John Richardson
Learning to Guide Multiple Heterogeneous Actors from a Single Human Demonstration via Automatic Curriculum Learning in StarCraft II
May 11, 2022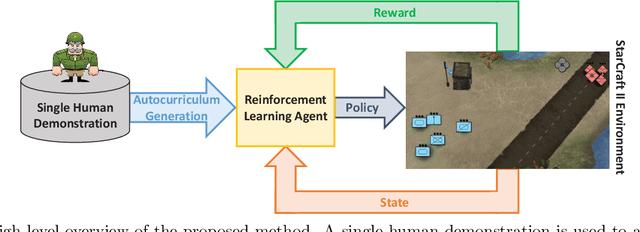


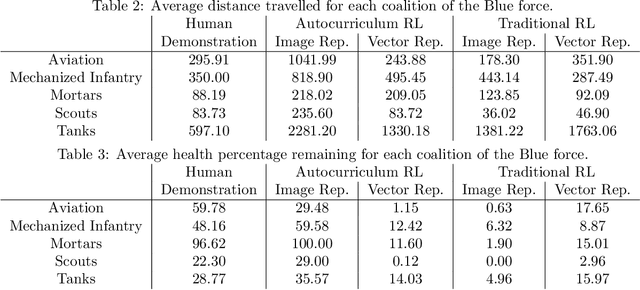
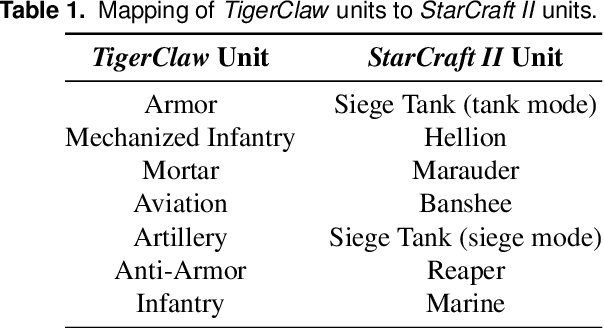
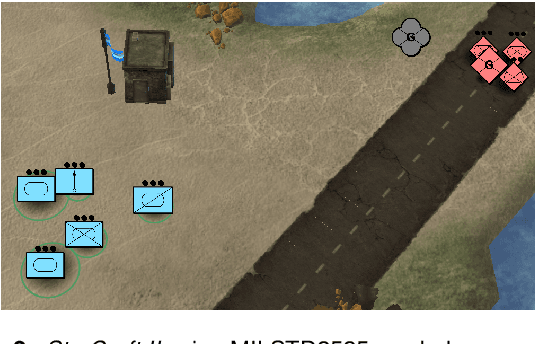
Abstract:Traditionally, learning from human demonstrations via direct behavior cloning can lead to high-performance policies given that the algorithm has access to large amounts of high-quality data covering the most likely scenarios to be encountered when the agent is operating. However, in real-world scenarios, expert data is limited and it is desired to train an agent that learns a behavior policy general enough to handle situations that were not demonstrated by the human expert. Another alternative is to learn these policies with no supervision via deep reinforcement learning, however, these algorithms require a large amount of computing time to perform well on complex tasks with high-dimensional state and action spaces, such as those found in StarCraft II. Automatic curriculum learning is a recent mechanism comprised of techniques designed to speed up deep reinforcement learning by adjusting the difficulty of the current task to be solved according to the agent's current capabilities. Designing a proper curriculum, however, can be challenging for sufficiently complex tasks, and thus we leverage human demonstrations as a way to guide agent exploration during training. In this work, we aim to train deep reinforcement learning agents that can command multiple heterogeneous actors where starting positions and overall difficulty of the task are controlled by an automatically-generated curriculum from a single human demonstration. Our results show that an agent trained via automated curriculum learning can outperform state-of-the-art deep reinforcement learning baselines and match the performance of the human expert in a simulated command and control task in StarCraft II modeled over a real military scenario.
On games and simulators as a platform for development of artificial intelligence for command and control
Oct 21, 2021
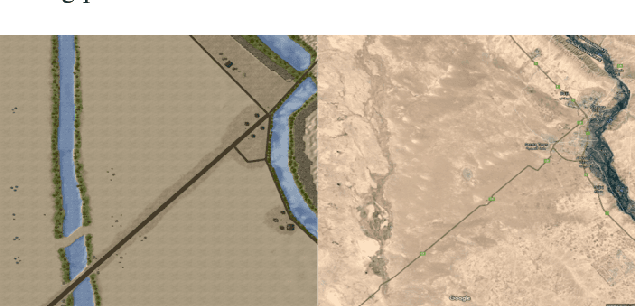
Abstract:Games and simulators can be a valuable platform to execute complex multi-agent, multiplayer, imperfect information scenarios with significant parallels to military applications: multiple participants manage resources and make decisions that command assets to secure specific areas of a map or neutralize opposing forces. These characteristics have attracted the artificial intelligence (AI) community by supporting development of algorithms with complex benchmarks and the capability to rapidly iterate over new ideas. The success of artificial intelligence algorithms in real-time strategy games such as StarCraft II have also attracted the attention of the military research community aiming to explore similar techniques in military counterpart scenarios. Aiming to bridge the connection between games and military applications, this work discusses past and current efforts on how games and simulators, together with the artificial intelligence algorithms, have been adapted to simulate certain aspects of military missions and how they might impact the future battlefield. This paper also investigates how advances in virtual reality and visual augmentation systems open new possibilities in human interfaces with gaming platforms and their military parallels.
Lingvo: a Modular and Scalable Framework for Sequence-to-Sequence Modeling
Feb 21, 2019
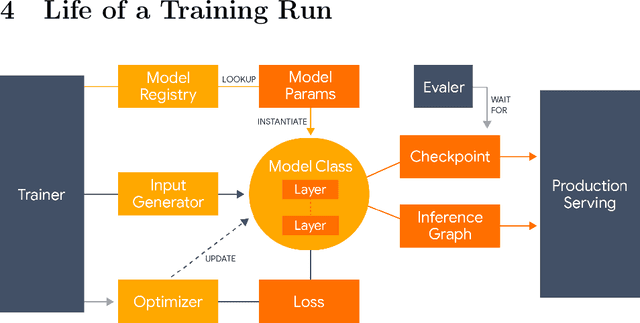
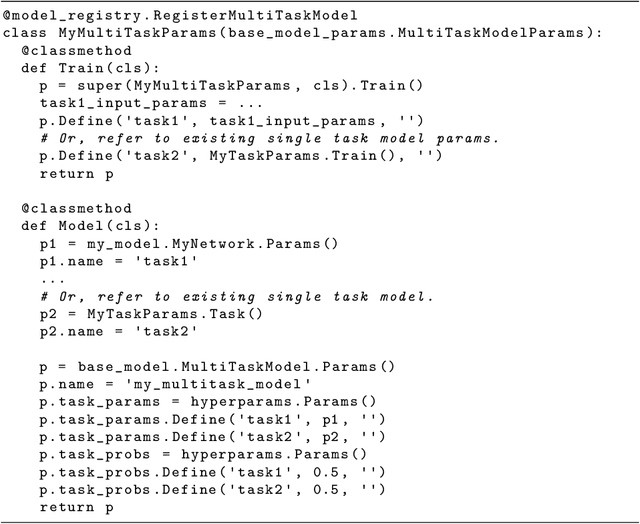
Abstract:Lingvo is a Tensorflow framework offering a complete solution for collaborative deep learning research, with a particular focus towards sequence-to-sequence models. Lingvo models are composed of modular building blocks that are flexible and easily extensible, and experiment configurations are centralized and highly customizable. Distributed training and quantized inference are supported directly within the framework, and it contains existing implementations of a large number of utilities, helper functions, and the newest research ideas. Lingvo has been used in collaboration by dozens of researchers in more than 20 papers over the last two years. This document outlines the underlying design of Lingvo and serves as an introduction to the various pieces of the framework, while also offering examples of advanced features that showcase the capabilities of the framework.
SentencePiece: A simple and language independent subword tokenizer and detokenizer for Neural Text Processing
Aug 19, 2018
Abstract:This paper describes SentencePiece, a language-independent subword tokenizer and detokenizer designed for Neural-based text processing, including Neural Machine Translation. It provides open-source C++ and Python implementations for subword units. While existing subword segmentation tools assume that the input is pre-tokenized into word sequences, SentencePiece can train subword models directly from raw sentences, which allows us to make a purely end-to-end and language independent system. We perform a validation experiment of NMT on English-Japanese machine translation, and find that it is possible to achieve comparable accuracy to direct subword training from raw sentences. We also compare the performance of subword training and segmentation with various configurations. SentencePiece is available under the Apache 2 license at https://github.com/google/sentencepiece.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge