit degrees of freedom (DoF) in HFL, which are (i) adaptive UE clustering via Jenks optimization and (ii) adaptive weight selection via a damped Newton method. Numerical results show that HFL achieves superior test accuracy at low SNR when both DoF are exploited.
Evolution of UE in Massive MIMO Systems for 6G: From Passive to Active
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:As wireless networks continue to evolve, stringent latency and reliability requirements and highly dynamic channels expose fundamental limitations of gNB-centric massive multiple-input multiple-output (mMIMO) architectures, motivating a rethinking of the user equipment (UE) role. In response, the UE is transitioning from a passive transceiver into an active entity that directly contributes to system-level performance. In this context, this article examines the evolving role of the UE in mMIMO systems during the transition from fifth-generation (5G) to sixth-generation (6G), bridging third generation partnership project (3GPP) standardization, device implementation, and architectural innovation. Through a chronological review of 3GPP Releases 15 to 19, we highlight the progression of UE functionalities from basic channel state information (CSI) reporting to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)-based CSI enhancement and UE-initiated beam management. We further examine key implementation challenges, including multi-panel UE (MPUE) architectures, on-device intelligent processing, and energy-efficient operation, and then discuss corresponding architectural innovations under practical constraints. Using digital-twin-based evaluations, we validate the impact of emerging UE-centric functionalities, illustrating that UE-initiated beam reporting improves throughput in realistic mobility scenarios, while a multi-panel architecture enhances link robustness compared with a single-panel UE.
Robust Transmission Design for Active RIS-Aided Systems
Apr 01, 2025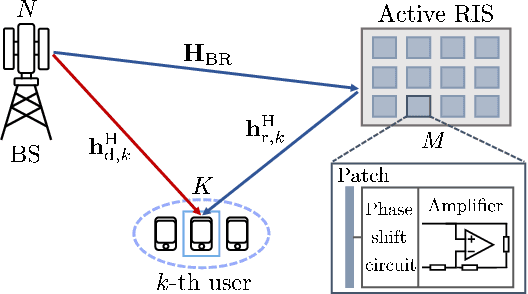
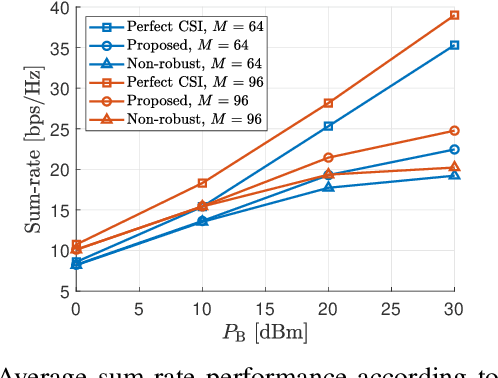
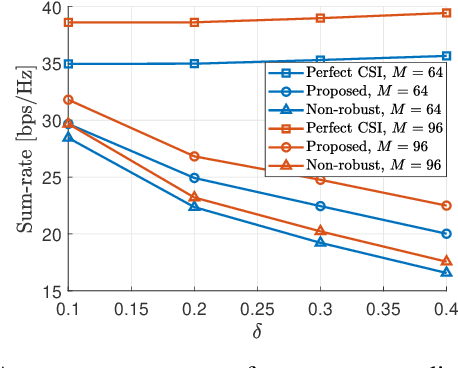
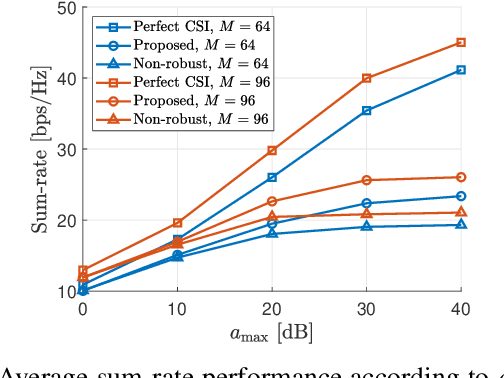
Abstract:Different from conventional passive reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs), incident signals and thermal noise can be amplified at active RISs. By exploiting the amplifying capability of active RISs, noticeable performance improvement can be expected when precise channel state information (CSI) is available. Since obtaining perfect CSI related to an RIS is difficult in practice, a robust transmission design is proposed in this paper to tackle the channel uncertainty issue, which will be more severe for active RIS-aided systems. To account for the worst-case scenario, the minimum achievable rate of each user is derived under a statistical CSI error model. Subsequently, an optimization problem is formulated to maximize the sum of the minimum achievable rate. Since the objective function is non-concave, the formulated problem is transformed into a tractable lower bound maximization problem, which is solved using an alternating optimization method. Numerical results show that the proposed robust design outperforms a baseline scheme that only exploits estimated CSI.
Machine Learning for Future Wireless Communications: Channel Prediction Perspectives
Feb 25, 2025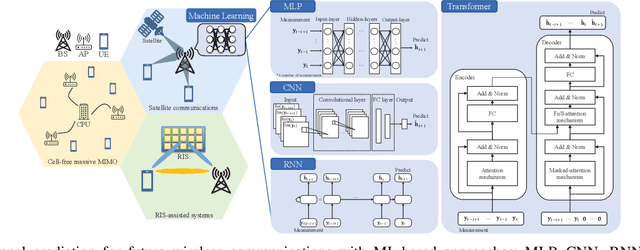
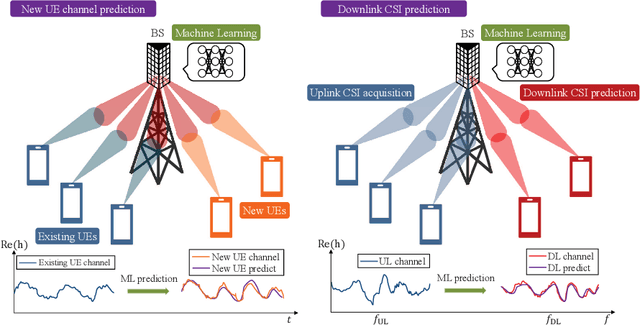
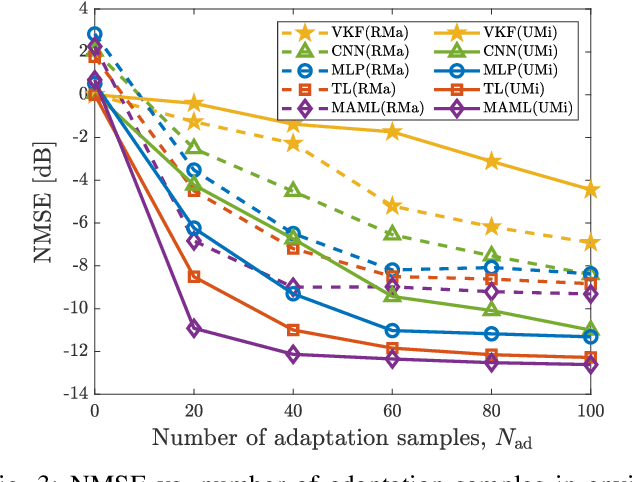
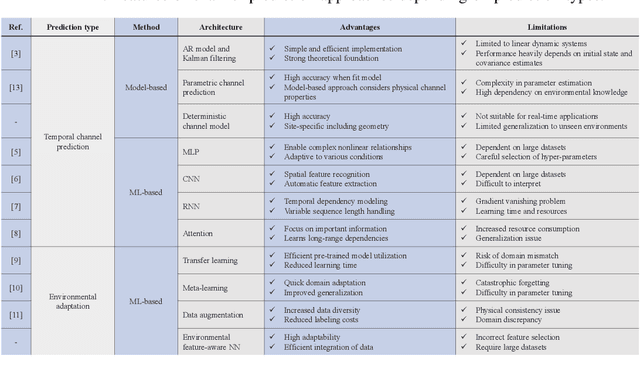
Abstract:Precise channel state knowledge is crucial in future wireless communication systems, which drives the need for accurate channel prediction without additional pilot overhead. While machine-learning (ML) methods for channel prediction show potential, existing approaches have limitations in their capability to adapt to environmental changes due to their extensive training requirements. In this paper, we introduce the channel prediction approaches in terms of the temporal channel prediction and the environmental adaptation. Then, we elaborate on the use of the advanced ML-based channel prediction to resolve the issues in traditional ML methods. The numerical results show that the advanced ML-based channel prediction has comparable accuracy with much less training overhead compared to conventional prediction methods. Also, we examine the training process, dataset characteristics, and the impact of source tasks and pre-trained models on channel prediction approaches. Finally, we discuss open challenges and possible future research directions of ML-based channel prediction.
Meta-Learning-Based People Counting and Localization Models Employing CSI from Commodity WiFi NICs
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we consider people counting and localization systems exploiting channel state information (CSI) measured from commodity WiFi network interface cards (NICs). While CSI has useful information of amplitude and phase to describe signal propagation in a measurement environment of interest, CSI measurement suffers from offsets due to various uncertainties. Moreover, an uncontrollable external environment where other WiFi devices communicate each other induces interfering signals, resulting in erroneous CSI captured at a receiver. In this paper, preprocessing of CSI is first proposed for offset removal, and it guarantees low-latency operation without any filtering process. Afterwards, we design people counting and localization models based on pre-training. To be adaptive to different measurement environments, meta-learning-based people counting and localization models are also proposed. Numerical results show that the proposed meta-learning-based people counting and localization models can achieve high sensing accuracy, compared to other learning schemes that follow simple training and test procedures.
An Experimental Multi-Band Channel Characterization in the Upper Mid-Band
Nov 19, 2024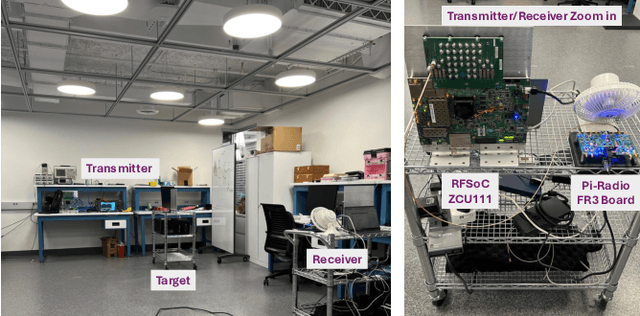
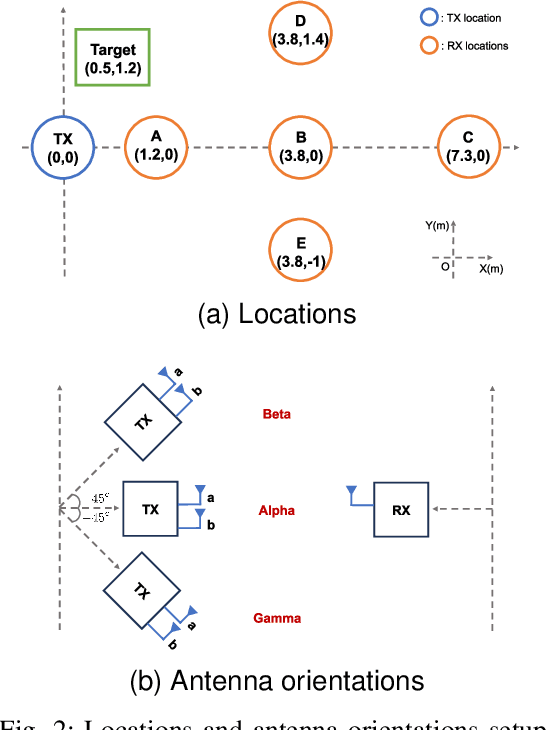
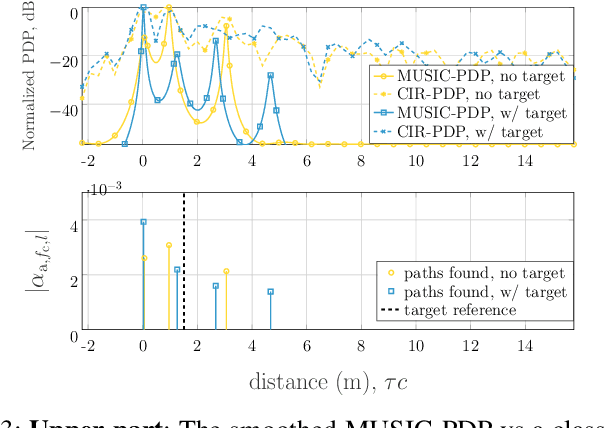
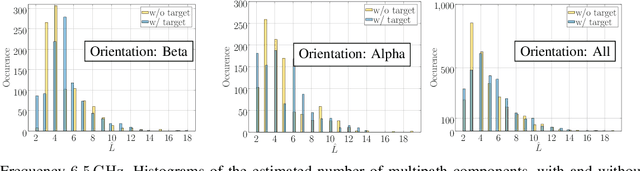
Abstract:The following paper provides a multi-band channel measurement analysis on the frequency range (FR)3. This study focuses on the FR3 low frequencies 6.5 GHz and 8.75 GHz with a setup tailored to the context of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), where the data are collected with and without the presence of a target. A method based on multiple signal classification (MUSIC) is used to refine the delays of the channel impulse response estimates. The results reveal that the channel at the lower frequency 6.5 GHz has additional distinguishable multipath components in the presence of the target, while the one associated with the higher frequency 8.75 GHz has more blockage. The set of results reported in this paper serves as a benchmark for future multi-band studies in the FR3 spectrum.
Channel-Coded Precoding for Multi-User MISO Systems
Oct 30, 2024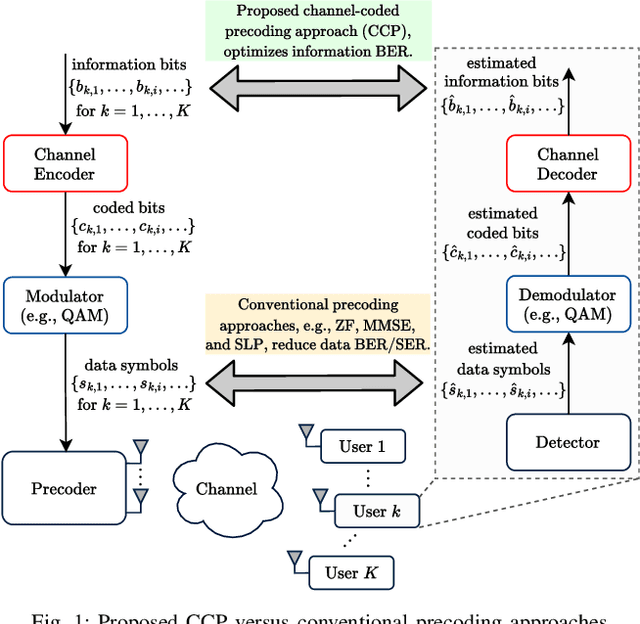
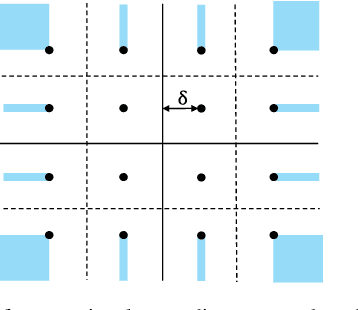
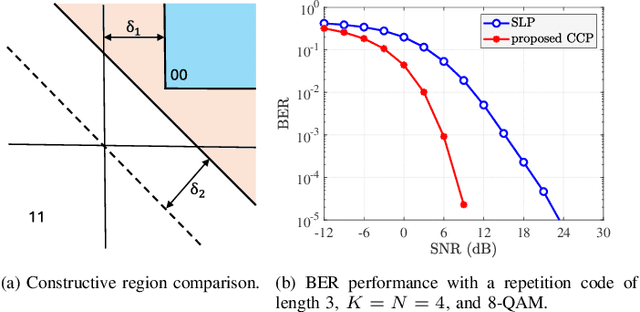
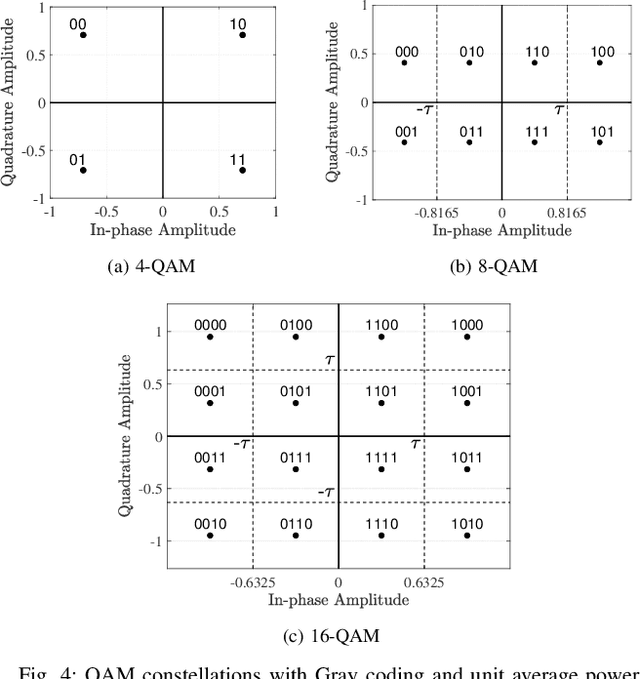
Abstract:Precoding is a critical and long-standing technique in multi-user communication systems. However, the majority of existing precoding methods do not consider channel coding in their designs. In this paper, we consider the precoding problem in multi-user multiple-input single-output (MISO) systems, incorporating channel coding into the design. By leveraging the error-correcting capability of channel codes we increase the degrees of freedom in the transmit signal design, thereby enhancing the overall system performance. We first propose a novel data-dependent precoding framework for coded MISO systems, referred to as channel-coded precoding (CCP), which maximizes the probability that information bits can be correctly recovered by the channel decoder. This proposed CCP framework allows the transmit signals to produce data symbol errors at the users' receivers, as long as the overall information BER performance can be improved. We develop the CCP framework for both one-bit and multi-bit error-correcting capacity and devise a projected gradient-based approach to solve the design problem. We also develop a robust CCP framework for the case where knowledge of perfect channel state information (CSI) is unavailable at the transmitter, taking into account the effect of both noise and channel estimation errors. Finally, we conduct numerous simulations to verify the effectiveness of the proposed CCP and its superiority compared to existing precoding methods, and we identify situations where the proposed CCP yields the most significant gains.
RIS-Enabled Cellular Systems Operated by Different Service Providers
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:In realistic cellular communication systems, multiple service providers will operate within different frequency ranges. Each serving cell, which is managed by a distinct service provider, is designed individually due to the orthogonal frequencies. However, when a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is deployed for a certain cell, the RIS still incurs reflective channels for the overall system since the RIS reflects signals across all frequency ranges. This may cause severe undesired performance degradation for the other cells unless the reflection coefficients are properly designed. To tackle this issue, by utilizing the Riemannian manifold optimization method, an RIS reflection coefficients design is proposed in this paper to maximize the performance improvements of the cell that deploys the RIS while minimizing the undesired performance degradation for the other cells simultaneously. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed design can effectively balance the two objectives for practical scenarios.
Machine Learning-based Channel Prediction in Wideband Massive MIMO Systems with Small Overhead for Online Training
Aug 22, 2024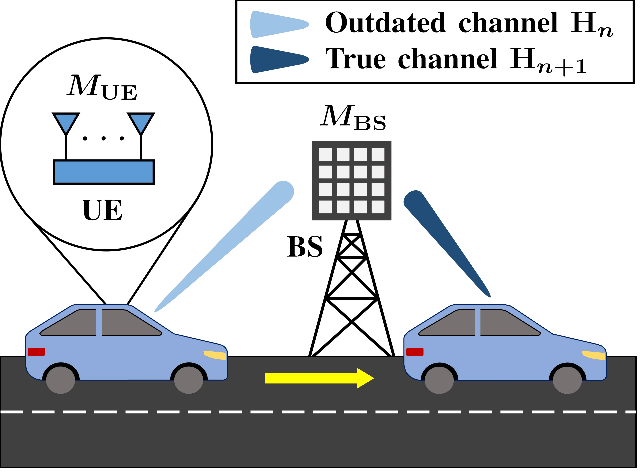

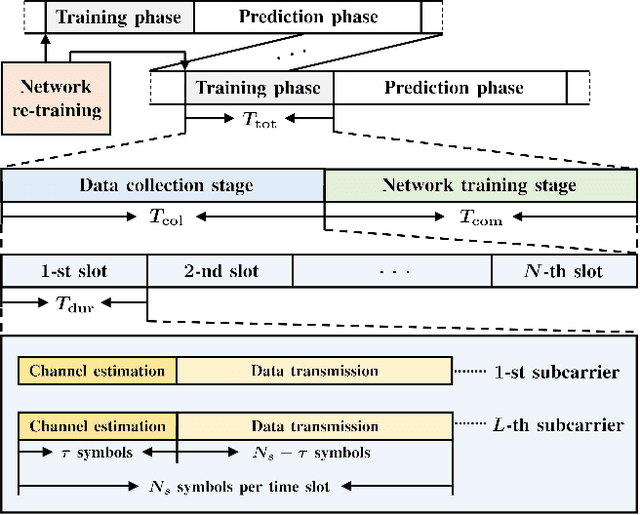

Abstract:Channel prediction compensates for outdated channel state information in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems. Machine learning (ML) techniques have recently been implemented to design channel predictors by leveraging the temporal correlation of wireless channels. However, most ML-based channel prediction techniques have only considered offline training when generating channel predictors, which can result in poor performance when encountering channel environments different from the ones they were trained on. To ensure prediction performance in varying channel conditions, we propose an online re-training framework that trains the channel predictor from scratch to effectively capture and respond to changes in the wireless environment. The training time includes data collection time and neural network training time, and should be minimized for practical channel predictors. To reduce the training time, especially data collection time, we propose a novel ML-based channel prediction technique called aggregated learning (AL) approach for wideband massive MIMO systems. In the proposed AL approach, the training data can be split and aggregated either in an array domain or frequency domain, which are the channel domains of MIMO-OFDM systems. This processing can significantly reduce the time for data collection. Our numerical results show that the AL approach even improves channel prediction performance in various scenarios with small training time overhead.
Stochastic Geometry Analysis of RIS-Assisted Cellular Networks with Reflective Intelligent Surfaces on Roads
Aug 09, 2024Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) provide alternative routes for reflected signals to network users, offering numerous applications. This paper explores an innovative approach of strategically deploying RISs along road areas to leverage various propagation and blockage conditions present in cellular networks with roads. To address the local network geometries shown by such networks, we use a stochastic geometry framework, specifically the Cox point processes, to model the locations of RISs and vehicle users. Then, we define the coverage probability as the chance that either a base station or an RIS is in line of sight (LOS) of the typical user and that the LOS signal has a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) greater than a threshold. We derive the coverage probability as a function of key parameters such as RIS density and path loss exponent. We observe that the network geometry highly affects the coverage and that the proposed RIS deployment effectively leverages the underlying difference of attenuation and blockage, significantly increasing the coverage of vehicle users in the network. With experimental results addressing the impact of key variables to network performance, this work serves as a versatile tool for designing, analyzing, and optimizing RIS-assisted cellular networks with many vehicles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge