Ismail Rasim Ulgen
Can Emotion Fool Anti-spoofing?
May 29, 2025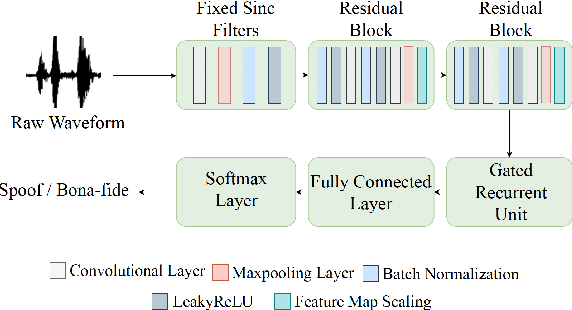
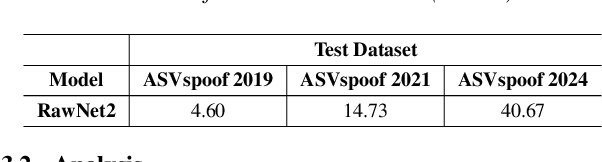
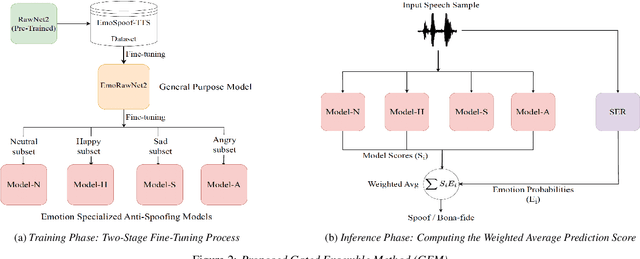
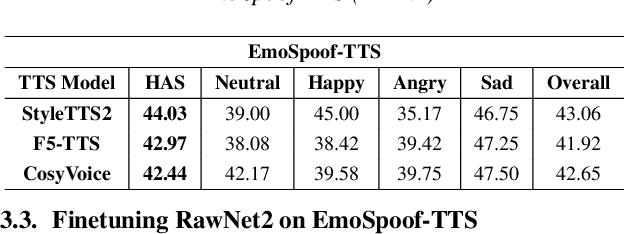
Abstract:Traditional anti-spoofing focuses on models and datasets built on synthetic speech with mostly neutral state, neglecting diverse emotional variations. As a result, their robustness against high-quality, emotionally expressive synthetic speech is uncertain. We address this by introducing EmoSpoof-TTS, a corpus of emotional text-to-speech samples. Our analysis shows existing anti-spoofing models struggle with emotional synthetic speech, exposing risks of emotion-targeted attacks. Even trained on emotional data, the models underperform due to limited focus on emotional aspect and show performance disparities across emotions. This highlights the need for emotion-focused anti-spoofing paradigm in both dataset and methodology. We propose GEM, a gated ensemble of emotion-specialized models with a speech emotion recognition gating network. GEM performs effectively across all emotions and neutral state, improving defenses against spoofing attacks. We release the EmoSpoof-TTS Dataset: https://emospoof-tts.github.io/Dataset/
Discrete Unit based Masking for Improving Disentanglement in Voice Conversion
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:Voice conversion (VC) aims to modify the speaker's identity while preserving the linguistic content. Commonly, VC methods use an encoder-decoder architecture, where disentangling the speaker's identity from linguistic information is crucial. However, the disentanglement approaches used in these methods are limited as the speaker features depend on the phonetic content of the utterance, compromising disentanglement. This dependency is amplified with attention-based methods. To address this, we introduce a novel masking mechanism in the input before speaker encoding, masking certain discrete speech units that correspond highly with phoneme classes. Our work aims to reduce the phonetic dependency of speaker features by restricting access to some phonetic information. Furthermore, since our approach is at the input level, it is applicable to any encoder-decoder based VC framework. Our approach improves disentanglement and conversion performance across multiple VC methods, showing significant effectiveness, particularly in attention-based method, with 44% relative improvement in objective intelligibility.
SelectTTS: Synthesizing Anyone's Voice via Discrete Unit-Based Frame Selection
Aug 30, 2024



Abstract:Synthesizing the voices of unseen speakers is a persisting challenge in multi-speaker text-to-speech (TTS). Most multi-speaker TTS models rely on modeling speaker characteristics through speaker conditioning during training. Modeling unseen speaker attributes through this approach has necessitated an increase in model complexity, which makes it challenging to reproduce results and improve upon them. We design a simple alternative to this. We propose SelectTTS, a novel method to select the appropriate frames from the target speaker and decode using frame-level self-supervised learning (SSL) features. We show that this approach can effectively capture speaker characteristics for unseen speakers, and achieves comparable results to other multi-speaker TTS frameworks in both objective and subjective metrics. With SelectTTS, we show that frame selection from the target speaker's speech is a direct way to achieve generalization in unseen speakers with low model complexity. We achieve better speaker similarity performance than SOTA baselines XTTS-v2 and VALL-E with over an 8x reduction in model parameters and a 270x reduction in training data
We Need Variations in Speech Synthesis: Sub-center Modelling for Speaker Embeddings
Jul 05, 2024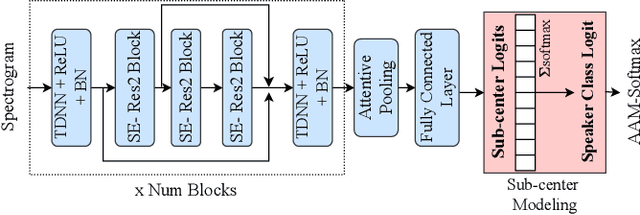
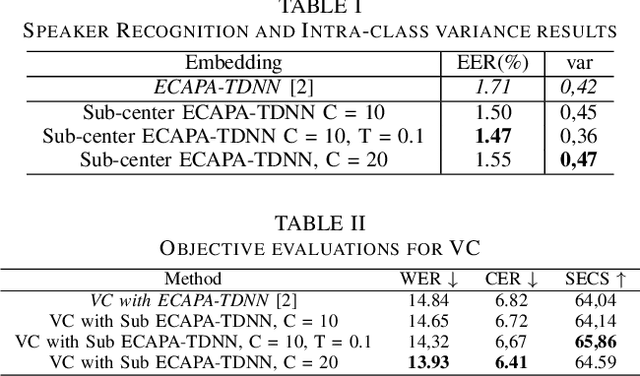
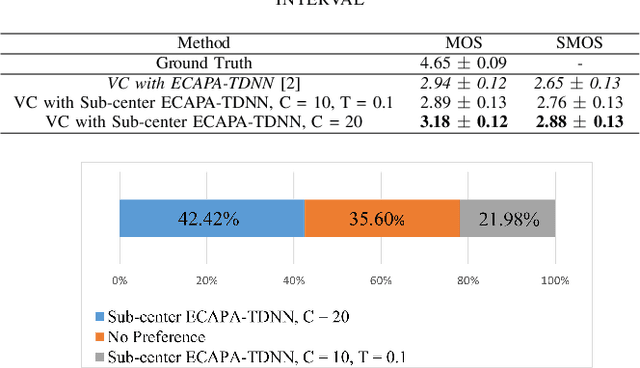
Abstract:In speech synthesis, modeling of rich emotions and prosodic variations present in human voice are crucial to synthesize natural speech. Although speaker embeddings have been widely used in personalized speech synthesis as conditioning inputs, they are designed to lose variation to optimize speaker recognition accuracy. Thus, they are suboptimal for speech synthesis in terms of modeling the rich variations at the output speech distribution. In this work, we propose a novel speaker embedding network which utilizes multiple class centers in the speaker classification training rather than a single class center as traditional embeddings. The proposed approach introduces variations in the speaker embedding while retaining the speaker recognition performance since model does not have to map all of the utterances of a speaker into a single class center. We apply our proposed embedding in voice conversion task and show that our method provides better naturalness and prosody in synthesized speech.
Towards Naturalistic Voice Conversion: NaturalVoices Dataset with an Automatic Processing Pipeline
Jun 06, 2024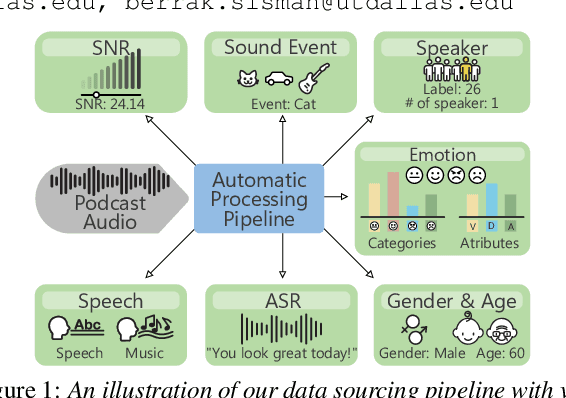
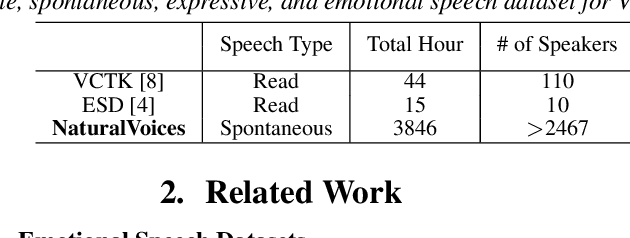
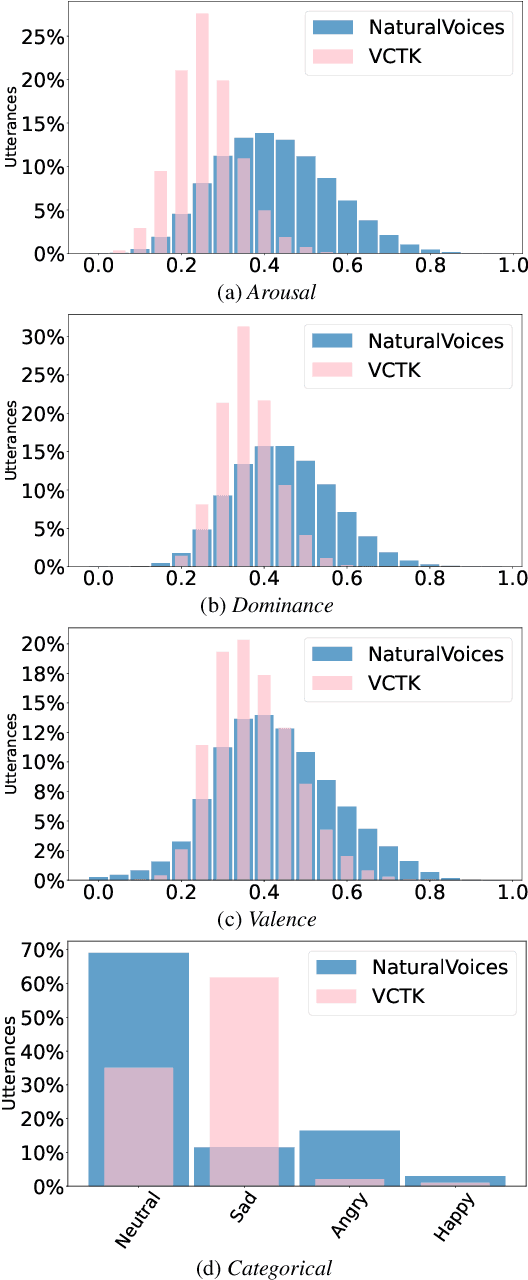
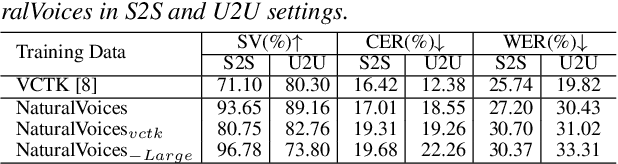
Abstract:Voice conversion (VC) research traditionally depends on scripted or acted speech, which lacks the natural spontaneity of real-life conversations. While natural speech data is limited for VC, our study focuses on filling in this gap. We introduce a novel data-sourcing pipeline that makes the release of a natural speech dataset for VC, named NaturalVoices. The pipeline extracts rich information in speech such as emotion and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) from raw podcast data, utilizing recent deep learning methods and providing flexibility and ease of use. NaturalVoices marks a large-scale, spontaneous, expressive, and emotional speech dataset, comprising over 3,800 hours speech sourced from the original podcasts in the MSP-Podcast dataset. Objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of using our pipeline for providing natural and expressive data for VC, suggesting the potential of NaturalVoices for broader speech generation tasks.
Revealing Emotional Clusters in Speaker Embeddings: A Contrastive Learning Strategy for Speech Emotion Recognition
Jan 19, 2024Abstract:Speaker embeddings carry valuable emotion-related information, which makes them a promising resource for enhancing speech emotion recognition (SER), especially with limited labeled data. Traditionally, it has been assumed that emotion information is indirectly embedded within speaker embeddings, leading to their under-utilization. Our study reveals a direct and useful link between emotion and state-of-the-art speaker embeddings in the form of intra-speaker clusters. By conducting a thorough clustering analysis, we demonstrate that emotion information can be readily extracted from speaker embeddings. In order to leverage this information, we introduce a novel contrastive pretraining approach applied to emotion-unlabeled data for speech emotion recognition. The proposed approach involves the sampling of positive and the negative examples based on the intra-speaker clusters of speaker embeddings. The proposed strategy, which leverages extensive emotion-unlabeled data, leads to a significant improvement in SER performance, whether employed as a standalone pretraining task or integrated into a multi-task pretraining setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge