Jiyang Wang
Block-As-Domain Adaptation for Workload Prediction from fNIRS Data
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is a non-intrusive way to measure cortical hemodynamic activity. Predicting cognitive workload from fNIRS data has taken on a diffuse set of methods. To be applicable in real-world settings, models are needed, which can perform well across different sessions as well as different subjects. However, most existing works assume that training and testing data come from the same subjects and/or cannot generalize well across never-before-seen subjects. Additional challenges imposed by fNIRS data include the high variations in inter-subject fNIRS data and also in intra-subject data collected across different blocks of sessions. To address these issues, we propose an effective method, referred to as the class-aware-block-aware domain adaptation (CABA-DA) which explicitly minimize intra-session variance by viewing different blocks from the same subject same session as different domains. We minimize the intra-class domain discrepancy and maximize the inter-class domain discrepancy accordingly. In addition, we propose an MLPMixer-based model for cognitive load classification. Experimental results demonstrate the proposed model has better performance compared with three different baseline models on three public-available datasets of cognitive workload. Two of them are collected from n-back tasks and one of them is from finger tapping. From our experiments, we also show the proposed contrastive learning method can also improve baseline models we compared with.
Vision-Language Models can Identify Distracted Driver Behavior from Naturalistic Videos
Jun 22, 2023Abstract:Recognizing the activities, causing distraction, in real-world driving scenarios is critical for ensuring the safety and reliability of both drivers and pedestrians on the roadways. Conventional computer vision techniques are typically data-intensive and require a large volume of annotated training data to detect and classify various distracted driving behaviors, thereby limiting their efficiency and scalability. We aim to develop a generalized framework that showcases robust performance with access to limited or no annotated training data. Recently, vision-language models have offered large-scale visual-textual pretraining that can be adapted to task-specific learning like distracted driving activity recognition. Vision-language pretraining models, such as CLIP, have shown significant promise in learning natural language-guided visual representations. This paper proposes a CLIP-based driver activity recognition approach that identifies driver distraction from naturalistic driving images and videos. CLIP's vision embedding offers zero-shot transfer and task-based finetuning, which can classify distracted activities from driving video data. Our results show that this framework offers state-of-the-art performance on zero-shot transfer and video-based CLIP for predicting the driver's state on two public datasets. We propose both frame-based and video-based frameworks developed on top of the CLIP's visual representation for distracted driving detection and classification task and report the results.
Synthetic Distracted Driving (SynDD1) dataset for analyzing distracted behaviors and various gaze zones of a driver
Apr 19, 2022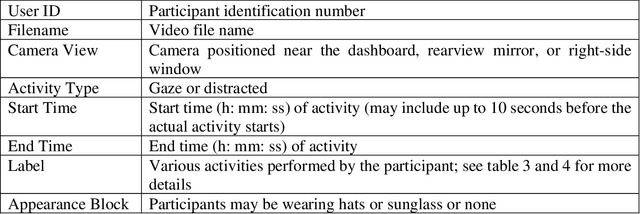
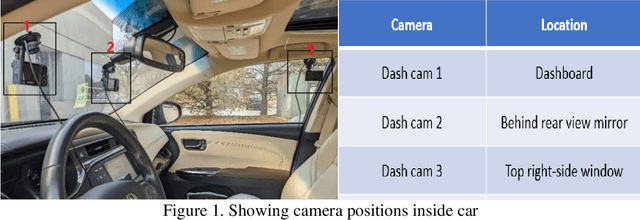


Abstract:This article presents a synthetic distracted driving (SynDD1) dataset for machine learning models to detect and analyze drivers' various distracted behavior and different gaze zones. We collected the data in a stationary vehicle using three in-vehicle cameras positioned at locations: on the dashboard, near the rearview mirror, and on the top right-side window corner. The dataset contains two activity types: distracted activities, and gaze zones for each participant and each activity type has two sets: without appearance blocks and with appearance blocks such as wearing a hat or sunglasses. The order and duration of each activity for each participant are random. In addition, the dataset contains manual annotations for each activity, having its start and end time annotated. Researchers could use this dataset to evaluate the performance of machine learning algorithms for the classification of various distracting activities and gaze zones of drivers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge