Jin-Lin Tang
Exploring and Exploiting the Asymmetric Valley of Deep Neural Networks
May 21, 2024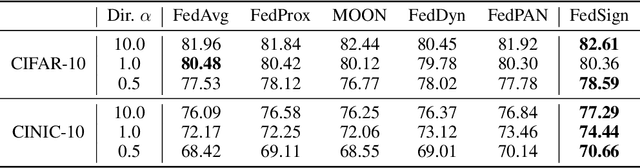
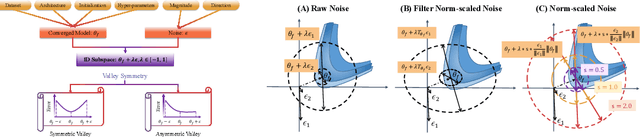
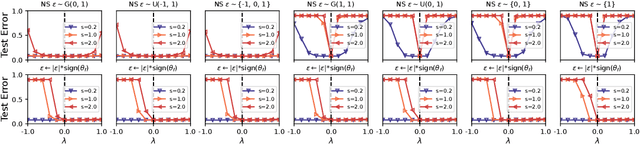
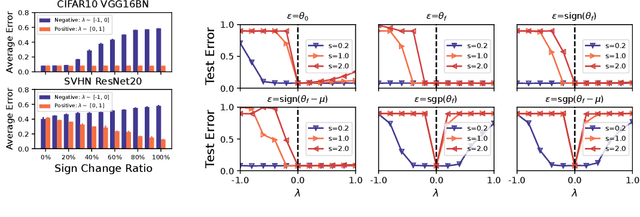
Abstract:Exploring the loss landscape offers insights into the inherent principles of deep neural networks (DNNs). Recent work suggests an additional asymmetry of the valley beyond the flat and sharp ones, yet without thoroughly examining its causes or implications. Our study methodically explores the factors affecting the symmetry of DNN valleys, encompassing (1) the dataset, network architecture, initialization, and hyperparameters that influence the convergence point; and (2) the magnitude and direction of the noise for 1D visualization. Our major observation shows that the {\it degree of sign consistency} between the noise and the convergence point is a critical indicator of valley symmetry. Theoretical insights from the aspects of ReLU activation and softmax function could explain the interesting phenomenon. Our discovery propels novel understanding and applications in the scenario of Model Fusion: (1) the efficacy of interpolating separate models significantly correlates with their sign consistency ratio, and (2) imposing sign alignment during federated learning emerges as an innovative approach for model parameter alignment.
Avoid Overfitting User Specific Information in Federated Keyword Spotting
Jun 17, 2022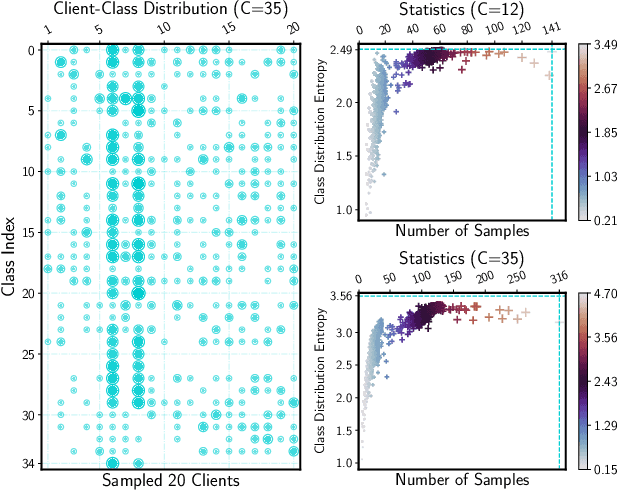
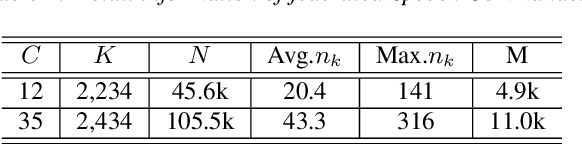
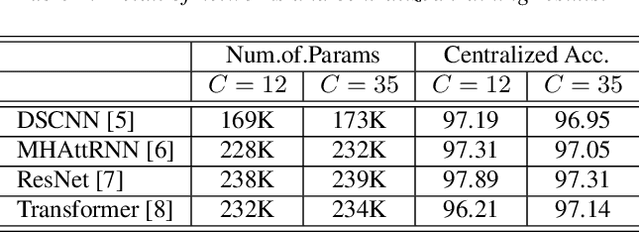
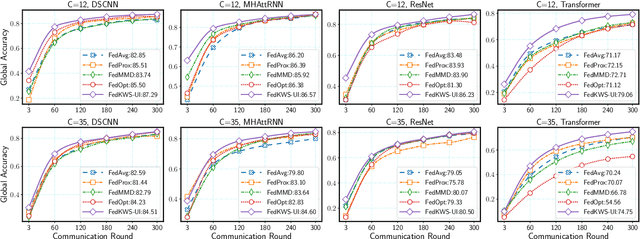
Abstract:Keyword spotting (KWS) aims to discriminate a specific wake-up word from other signals precisely and efficiently for different users. Recent works utilize various deep networks to train KWS models with all users' speech data centralized without considering data privacy. Federated KWS (FedKWS) could serve as a solution without directly sharing users' data. However, the small amount of data, different user habits, and various accents could lead to fatal problems, e.g., overfitting or weight divergence. Hence, we propose several strategies to encourage the model not to overfit user-specific information in FedKWS. Specifically, we first propose an adversarial learning strategy, which updates the downloaded global model against an overfitted local model and explicitly encourages the global model to capture user-invariant information. Furthermore, we propose an adaptive local training strategy, letting clients with more training data and more uniform class distributions undertake more local update steps. Equivalently, this strategy could weaken the negative impacts of those users whose data is less qualified. Our proposed FedKWS-UI could explicitly and implicitly learn user-invariant information in FedKWS. Abundant experimental results on federated Google Speech Commands verify the effectiveness of FedKWS-UI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge