Jingchen Sun
Craft: Cross-modal Aligned Features Improve Robustness of Prompt Tuning
Jul 24, 2024



Abstract:Prompt Tuning has emerged as a prominent research paradigm for adapting vision-language models to various downstream tasks. However, recent research indicates that prompt tuning methods often lead to overfitting due to limited training samples. In this paper, we propose a Cross-modal Aligned Feature Tuning (Craft) method to address this issue. Cross-modal alignment is conducted by first selecting anchors from the alternative domain and deriving relative representations of the embeddings for the selected anchors. Optimizing for a feature alignment loss over anchor-aligned text and image modalities creates a more unified text-image common space. Overfitting in prompt tuning also deteriorates model performance on out-of-distribution samples. To further improve the prompt model's robustness, we propose minimizing Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) over the anchor-aligned feature spaces to mitigate domain shift. The experiment on four different prompt tuning structures consistently shows the improvement of our method, with increases of up to $6.1\%$ in the Base-to-Novel generalization task, $5.8\%$ in the group robustness task, and $2.7\%$ in the out-of-distribution tasks. The code will be available at https://github.com/Jingchensun/Craft
Prompt Tuning based Adapter for Vision-Language Model Adaption
Mar 24, 2023Abstract:Large pre-trained vision-language (VL) models have shown significant promise in adapting to various downstream tasks. However, fine-tuning the entire network is challenging due to the massive number of model parameters. To address this issue, efficient adaptation methods such as prompt tuning have been proposed. We explore the idea of prompt tuning with multi-task pre-trained initialization and find it can significantly improve model performance. Based on our findings, we introduce a new model, termed Prompt-Adapter, that combines pre-trained prompt tunning with an efficient adaptation network. Our approach beat the state-of-the-art methods in few-shot image classification on the public 11 datasets, especially in settings with limited data instances such as 1 shot, 2 shots, 4 shots, and 8 shots images. Our proposed method demonstrates the promise of combining prompt tuning and parameter-efficient networks for efficient vision-language model adaptation. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/Jingchensun/prompt_adapter.
PIDNet: An Efficient Network for Dynamic Pedestrian Intrusion Detection
Sep 01, 2020
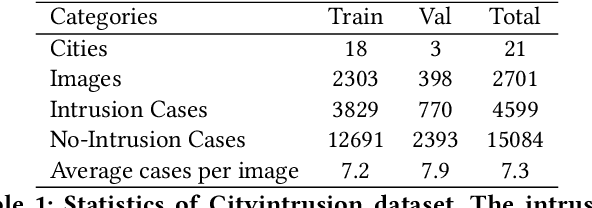
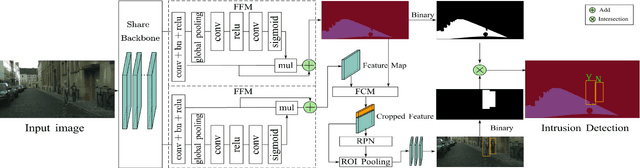
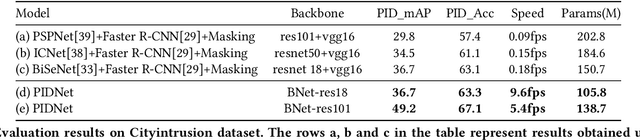
Abstract:Vision-based dynamic pedestrian intrusion detection (PID), judging whether pedestrians intrude an area-of-interest (AoI) by a moving camera, is an important task in mobile surveillance. The dynamically changing AoIs and a number of pedestrians in video frames increase the difficulty and computational complexity of determining whether pedestrians intrude the AoI, which makes previous algorithms incapable of this task. In this paper, we propose a novel and efficient multi-task deep neural network, PIDNet, to solve this problem. PIDNet is mainly designed by considering two factors: accurately segmenting the dynamically changing AoIs from a video frame captured by the moving camera and quickly detecting pedestrians from the generated AoI-contained areas. Three efficient network designs are proposed and incorporated into PIDNet to reduce the computational complexity: 1) a special PID task backbone for feature sharing, 2) a feature cropping module for feature cropping, and 3) a lighter detection branch network for feature compression. In addition, considering there are no public datasets and benchmarks in this field, we establish a benchmark dataset to evaluate the proposed network and give the corresponding evaluation metrics for the first time. Experimental results show that PIDNet can achieve 67.1% PID accuracy and 9.6 fps inference speed on the proposed dataset, which serves as a good baseline for the future vision-based dynamic PID study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge