Jinhai Huo
Mining Twitter to Assess the Determinants of Health Behavior towards Human Papillomavirus Vaccination in the United States
Jul 06, 2019
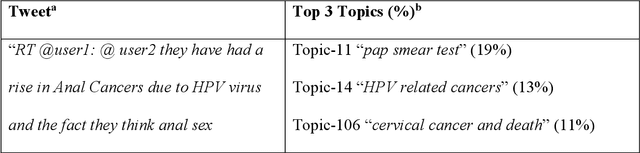
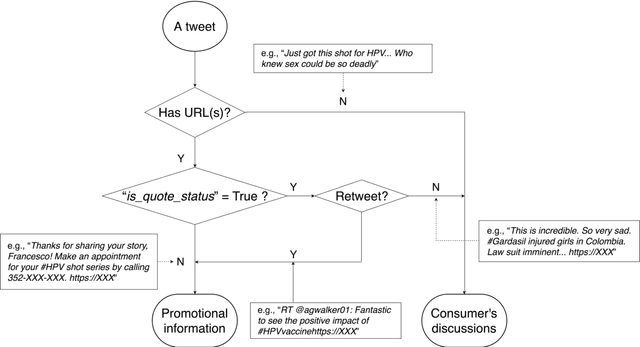
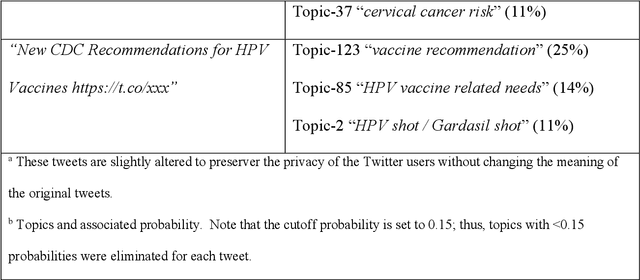
Abstract:Objectives To test the feasibility of using Twitter data to assess determinants of consumers' health behavior towards Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination informed by the Integrated Behavior Model (IBM). Methods We used three Twitter datasets spanning from 2014 to 2018. We preprocessed and geocoded the tweets, and then built a rule-based model that classified each tweet into either promotional information or consumers' discussions. We applied topic modeling to discover major themes, and subsequently explored the associations between the topics learned from consumers' discussions and the responses of HPV-related questions in the Health Information National Trends Survey (HINTS). Results We collected 2,846,495 tweets and analyzed 335,681 geocoded tweets. Through topic modeling, we identified 122 high-quality topics. The most discussed consumer topic is "cervical cancer screening"; while in promotional tweets, the most popular topic is to increase awareness of "HPV causes cancer". 87 out of the 122 topics are correlated between promotional information and consumers' discussions. Guided by IBM, we examined the alignment between our Twitter findings and the results obtained from HINTS. 35 topics can be mapped to HINTS questions by keywords, 112 topics can be mapped to IBM constructs, and 45 topics have statistically significant correlations with HINTS responses in terms of geographic distributions. Conclusion Not only mining Twitter to assess consumers' health behaviors can obtain results comparable to surveys but can yield additional insights via a theory-driven approach. Limitations exist, nevertheless, these encouraging results impel us to develop innovative ways of leveraging social media in the changing health communication landscape.
Understanding Perceptions and Attitudes in Breast Cancer Discussions on Twitter
May 22, 2019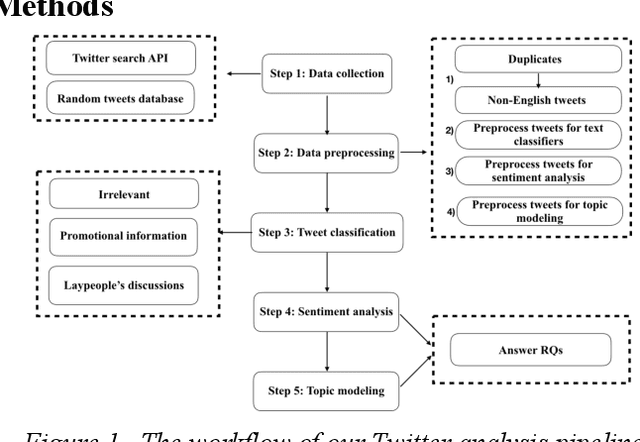
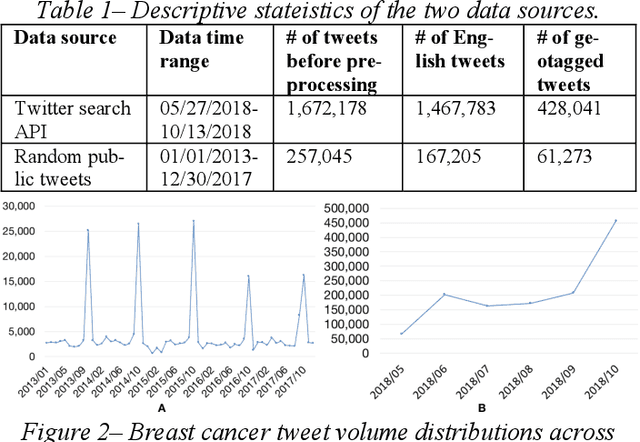
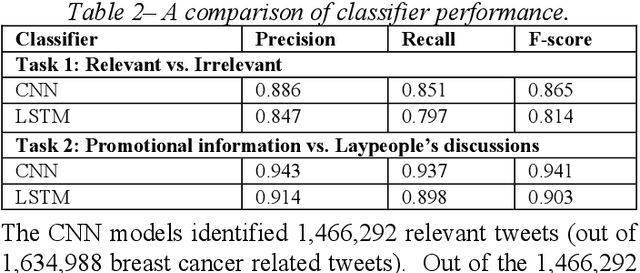
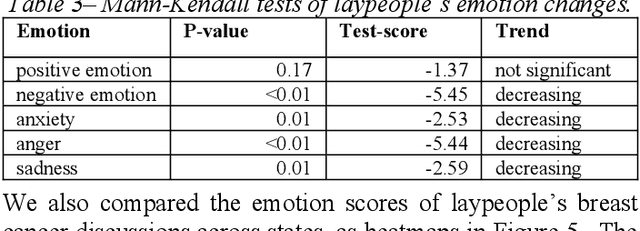
Abstract:Among American women, the rate of breast cancer is only second to lung cancer. An estimated 12.4% women will develop breast cancer over the course of their lifetime. The widespread use of social media across the socio-economic spectrum offers unparalleled ways to facilitate information sharing, in particular as it pertains to health. Social media is also used by many healthcare stakeholders, ranging from government agencies to healthcare industry, to disseminate health information and to engage patients. The purpose of this study is to investigate people's perceptions and attitudes relate to breast cancer, especially those that are related to physical activities, on Twitter. To achieve this, we first identified and collected tweets related to breast cancer; and then used topic modeling and sentiment analysis techniques to understanding discussion themes and quantify Twitter users' perceptions and emotions w.r.t breast cancer to answer 5 research questions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge