Julian Padget
Understanding the Vulnerability of CLIP to Image Compression
Nov 23, 2023Abstract:CLIP is a widely used foundational vision-language model that is used for zero-shot image recognition and other image-text alignment tasks. We demonstrate that CLIP is vulnerable to change in image quality under compression. This surprising result is further analysed using an attribution method-Integrated Gradients. Using this attribution method, we are able to better understand both quantitatively and qualitatively exactly the nature in which the compression affects the zero-shot recognition accuracy of this model. We evaluate this extensively on CIFAR-10 and STL-10. Our work provides the basis to understand this vulnerability of CLIP and can help us develop more effective methods to improve the robustness of CLIP and other vision-language models.
A Norm Emergence Framework for Normative MAS -- Position Paper
Apr 06, 2020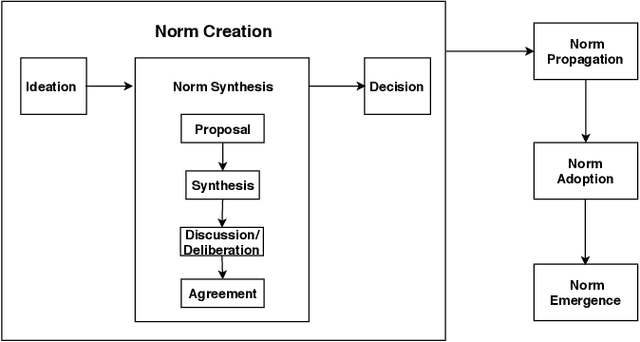
Abstract:Norm emergence is typically studied in the context of multiagent systems (MAS) where norms are implicit, and participating agents use simplistic decision-making mechanisms. These implicit norms are usually unconsciously shared and adopted through agent interaction. A norm is deemed to have emerged when a threshold or predetermined percentage of agents follow the "norm". Conversely, in normative MAS, norms are typically explicit and agents deliberately share norms through communication or are informed about norms by an authority, following which an agent decides whether to adopt the norm or not. The decision to adopt a norm by the agent can happen immediately after recognition or when an applicable situation arises. In this paper, we make the case that, similarly, a norm has emerged in a normative MAS when a percentage of agents adopt the norm. Furthermore, we posit that agents themselves can and should be involved in norm synthesis, and hence influence the norms governing the MAS, in line with Ostrom's eight principles. Consequently, we put forward a framework for the emergence of norms within a normative MAS, that allows participating agents to propose/request changes to the normative system, while special-purpose synthesizer agents formulate new norms or revisions in response to these requests. Synthesizers must collectively agree that the new norm or norm revision should proceed, and then finally be approved by an "Oracle". The normative system is then modified to incorporate the norm.
Practical Reasoning with Norms for Autonomous Software Agents (Full Edition)
Jan 28, 2017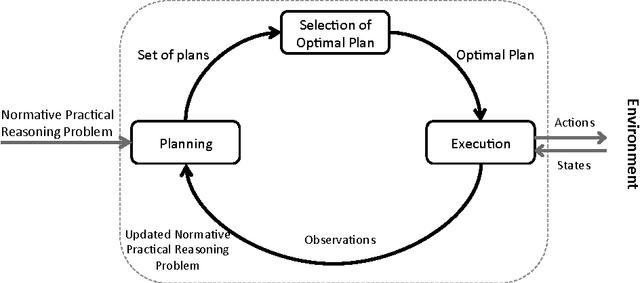
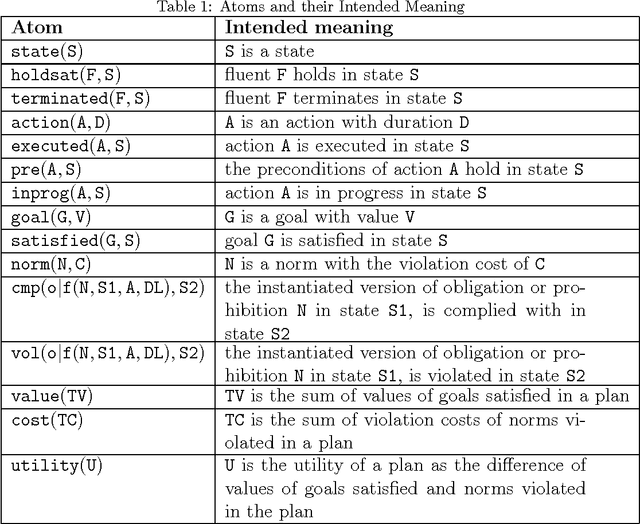

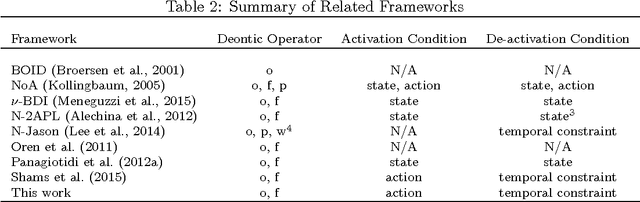
Abstract:Autonomous software agents operating in dynamic environments need to constantly reason about actions in pursuit of their goals, while taking into consideration norms which might be imposed on those actions. Normative practical reasoning supports agents making decisions about what is best for them to (not) do in a given situation. What makes practical reasoning challenging is the interplay between goals that agents are pursuing and the norms that the agents are trying to uphold. We offer a formalisation to allow agents to plan for multiple goals and norms in the presence of durative actions that can be executed concurrently. We compare plans based on decision-theoretic notions (i.e. utility) such that the utility gain of goals and utility loss of norm violations are the basis for this comparison. The set of optimal plans consists of plans that maximise the overall utility, each of which can be chosen by the agent to execute. We provide an implementation of our proposal in Answer Set Programming, thus allowing us to state the original problem in terms of a logic program that can be queried for solutions with specific properties. The implementation is proven to be sound and complete.
Artificial Prediction Markets for Online Prediction of Continuous Variables-A Preliminary Report
Aug 11, 2015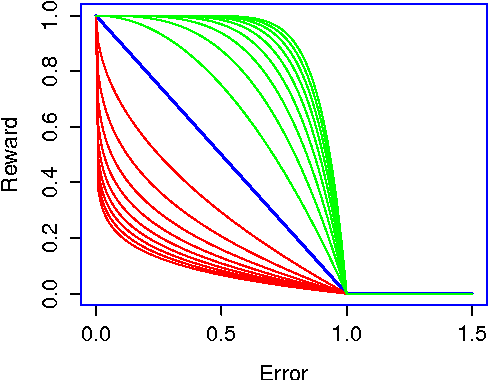
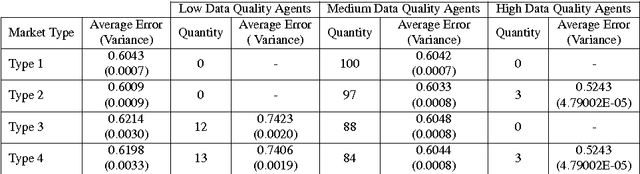
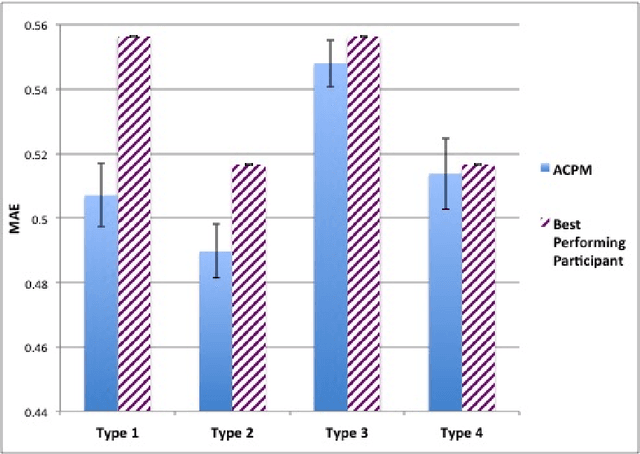
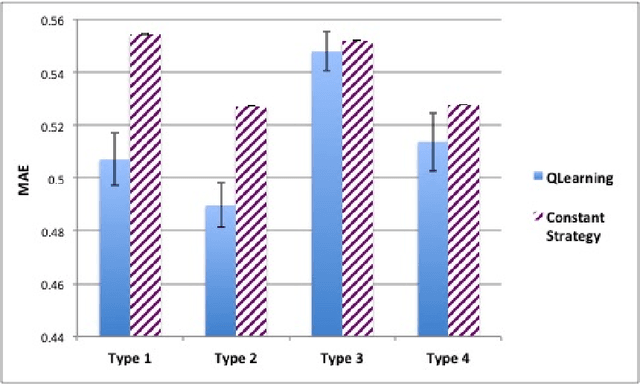
Abstract:We propose the Artificial Continuous Prediction Market (ACPM) as a means to predict a continuous real value, by integrating a range of data sources and aggregating the results of different machine learning (ML) algorithms. ACPM adapts the concept of the (physical) prediction market to address the prediction of real values instead of discrete events. Each ACPM participant has a data source, a ML algorithm and a local decision-making procedure that determines what to bid on what value. The contributions of ACPM are: (i) adaptation to changes in data quality by the use of learning in: (a) the market, which weights each market participant to adjust the influence of each on the market prediction and (b) the participants, which use a Q-learning based trading strategy to incorporate the market prediction into their subsequent predictions, (ii) resilience to a changing population of low- and high-performing participants. We demonstrate the effectiveness of ACPM by application to an influenza-like illnesses data set, showing ACPM out-performs a range of well-known regression models and is resilient to variation in data source quality.
Normative design using inductive learning
Jul 25, 2011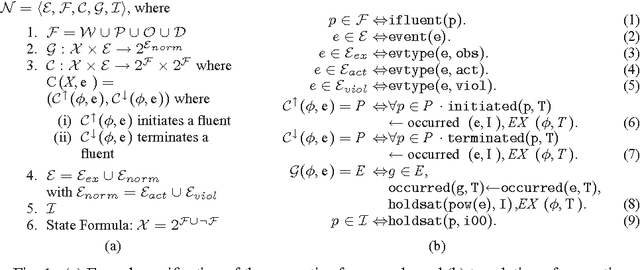
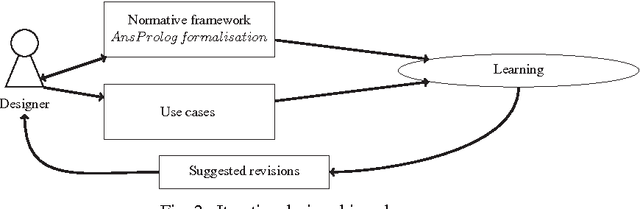
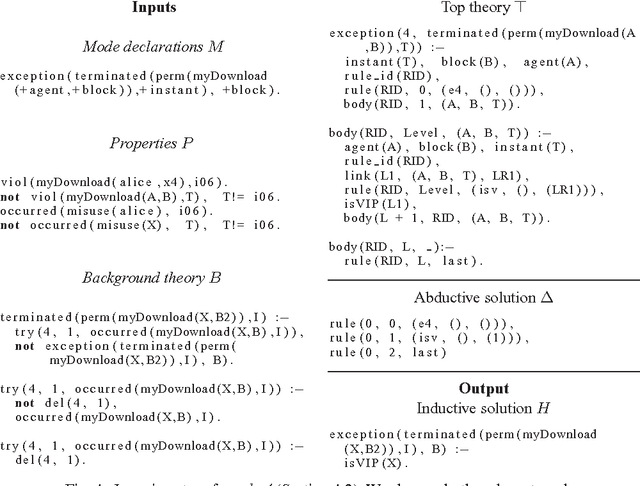
Abstract:In this paper we propose a use-case-driven iterative design methodology for normative frameworks, also called virtual institutions, which are used to govern open systems. Our computational model represents the normative framework as a logic program under answer set semantics (ASP). By means of an inductive logic programming approach, implemented using ASP, it is possible to synthesise new rules and revise the existing ones. The learning mechanism is guided by the designer who describes the desired properties of the framework through use cases, comprising (i) event traces that capture possible scenarios, and (ii) a state that describes the desired outcome. The learning process then proposes additional rules, or changes to current rules, to satisfy the constraints expressed in the use cases. Thus, the contribution of this paper is a process for the elaboration and revision of a normative framework by means of a semi-automatic and iterative process driven from specifications of (un)desirable behaviour. The process integrates a novel and general methodology for theory revision based on ASP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge