Jose J. Valero-Mas
Instituto Universitario de Investigación Informática, University of Alicante, Alicante, Spain
Self-Supervised Learning for Text Recognition: A Critical Survey
Jul 29, 2024Abstract:Text Recognition (TR) refers to the research area that focuses on retrieving textual information from images, a topic that has seen significant advancements in the last decade due to the use of Deep Neural Networks (DNN). However, these solutions often necessitate vast amounts of manually labeled or synthetic data. Addressing this challenge, Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) has gained attention by utilizing large datasets of unlabeled data to train DNN, thereby generating meaningful and robust representations. Although SSL was initially overlooked in TR because of its unique characteristics, recent years have witnessed a surge in the development of SSL methods specifically for this field. This rapid development, however, has led to many methods being explored independently, without taking previous efforts in methodology or comparison into account, thereby hindering progress in the field of research. This paper, therefore, seeks to consolidate the use of SSL in the field of TR, offering a critical and comprehensive overview of the current state of the art. We will review and analyze the existing methods, compare their results, and highlight inconsistencies in the current literature. This thorough analysis aims to provide general insights into the field, propose standardizations, identify new research directions, and foster its proper development.
Spatial Context-based Self-Supervised Learning for Handwritten Text Recognition
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Handwritten Text Recognition (HTR) is a relevant problem in computer vision, and implies unique challenges owing to its inherent variability and the rich contextualization required for its interpretation. Despite the success of Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) in computer vision, its application to HTR has been rather scattered, leaving key SSL methodologies unexplored. This work focuses on one of them, namely Spatial Context-based SSL. We investigate how this family of approaches can be adapted and optimized for HTR and propose new workflows that leverage the unique features of handwritten text. Our experiments demonstrate that the methods considered lead to advancements in the state-of-the-art of SSL for HTR in a number of benchmark cases.
Identifying Student Profiles Within Online Judge Systems Using Explainable Artificial Intelligence
Jan 29, 2024



Abstract:Online Judge (OJ) systems are typically considered within programming-related courses as they yield fast and objective assessments of the code developed by the students. Such an evaluation generally provides a single decision based on a rubric, most commonly whether the submission successfully accomplished the assignment. Nevertheless, since in an educational context such information may be deemed insufficient, it would be beneficial for both the student and the instructor to receive additional feedback about the overall development of the task. This work aims to tackle this limitation by considering the further exploitation of the information gathered by the OJ and automatically inferring feedback for both the student and the instructor. More precisely, we consider the use of learning-based schemes -- particularly, multi-instance learning (MIL) and classical machine learning formulations -- to model student behavior. Besides, explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) is contemplated to provide human-understandable feedback. The proposal has been evaluated considering a case of study comprising 2500 submissions from roughly 90 different students from a programming-related course in a computer science degree. The results obtained validate the proposal: The model is capable of significantly predicting the user outcome (either passing or failing the assignment) solely based on the behavioral pattern inferred by the submissions provided to the OJ. Moreover, the proposal is able to identify prone-to-fail student groups and profiles as well as other relevant information, which eventually serves as feedback to both the student and the instructor.
Predicting performance difficulty from piano sheet music images
Sep 28, 2023



Abstract:Estimating the performance difficulty of a musical score is crucial in music education for adequately designing the learning curriculum of the students. Although the Music Information Retrieval community has recently shown interest in this task, existing approaches mainly use machine-readable scores, leaving the broader case of sheet music images unaddressed. Based on previous works involving sheet music images, we use a mid-level representation, bootleg score, describing notehead positions relative to staff lines coupled with a transformer model. This architecture is adapted to our task by introducing an encoding scheme that reduces the encoded sequence length to one-eighth of the original size. In terms of evaluation, we consider five datasets -- more than 7500 scores with up to 9 difficulty levels -- , two of them particularly compiled for this work. The results obtained when pretraining the scheme on the IMSLP corpus and fine-tuning it on the considered datasets prove the proposal's validity, achieving the best-performing model with a balanced accuracy of 40.34\% and a mean square error of 1.33. Finally, we provide access to our code, data, and models for transparency and reproducibility.
Multilabel Prototype Generation for Data Reduction in k-Nearest Neighbour classification
Jul 22, 2022



Abstract:Prototype Generation (PG) methods are typically considered for improving the efficiency of the $k$-Nearest Neighbour ($k$NN) classifier when tackling high-size corpora. Such approaches aim at generating a reduced version of the corpus without decreasing the classification performance when compared to the initial set. Despite their large application in multiclass scenarios, very few works have addressed the proposal of PG methods for the multilabel space. In this regard, this work presents the novel adaptation of four multiclass PG strategies to the multilabel case. These proposals are evaluated with three multilabel $k$NN-based classifiers, 12 corpora comprising a varied range of domains and corpus sizes, and different noise scenarios artificially induced in the data. The results obtained show that the proposed adaptations are capable of significantly improving -- both in terms of efficiency and classification performance -- the only reference multilabel PG work in the literature as well as the case in which no PG method is applied, also presenting a statistically superior robustness in noisy scenarios. Moreover, these novel PG strategies allow prioritising either the efficiency or efficacy criteria through its configuration depending on the target scenario, hence covering a wide area in the solution space not previously filled by other works.
Late multimodal fusion for image and audio music transcription
Apr 06, 2022


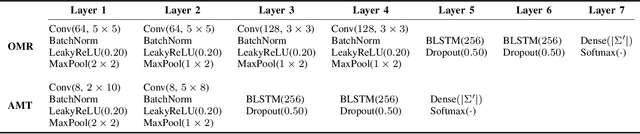
Abstract:Music transcription, which deals with the conversion of music sources into a structured digital format, is a key problem for Music Information Retrieval (MIR). When addressing this challenge in computational terms, the MIR community follows two lines of research: music documents, which is the case of Optical Music Recognition (OMR), or audio recordings, which is the case of Automatic Music Transcription (AMT). The different nature of the aforementioned input data has conditioned these fields to develop modality-specific frameworks. However, their recent definition in terms of sequence labeling tasks leads to a common output representation, which enables research on a combined paradigm. In this respect, multimodal image and audio music transcription comprises the challenge of effectively combining the information conveyed by image and audio modalities. In this work, we explore this question at a late-fusion level: we study four combination approaches in order to merge, for the first time, the hypotheses regarding end-to-end OMR and AMT systems in a lattice-based search space. The results obtained for a series of performance scenarios -- in which the corresponding single-modality models yield different error rates -- showed interesting benefits of these approaches. In addition, two of the four strategies considered significantly improve the corresponding unimodal standard recognition frameworks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge