João P. Neto
Privacy-Preserving Multi-Document Summarization
Aug 06, 2015
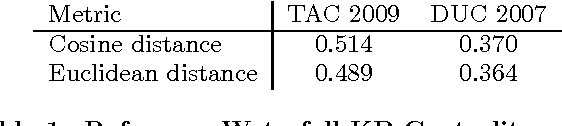

Abstract:State-of-the-art extractive multi-document summarization systems are usually designed without any concern about privacy issues, meaning that all documents are open to third parties. In this paper we propose a privacy-preserving approach to multi-document summarization. Our approach enables other parties to obtain summaries without learning anything else about the original documents' content. We use a hashing scheme known as Secure Binary Embeddings to convert documents representation containing key phrases and bag-of-words into bit strings, allowing the computation of approximate distances, instead of exact ones. Our experiments indicate that our system yields similar results to its non-private counterpart on standard multi-document evaluation datasets.
Extending a Single-Document Summarizer to Multi-Document: a Hierarchical Approach
Jul 10, 2015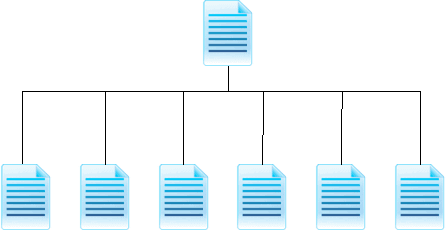
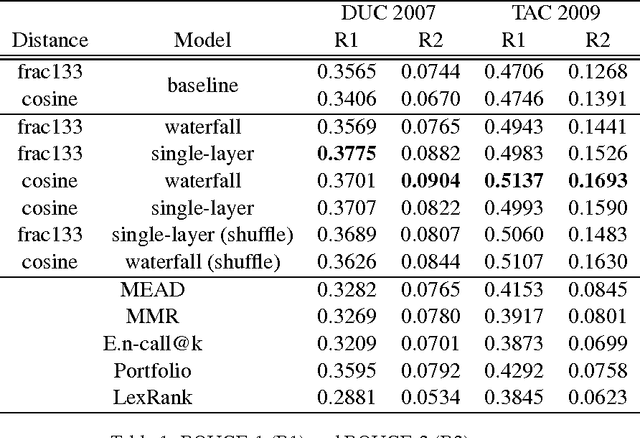
Abstract:The increasing amount of online content motivated the development of multi-document summarization methods. In this work, we explore straightforward approaches to extend single-document summarization methods to multi-document summarization. The proposed methods are based on the hierarchical combination of single-document summaries, and achieves state of the art results.
Ensemble Detection of Single & Multiple Events at Sentence-Level
Mar 24, 2014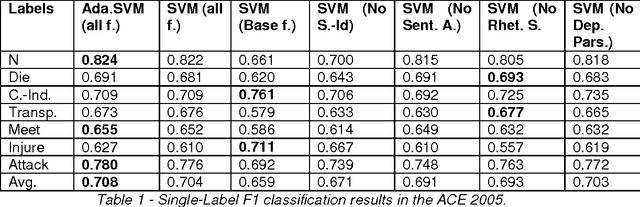
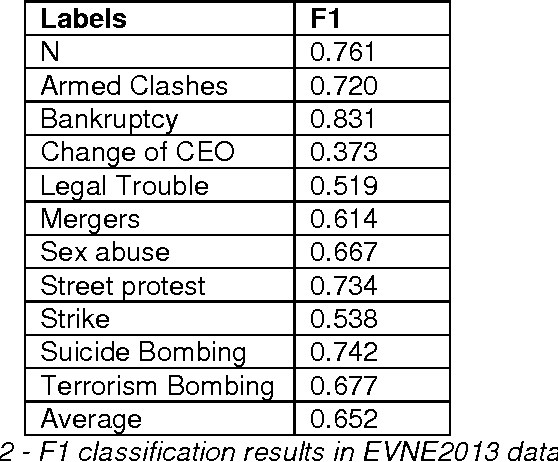
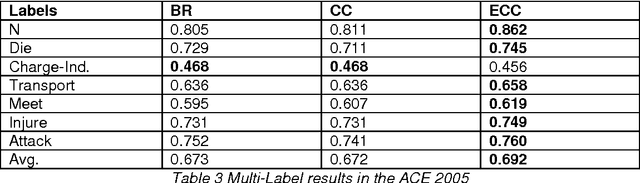
Abstract:Event classification at sentence level is an important Information Extraction task with applications in several NLP, IR, and personalization systems. Multi-label binary relevance (BR) are the state-of-art methods. In this work, we explored new multi-label methods known for capturing relations between event types. These new methods, such as the ensemble Chain of Classifiers, improve the F1 on average across the 6 labels by 2.8% over the Binary Relevance. The low occurrence of multi-label sentences motivated the reduction of the hard imbalanced multi-label classification problem with low number of occurrences of multiple labels per instance to an more tractable imbalanced multiclass problem with better results (+ 4.6%). We report the results of adding new features, such as sentiment strength, rhetorical signals, domain-id (source-id and date), and key-phrases in both single-label and multi-label event classification scenarios.
Co-Multistage of Multiple Classifiers for Imbalanced Multiclass Learning
Jan 24, 2014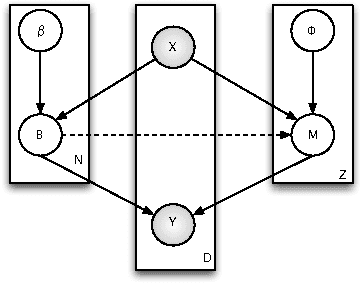
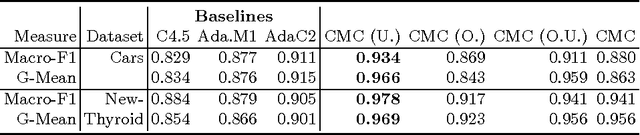
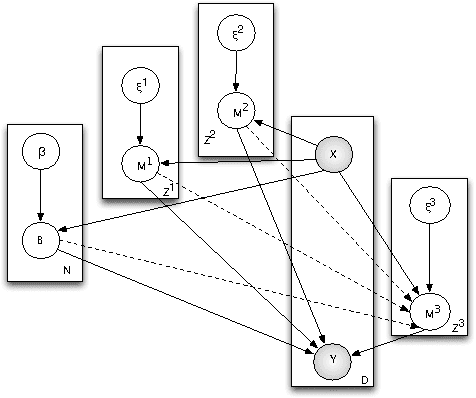
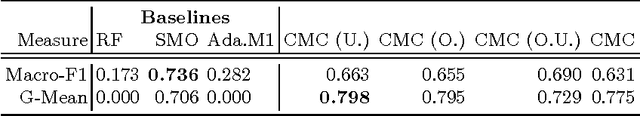
Abstract:In this work, we propose two stochastic architectural models (CMC and CMC-M) with two layers of classifiers applicable to datasets with one and multiple skewed classes. This distinction becomes important when the datasets have a large number of classes. Therefore, we present a novel solution to imbalanced multiclass learning with several skewed majority classes, which improves minority classes identification. This fact is particularly important for text classification tasks, such as event detection. Our models combined with pre-processing sampling techniques improved the classification results on six well-known datasets. Finally, we have also introduced a new metric SG-Mean to overcome the multiplication by zero limitation of G-Mean.
Recognition of Named-Event Passages in News Articles
Jun 20, 2013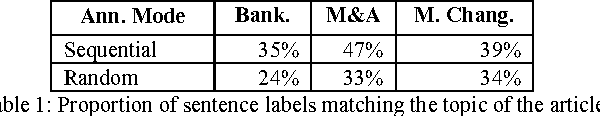


Abstract:We extend the concept of Named Entities to Named Events - commonly occurring events such as battles and earthquakes. We propose a method for finding specific passages in news articles that contain information about such events and report our preliminary evaluation results. Collecting "Gold Standard" data presents many problems, both practical and conceptual. We present a method for obtaining such data using the Amazon Mechanical Turk service.
Key Phrase Extraction of Lightly Filtered Broadcast News
Jun 20, 2013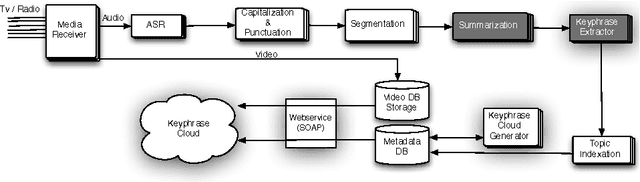

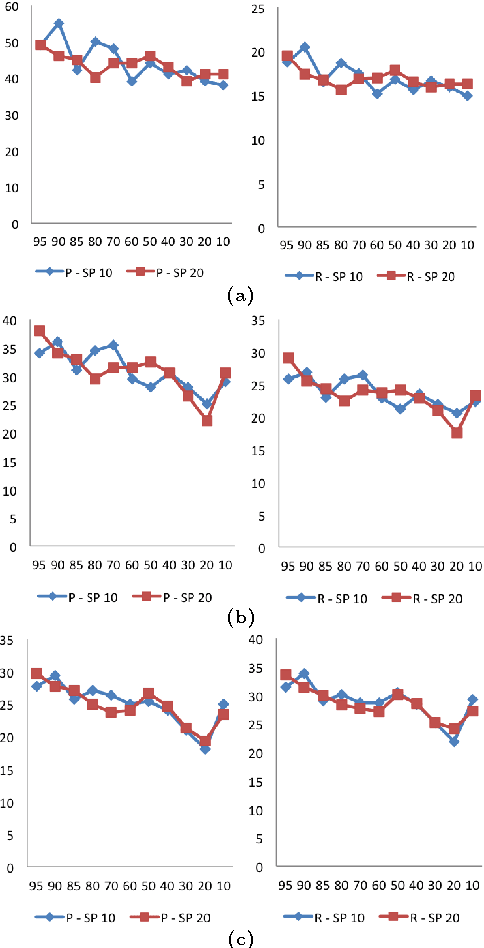
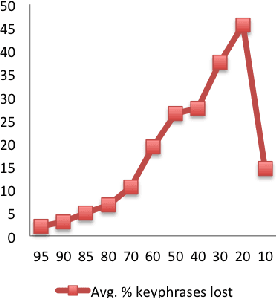
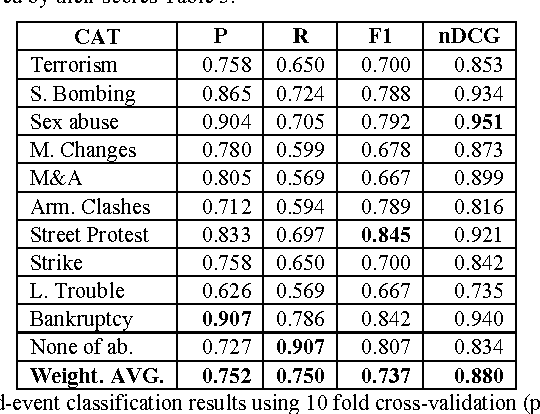
Abstract:This paper explores the impact of light filtering on automatic key phrase extraction (AKE) applied to Broadcast News (BN). Key phrases are words and expressions that best characterize the content of a document. Key phrases are often used to index the document or as features in further processing. This makes improvements in AKE accuracy particularly important. We hypothesized that filtering out marginally relevant sentences from a document would improve AKE accuracy. Our experiments confirmed this hypothesis. Elimination of as little as 10% of the document sentences lead to a 2% improvement in AKE precision and recall. AKE is built over MAUI toolkit that follows a supervised learning approach. We trained and tested our AKE method on a gold standard made of 8 BN programs containing 110 manually annotated news stories. The experiments were conducted within a Multimedia Monitoring Solution (MMS) system for TV and radio news/programs, running daily, and monitoring 12 TV and 4 radio channels.
Supervised Topical Key Phrase Extraction of News Stories using Crowdsourcing, Light Filtering and Co-reference Normalization
Jun 20, 2013
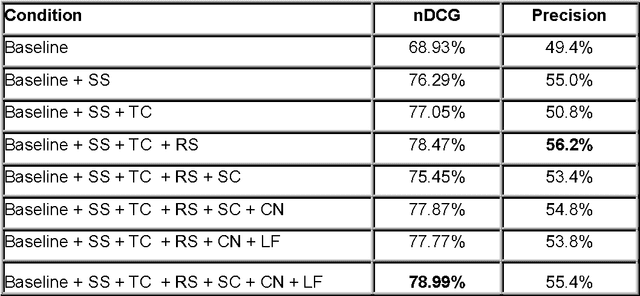
Abstract:Fast and effective automated indexing is critical for search and personalized services. Key phrases that consist of one or more words and represent the main concepts of the document are often used for the purpose of indexing. In this paper, we investigate the use of additional semantic features and pre-processing steps to improve automatic key phrase extraction. These features include the use of signal words and freebase categories. Some of these features lead to significant improvements in the accuracy of the results. We also experimented with 2 forms of document pre-processing that we call light filtering and co-reference normalization. Light filtering removes sentences from the document, which are judged peripheral to its main content. Co-reference normalization unifies several written forms of the same named entity into a unique form. We also needed a "Gold Standard" - a set of labeled documents for training and evaluation. While the subjective nature of key phrase selection precludes a true "Gold Standard", we used Amazon's Mechanical Turk service to obtain a useful approximation. Our data indicates that the biggest improvements in performance were due to shallow semantic features, news categories, and rhetorical signals (nDCG 78.47% vs. 68.93%). The inclusion of deeper semantic features such as Freebase sub-categories was not beneficial by itself, but in combination with pre-processing, did cause slight improvements in the nDCG scores.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge