Jinshu Chen
DreamStyle: A Unified Framework for Video Stylization
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Video stylization, an important downstream task of video generation models, has not yet been thoroughly explored. Its input style conditions typically include text, style image, and stylized first frame. Each condition has a characteristic advantage: text is more flexible, style image provides a more accurate visual anchor, and stylized first frame makes long-video stylization feasible. However, existing methods are largely confined to a single type of style condition, which limits their scope of application. Additionally, their lack of high-quality datasets leads to style inconsistency and temporal flicker. To address these limitations, we introduce DreamStyle, a unified framework for video stylization, supporting (1) text-guided, (2) style-image-guided, and (3) first-frame-guided video stylization, accompanied by a well-designed data curation pipeline to acquire high-quality paired video data. DreamStyle is built on a vanilla Image-to-Video (I2V) model and trained using a Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) with token-specific up matrices that reduces the confusion among different condition tokens. Both qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate that DreamStyle is competent in all three video stylization tasks, and outperforms the competitors in style consistency and video quality.
Customize Your Own Paired Data via Few-shot Way
May 21, 2024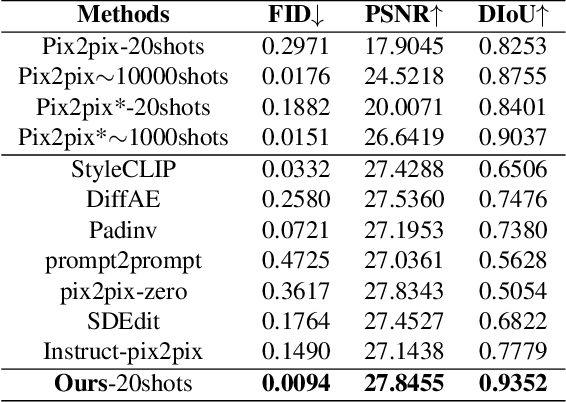
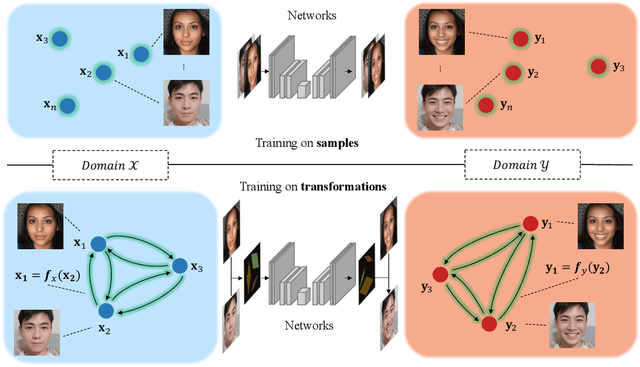
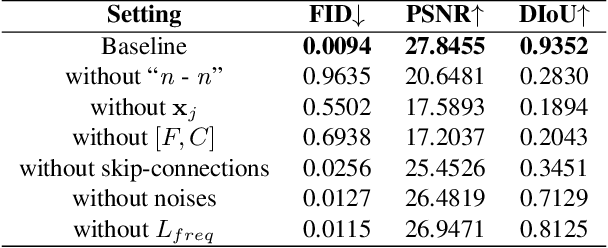
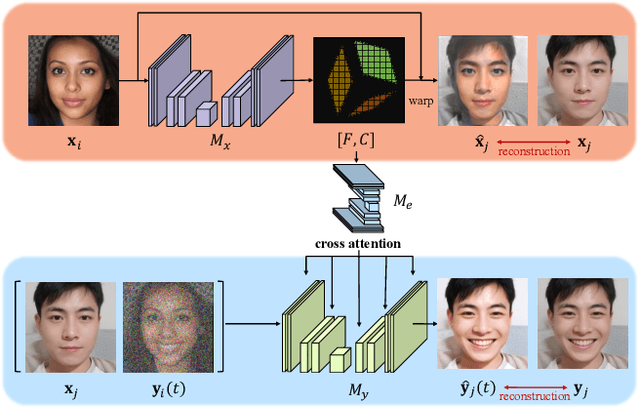
Abstract:Existing solutions to image editing tasks suffer from several issues. Though achieving remarkably satisfying generated results, some supervised methods require huge amounts of paired training data, which greatly limits their usages. The other unsupervised methods take full advantage of large-scale pre-trained priors, thus being strictly restricted to the domains where the priors are trained on and behaving badly in out-of-distribution cases. The task we focus on is how to enable the users to customize their desired effects through only few image pairs. In our proposed framework, a novel few-shot learning mechanism based on the directional transformations among samples is introduced and expands the learnable space exponentially. Adopting a diffusion model pipeline, we redesign the condition calculating modules in our model and apply several technical improvements. Experimental results demonstrate the capabilities of our method in various cases.
MOGAN: Morphologic-structure-aware Generative Learning from a Single Image
Mar 04, 2021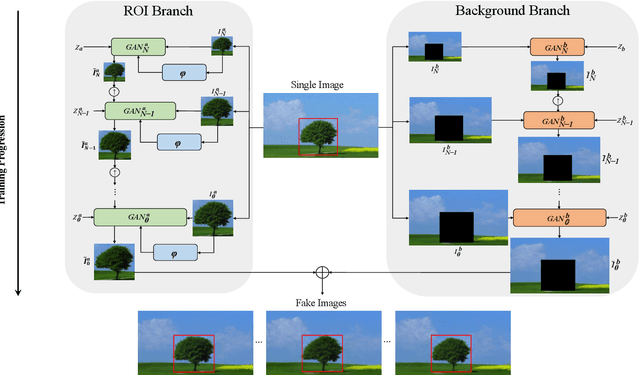
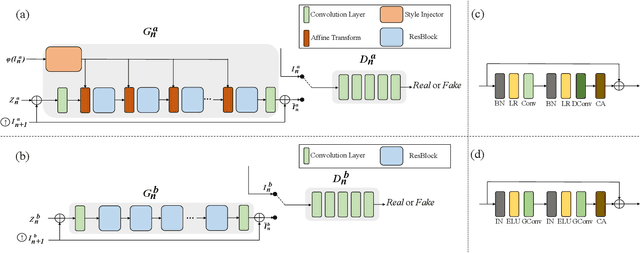
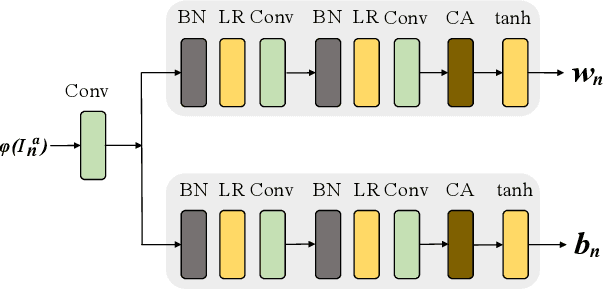
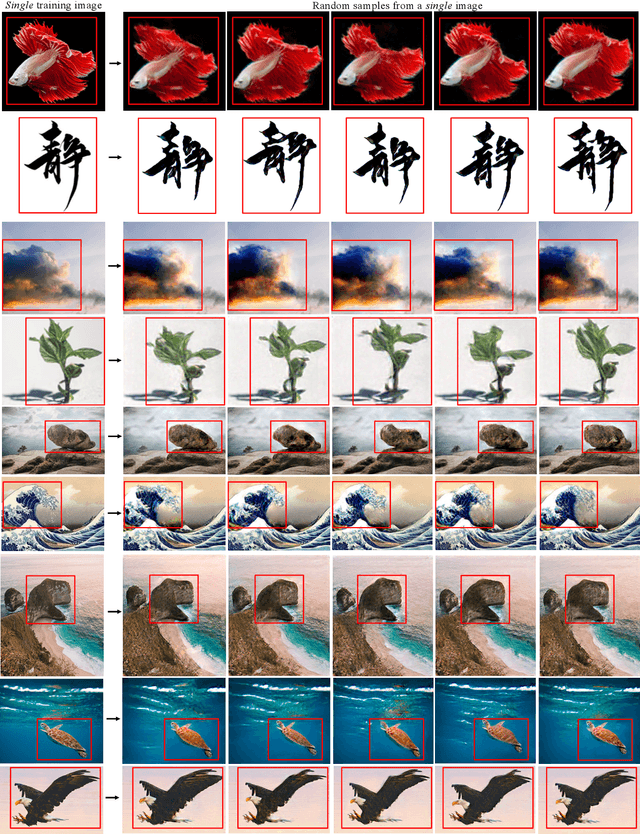
Abstract:In most interactive image generation tasks, given regions of interest (ROI) by users, the generated results are expected to have adequate diversities in appearance while maintaining correct and reasonable structures in original images. Such tasks become more challenging if only limited data is available. Recently proposed generative models complete training based on only one image. They pay much attention to the monolithic feature of the sample while ignoring the actual semantic information of different objects inside the sample. As a result, for ROI-based generation tasks, they may produce inappropriate samples with excessive randomicity and without maintaining the related objects' correct structures. To address this issue, this work introduces a MOrphologic-structure-aware Generative Adversarial Network named MOGAN that produces random samples with diverse appearances and reliable structures based on only one image. For training for ROI, we propose to utilize the data coming from the original image being augmented and bring in a novel module to transform such augmented data into knowledge containing both structures and appearances, thus enhancing the model's comprehension of the sample. To learn the rest areas other than ROI, we employ binary masks to ensure the generation isolated from ROI. Finally, we set parallel and hierarchical branches of the mentioned learning process. Compared with other single image GAN schemes, our approach focuses on internal features including the maintenance of rational structures and variation on appearance. Experiments confirm a better capacity of our model on ROI-based image generation tasks than its competitive peers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge