Jinghang Gu
Multi-layer Sequence Labeling-based Joint Biomedical Event Extraction
Aug 14, 2024


Abstract:In recent years, biomedical event extraction has been dominated by complicated pipeline and joint methods, which need to be simplified. In addition, existing work has not effectively utilized trigger word information explicitly. Hence, we propose MLSL, a method based on multi-layer sequence labeling for joint biomedical event extraction. MLSL does not introduce prior knowledge and complex structures. Moreover, it explicitly incorporates the information of candidate trigger words into the sequence labeling to learn the interaction relationships between trigger words and argument roles. Based on this, MLSL can learn well with just a simple workflow. Extensive experimentation demonstrates the superiority of MLSL in terms of extraction performance compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
Pipelined Biomedical Event Extraction Rivaling Joint Learning
Mar 19, 2024


Abstract:Biomedical event extraction is an information extraction task to obtain events from biomedical text, whose targets include the type, the trigger, and the respective arguments involved in an event. Traditional biomedical event extraction usually adopts a pipelined approach, which contains trigger identification, argument role recognition, and finally event construction either using specific rules or by machine learning. In this paper, we propose an n-ary relation extraction method based on the BERT pre-training model to construct Binding events, in order to capture the semantic information about an event's context and its participants. The experimental results show that our method achieves promising results on the GE11 and GE13 corpora of the BioNLP shared task with F1 scores of 63.14% and 59.40%, respectively. It demonstrates that by significantly improving theperformance of Binding events, the overall performance of the pipelined event extraction approach or even exceeds those of current joint learning methods.
Joint Learning-based Causal Relation Extraction from Biomedical Literature
Aug 02, 2022
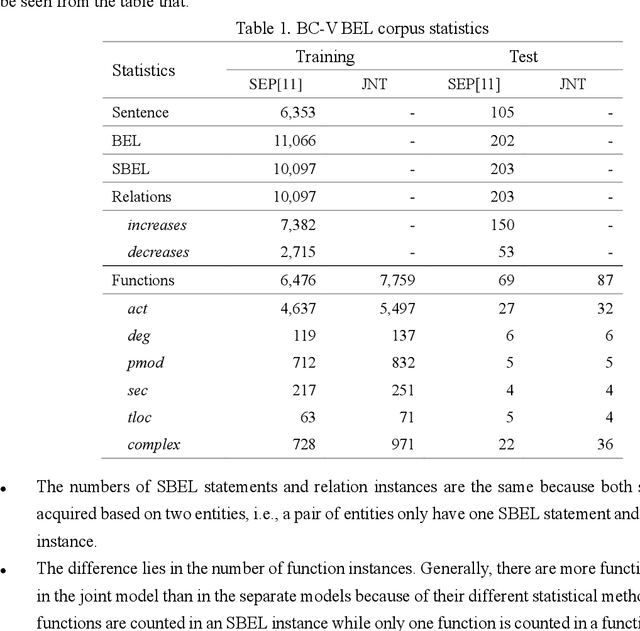
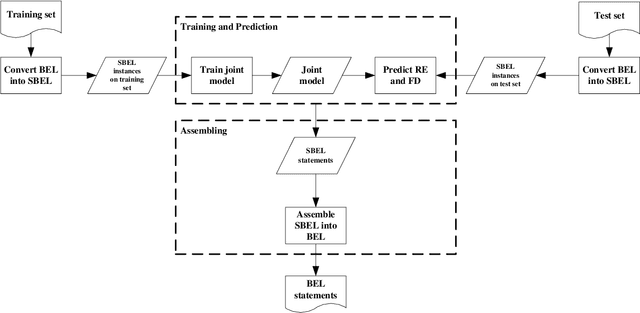
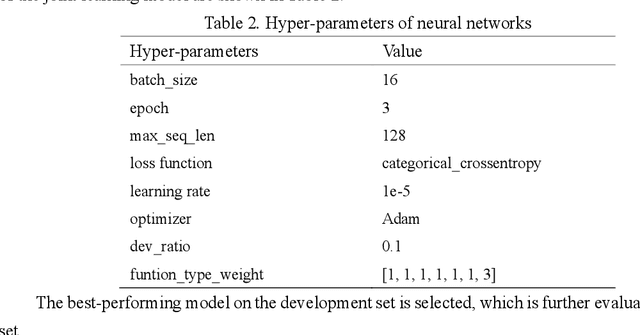
Abstract:Causal relation extraction of biomedical entities is one of the most complex tasks in biomedical text mining, which involves two kinds of information: entity relations and entity functions. One feasible approach is to take relation extraction and function detection as two independent sub-tasks. However, this separate learning method ignores the intrinsic correlation between them and leads to unsatisfactory performance. In this paper, we propose a joint learning model, which combines entity relation extraction and entity function detection to exploit their commonality and capture their inter-relationship, so as to improve the performance of biomedical causal relation extraction. Meanwhile, during the model training stage, different function types in the loss function are assigned different weights. Specifically, the penalty coefficient for negative function instances increases to effectively improve the precision of function detection. Experimental results on the BioCreative-V Track 4 corpus show that our joint learning model outperforms the separate models in BEL statement extraction, achieving the F1 scores of 58.4% and 37.3% on the test set in Stage 2 and Stage 1 evaluations, respectively. This demonstrates that our joint learning system reaches the state-of-the-art performance in Stage 2 compared with other systems.
Multi-label classification for biomedical literature: an overview of the BioCreative VII LitCovid Track for COVID-19 literature topic annotations
Apr 20, 2022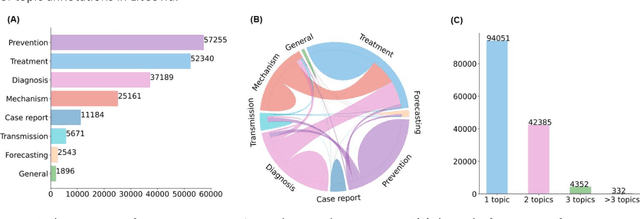
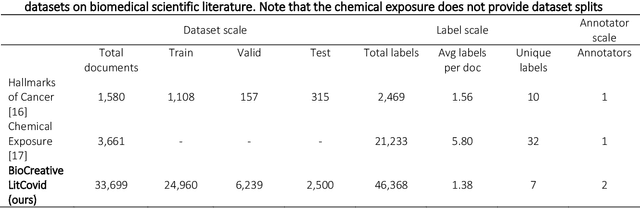
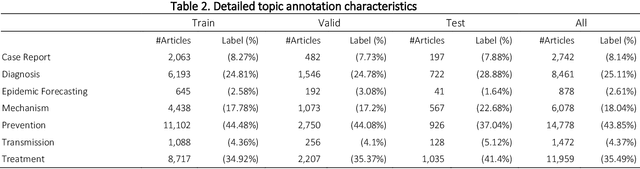
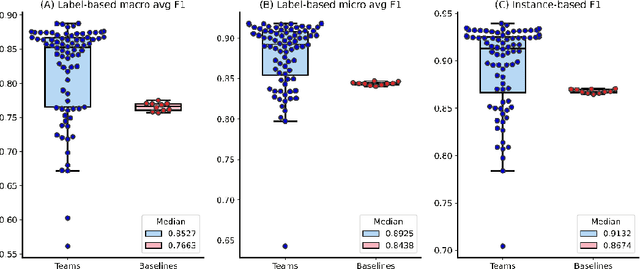
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has been severely impacting global society since December 2019. Massive research has been undertaken to understand the characteristics of the virus and design vaccines and drugs. The related findings have been reported in biomedical literature at a rate of about 10,000 articles on COVID-19 per month. Such rapid growth significantly challenges manual curation and interpretation. For instance, LitCovid is a literature database of COVID-19-related articles in PubMed, which has accumulated more than 200,000 articles with millions of accesses each month by users worldwide. One primary curation task is to assign up to eight topics (e.g., Diagnosis and Treatment) to the articles in LitCovid. Despite the continuing advances in biomedical text mining methods, few have been dedicated to topic annotations in COVID-19 literature. To close the gap, we organized the BioCreative LitCovid track to call for a community effort to tackle automated topic annotation for COVID-19 literature. The BioCreative LitCovid dataset, consisting of over 30,000 articles with manually reviewed topics, was created for training and testing. It is one of the largest multilabel classification datasets in biomedical scientific literature. 19 teams worldwide participated and made 80 submissions in total. Most teams used hybrid systems based on transformers. The highest performing submissions achieved 0.8875, 0.9181, and 0.9394 for macro F1-score, micro F1-score, and instance-based F1-score, respectively. The level of participation and results demonstrate a successful track and help close the gap between dataset curation and method development. The dataset is publicly available via https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/lu/LitCovid/biocreative/ for benchmarking and further development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge