Junchen Lu
EmotionRankCLAP: Bridging Natural Language Speaking Styles and Ordinal Speech Emotion via Rank-N-Contrast
May 29, 2025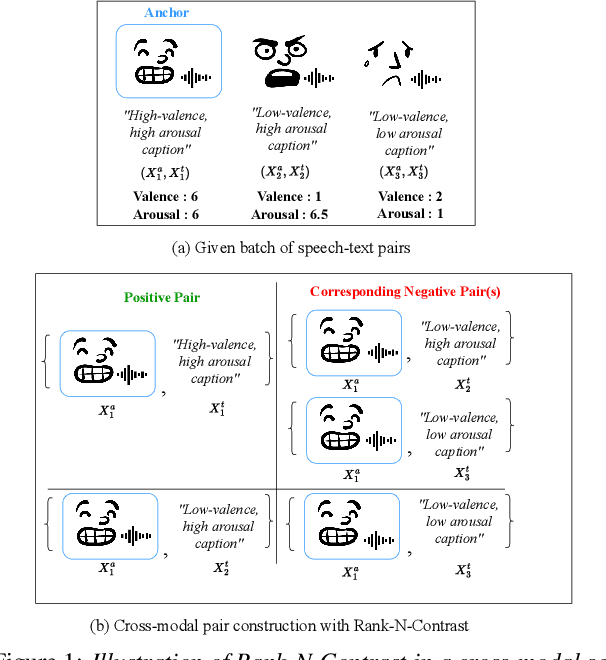
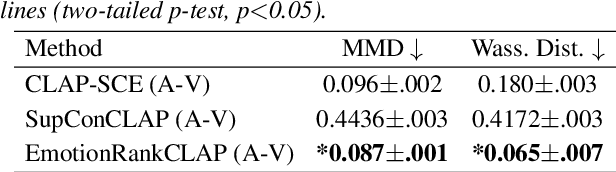

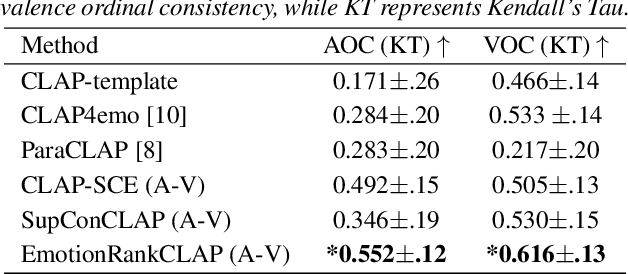
Abstract:Current emotion-based contrastive language-audio pretraining (CLAP) methods typically learn by na\"ively aligning audio samples with corresponding text prompts. Consequently, this approach fails to capture the ordinal nature of emotions, hindering inter-emotion understanding and often resulting in a wide modality gap between the audio and text embeddings due to insufficient alignment. To handle these drawbacks, we introduce EmotionRankCLAP, a supervised contrastive learning approach that uses dimensional attributes of emotional speech and natural language prompts to jointly capture fine-grained emotion variations and improve cross-modal alignment. Our approach utilizes a Rank-N-Contrast objective to learn ordered relationships by contrasting samples based on their rankings in the valence-arousal space. EmotionRankCLAP outperforms existing emotion-CLAP methods in modeling emotion ordinality across modalities, measured via a cross-modal retrieval task.
SelectTTS: Synthesizing Anyone's Voice via Discrete Unit-Based Frame Selection
Aug 30, 2024



Abstract:Synthesizing the voices of unseen speakers is a persisting challenge in multi-speaker text-to-speech (TTS). Most multi-speaker TTS models rely on modeling speaker characteristics through speaker conditioning during training. Modeling unseen speaker attributes through this approach has necessitated an increase in model complexity, which makes it challenging to reproduce results and improve upon them. We design a simple alternative to this. We propose SelectTTS, a novel method to select the appropriate frames from the target speaker and decode using frame-level self-supervised learning (SSL) features. We show that this approach can effectively capture speaker characteristics for unseen speakers, and achieves comparable results to other multi-speaker TTS frameworks in both objective and subjective metrics. With SelectTTS, we show that frame selection from the target speaker's speech is a direct way to achieve generalization in unseen speakers with low model complexity. We achieve better speaker similarity performance than SOTA baselines XTTS-v2 and VALL-E with over an 8x reduction in model parameters and a 270x reduction in training data
Style Mixture of Experts for Expressive Text-To-Speech Synthesis
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in style transfer text-to-speech (TTS) have improved the expressiveness of synthesized speech. Despite these advancements, encoding stylistic information from diverse and unseen reference speech remains challenging. This paper introduces StyleMoE, an approach that divides the embedding space, modeled by the style encoder, into tractable subsets handled by style experts. The proposed method replaces the style encoder in a TTS system with a Mixture of Experts (MoE) layer. By utilizing a gating network to route reference speeches to different style experts, each expert specializes in aspects of the style space during optimization. Our experiments objectively and subjectively demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method in increasing the coverage of the style space for diverse and unseen styles. This approach can enhance the performance of existing state-of-the-art style transfer TTS models, marking the first study of MoE in style transfer TTS to our knowledge.
Converting Anyone's Voice: End-to-End Expressive Voice Conversion with a Conditional Diffusion Model
May 02, 2024



Abstract:Expressive voice conversion (VC) conducts speaker identity conversion for emotional speakers by jointly converting speaker identity and emotional style. Emotional style modeling for arbitrary speakers in expressive VC has not been extensively explored. Previous approaches have relied on vocoders for speech reconstruction, which makes speech quality heavily dependent on the performance of vocoders. A major challenge of expressive VC lies in emotion prosody modeling. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a fully end-to-end expressive VC framework based on a conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM). We utilize speech units derived from self-supervised speech models as content conditioning, along with deep features extracted from speech emotion recognition and speaker verification systems to model emotional style and speaker identity. Objective and subjective evaluations show the effectiveness of our framework. Codes and samples are publicly available.
High-Quality Automatic Voice Over with Accurate Alignment: Supervision through Self-Supervised Discrete Speech Units
Jun 29, 2023



Abstract:The goal of Automatic Voice Over (AVO) is to generate speech in sync with a silent video given its text script. Recent AVO frameworks built upon text-to-speech synthesis (TTS) have shown impressive results. However, the current AVO learning objective of acoustic feature reconstruction brings in indirect supervision for inter-modal alignment learning, thus limiting the synchronization performance and synthetic speech quality. To this end, we propose a novel AVO method leveraging the learning objective of self-supervised discrete speech unit prediction, which not only provides more direct supervision for the alignment learning, but also alleviates the mismatch between the text-video context and acoustic features. Experimental results show that our proposed method achieves remarkable lip-speech synchronization and high speech quality by outperforming baselines in both objective and subjective evaluations. Code and speech samples are publicly available.
VisualTTS: TTS with Accurate Lip-Speech Synchronization for Automatic Voice Over
Oct 09, 2021


Abstract:In this paper, we formulate a novel task to synthesize speech in sync with a silent pre-recorded video, denoted as automatic voice over (AVO). Unlike traditional speech synthesis, AVO seeks to generate not only human-sounding speech, but also perfect lip-speech synchronization. A natural solution to AVO is to condition the speech rendering on the temporal progression of lip sequence in the video. We propose a novel text-to-speech model that is conditioned on visual input, named VisualTTS, for accurate lip-speech synchronization. The proposed VisualTTS adopts two novel mechanisms that are 1) textual-visual attention, and 2) visual fusion strategy during acoustic decoding, which both contribute to forming accurate alignment between the input text content and lip motion in input lip sequence. Experimental results show that VisualTTS achieves accurate lip-speech synchronization and outperforms all baseline systems.
VAW-GAN for Singing Voice Conversion with Non-parallel Training Data
Aug 12, 2020



Abstract:Singing voice conversion aims to convert singer's voice from source to target without changing singing content. Parallel training data is typically required for the training of singing voice conversion system, that is however not practical in real-life applications. Recent encoder-decoder structures, such as variational autoencoding Wasserstein generative adversarial network (VAW-GAN), provide an effective way to learn a mapping through non-parallel training data. In this paper, we propose a singing voice conversion framework that is based on VAW-GAN. We train an encoder to disentangle singer identity and singing prosody (F0 contour) from phonetic content. By conditioning on singer identity and F0, the decoder generates output spectral features with unseen target singer identity, and improves the F0 rendering. Experimental results show that the proposed framework achieves better performance than the baseline frameworks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge