Jin Hwa Lee
Distinct Computations Emerge From Compositional Curricula in In-Context Learning
Jun 16, 2025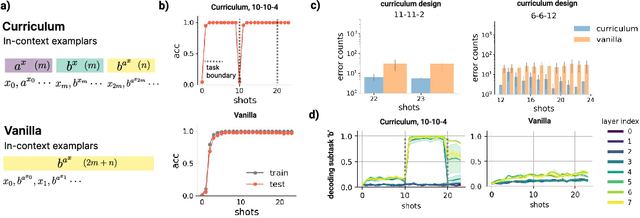
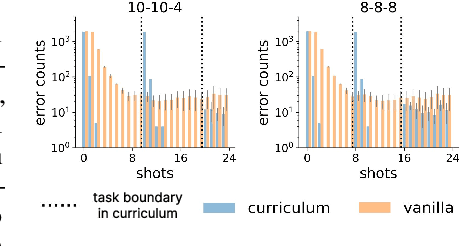
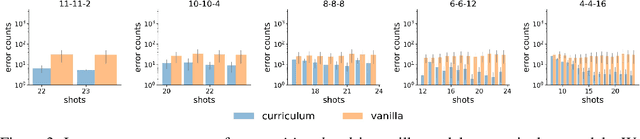
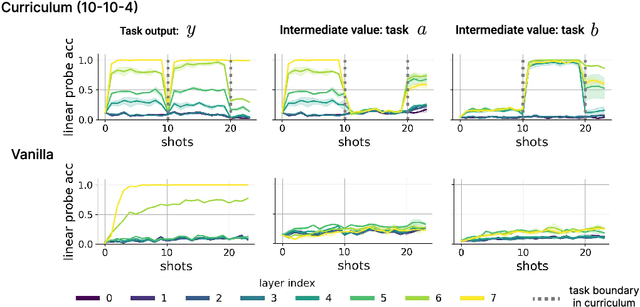
Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) research often considers learning a function in-context through a uniform sample of input-output pairs. Here, we investigate how presenting a compositional subtask curriculum in context may alter the computations a transformer learns. We design a compositional algorithmic task based on the modular exponential-a double exponential task composed of two single exponential subtasks and train transformer models to learn the task in-context. We compare (a) models trained using an in-context curriculum consisting of single exponential subtasks and, (b) models trained directly on the double exponential task without such a curriculum. We show that models trained with a subtask curriculum can perform zero-shot inference on unseen compositional tasks and are more robust given the same context length. We study how the task and subtasks are represented across the two training regimes. We find that the models employ diverse strategies modulated by the specific curriculum design.
Don't Cut Corners: Exact Conditions for Modularity in Biologically Inspired Representations
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Why do biological and artificial neurons sometimes modularise, each encoding a single meaningful variable, and sometimes entangle their representation of many variables? In this work, we develop a theory of when biologically inspired representations -- those that are nonnegative and energy efficient -- modularise with respect to source variables (sources). We derive necessary and sufficient conditions on a sample of sources that determine whether the neurons in an optimal biologically-inspired linear autoencoder modularise. Our theory applies to any dataset, extending far beyond the case of statistical independence studied in previous work. Rather, we show that sources modularise if their support is "sufficiently spread". From this theory, we extract and validate predictions in a variety of empirical studies on how data distribution affects modularisation in nonlinear feedforward and recurrent neural networks trained on supervised and unsupervised tasks. Furthermore, we apply these ideas to neuroscience data. First, we explain why two studies that recorded prefrontal activity in working memory tasks conflict on whether memories are encoded in orthogonal subspaces: the support of the sources differed due to a critical discrepancy in experimental protocol. Second, we use similar arguments to understand why preparatory and potent subspaces in RNN models of motor cortex are only sometimes orthogonal. Third, we study spatial and reward information mixing in entorhinal recordings, and show our theory matches data better than previous work. And fourth, we suggest a suite of surprising settings in which neurons can be (or appear) mixed selective, without requiring complex nonlinear readouts as in traditional theories. In sum, our theory prescribes precise conditions on when neural activities modularise, providing tools for inducing and elucidating modular representations in brains and machines.
Geometric Signatures of Compositionality Across a Language Model's Lifetime
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Compositionality, the notion that the meaning of an expression is constructed from the meaning of its parts and syntactic rules, permits the infinite productivity of human language. For the first time, artificial language models (LMs) are able to match human performance in a number of compositional generalization tasks. However, much remains to be understood about the representational mechanisms underlying these abilities. We take a high-level geometric approach to this problem by relating the degree of compositionality in a dataset to the intrinsic dimensionality of its representations under an LM, a measure of feature complexity. We find not only that the degree of dataset compositionality is reflected in representations' intrinsic dimensionality, but that the relationship between compositionality and geometric complexity arises due to learned linguistic features over training. Finally, our analyses reveal a striking contrast between linear and nonlinear dimensionality, showing that they respectively encode formal and semantic aspects of linguistic composition.
Learnable latent embeddings for joint behavioral and neural analysis
Apr 01, 2022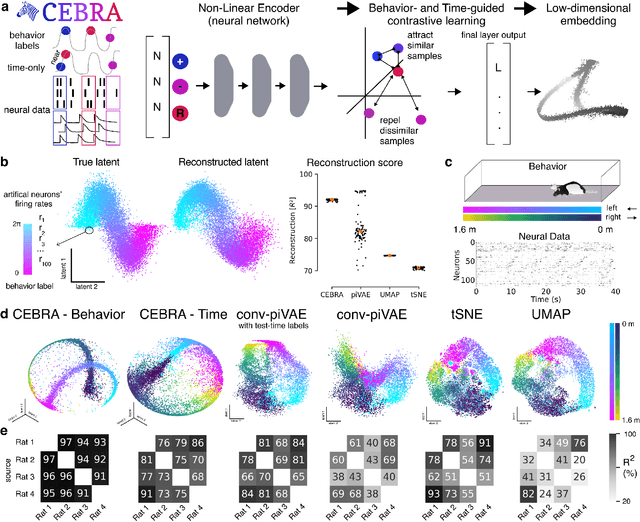
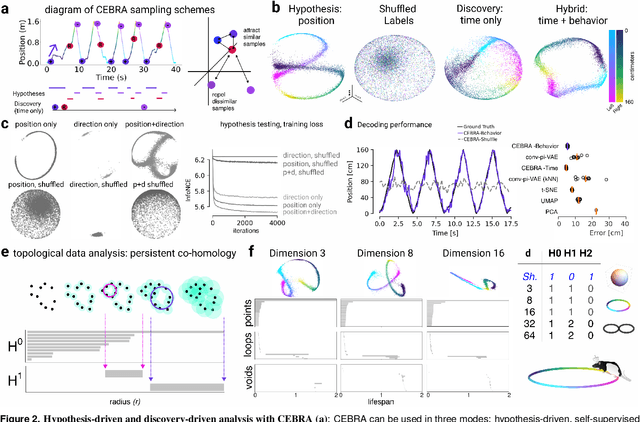
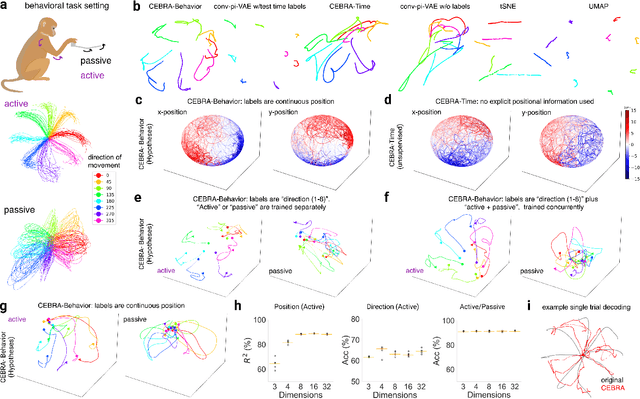
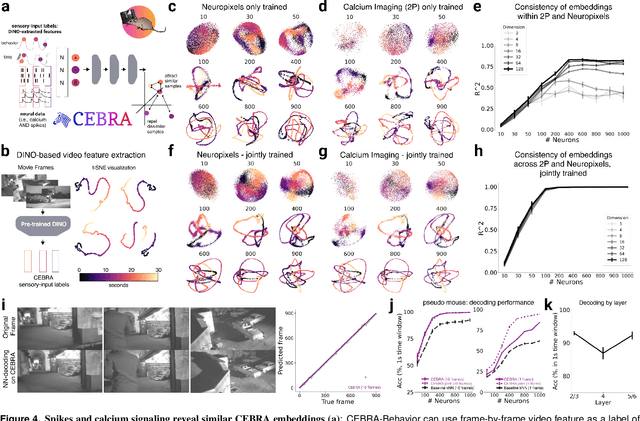
Abstract:Mapping behavioral actions to neural activity is a fundamental goal of neuroscience. As our ability to record large neural and behavioral data increases, there is growing interest in modeling neural dynamics during adaptive behaviors to probe neural representations. In particular, neural latent embeddings can reveal underlying correlates of behavior, yet, we lack non-linear techniques that can explicitly and flexibly leverage joint behavior and neural data. Here, we fill this gap with a novel method, CEBRA, that jointly uses behavioral and neural data in a hypothesis- or discovery-driven manner to produce consistent, high-performance latent spaces. We validate its accuracy and demonstrate our tool's utility for both calcium and electrophysiology datasets, across sensory and motor tasks, and in simple or complex behaviors across species. It allows for single and multi-session datasets to be leveraged for hypothesis testing or can be used label-free. Lastly, we show that CEBRA can be used for the mapping of space, uncovering complex kinematic features, and rapid, high-accuracy decoding of natural movies from visual cortex.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge