Jung Woo Kim
Encryption-Friendly LLM Architecture
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) offer personalized responses based on user interactions, but this use case raises serious privacy concerns. Homomorphic encryption (HE) is a cryptographic protocol supporting arithmetic computations in encrypted states and provides a potential solution for privacy-preserving machine learning (PPML). However, the computational intensity of transformers poses challenges for applying HE to LLMs. In this work, we propose a modified HE-friendly transformer architecture with an emphasis on inference following personalized (private) fine-tuning. Utilizing LoRA fine-tuning and Gaussian kernels, we achieve significant computational speedups -- 6.94x for fine-tuning and 2.3x for inference -- while maintaining performance comparable to plaintext models. Our findings provide a viable proof of concept for offering privacy-preserving LLM services in areas where data protection is crucial.
HETAL: Efficient Privacy-preserving Transfer Learning with Homomorphic Encryption
Mar 21, 2024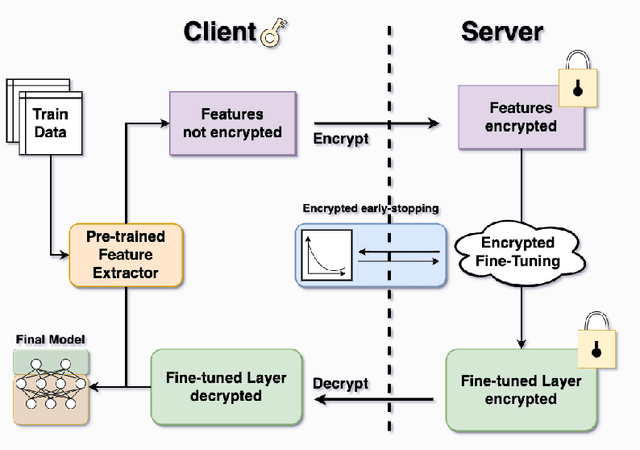
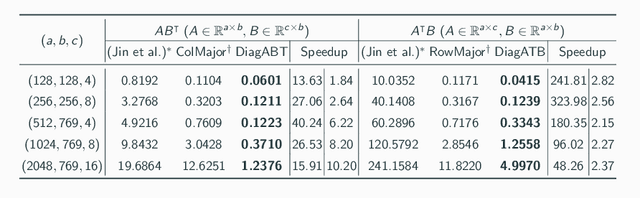
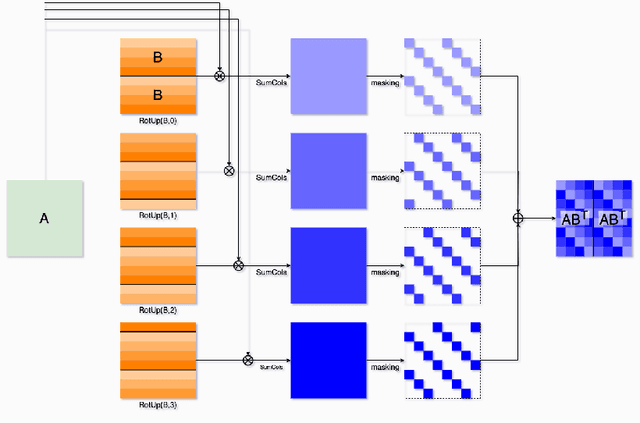
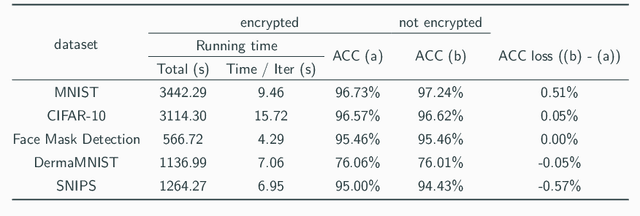
Abstract:Transfer learning is a de facto standard method for efficiently training machine learning models for data-scarce problems by adding and fine-tuning new classification layers to a model pre-trained on large datasets. Although numerous previous studies proposed to use homomorphic encryption to resolve the data privacy issue in transfer learning in the machine learning as a service setting, most of them only focused on encrypted inference. In this study, we present HETAL, an efficient Homomorphic Encryption based Transfer Learning algorithm, that protects the client's privacy in training tasks by encrypting the client data using the CKKS homomorphic encryption scheme. HETAL is the first practical scheme that strictly provides encrypted training, adopting validation-based early stopping and achieving the accuracy of nonencrypted training. We propose an efficient encrypted matrix multiplication algorithm, which is 1.8 to 323 times faster than prior methods, and a highly precise softmax approximation algorithm with increased coverage. The experimental results for five well-known benchmark datasets show total training times of 567-3442 seconds, which is less than an hour.
HAE-RAE Bench: Evaluation of Korean Knowledge in Language Models
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) pretrained on massive corpora exhibit remarkable capabilities across a wide range of tasks, however, the attention given to non-English languages has been limited in this field of research. To address this gap and assess the proficiency of language models in the Korean language and culture, we present HAE-RAE Bench, covering 6 tasks including vocabulary, history, and general knowledge. Our evaluation of language models on this benchmark highlights the potential advantages of employing Large Language-Specific Models(LLSMs) over a comprehensive, universal model like GPT-3.5. Remarkably, our study reveals that models approximately 13 times smaller than GPT-3.5 can exhibit similar performance levels in terms of language-specific knowledge retrieval. This observation underscores the importance of homogeneous corpora for training professional-level language-specific models. On the contrary, we also observe a perplexing performance dip in these smaller LMs when they are tasked to generate structured answers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge